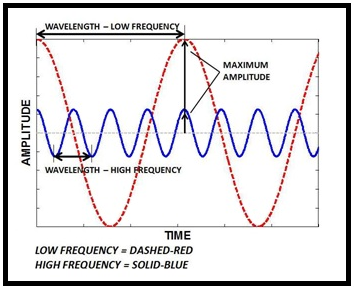
Problem 3.1QP: Define these terms: potential energy, kinetic energy, law of conservation of energy. Problem 3.2QP: What are the units for energy commonly employed in chemistry? The SI unit of energy is joule (J). It... Problem 3.3QP: A truck initially traveling at 60 km/h is brought to a complete stop at a traffic light. Does this... Problem 3.4QP: Describe the interconversions of forms of energy occurring in these processes: (a) You throw a... Problem 3.5QP Problem 3.6QP Problem 3.7QP Problem 3.8QP Problem 3.9QP Problem 3.10QP: (a) How much greater is the electrostatic energy between charges of +4 and 3 than charges of +2 and... Problem 3.11QP Problem 3.12QP Problem 3.13QP: List the types of electromagnetic radiation, starting with the radiation having the longest... Problem 3.14QP Problem 3.15QP Problem 3.16QP Problem 3.17QP: The SI unit of time is the second, which is defined as 9,192,631,770 cycles of radiation associated... Problem 3.18QP Problem 3.19QP Problem 3.20QP: Four waves represent light in four different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: visible,... Problem 3.21QP Problem 3.22QP Problem 3.23QP Problem 3.24QP: What is a photon? What role did Einsteins explanation of the photoelectric effect play in the... Problem 3.25QP: A photon has a wavelength of 705 nm. Calculate the energy of the photon in joules. Problem 3.26QP: The blue color of the sky results from the scattering of sunlight by one of the components of air.... Problem 3.27QP: A photon has a frequency of 6.5 109 Hz. (a) Convert this frequency into wavelength (nm). Does this... Problem 3.28QP Problem 3.29QP Problem 3.30QP Problem 3.31QP Problem 3.32QP: A particular form of electromagnetic radiation has a frequency of 9.87 1015 Hz. (a) What is its... Problem 3.33QP: Photosynthesis makes use of visible light to bring about chemical changes. Explain why heat energy... Problem 3.34QP: The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 1017... Problem 3.35QP Problem 3.36QP: The binding energy of magnesium metal is 5.86 1019 J. Calculate the minimum frequency of light... Problem 3.37QP: What is the kinetic energy of the ejected electron if light of frequency 2.00 1015 s1 is used to... Problem 3.38QP: A red light was shined onto a metal sample and the result shown in (i) was observed. When the light... Problem 3.39QP: A photoelectric experiment was performed by separately shining a laser at 450 nm (blue light) and a... Problem 3.1VC: Which of the following best explains why we see only four lines in the emission spectrum of... Problem 3.2VC: One way to see the emission spectrum of hydrogen is to view the hydrogen in an electric discharge... Problem 3.3VC: How many lines would we see in the emission spectrum of hydrogen if the downward transitions from... Problem 3.4VC: For a hydrogen atom in which the electron has been excited to n = 4, how many different transitions... Problem 3.40QP Problem 3.41QP Problem 3.42QP: Briefly describe Bohrs theory of the hydrogen atom and how it explains the appearance of an emission... Problem 3.43QP: Explain the meaning of the negative sign in Equation 3.8. Problem 3.44QP: Consider the following energy levels of a hypothetical atom: E4: 1.0 1019 J E3: 5.0 1019 J E2: 10 ... Problem 3.45QP Problem 3.46QP: Calculate the wavelength (in nanometers) of a photon emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron... Problem 3.47QP: Calculate the frequency (hertz) and wavelength (nanometers) of the emitted photon when election... Problem 3.48QP: What wavelength of light is needed to excite the election in the hydrogen atom from the ground state... Problem 3.49QP: An electron in the hydrogen atom makes a transition from an energy state of principal quantum number... Problem 3.50QP: Explain why elements produce their own characteristic colors when they emit photons. Problem 3.51QP: Some copper-containing substances emit green light when they are heated in a flame. How would you... Problem 3.52QP Problem 3.53QP Problem 3.54QP Problem 3.55QP: Why is Equation 3.11 meaningful only for submicroscopic particles, such as electrons and atoms, and... Problem 3.56QP Problem 3.57QP: Thermal neutrons are neutrons that move at speeds comparable to those of panicles in air at room... Problem 3.58QP: Protons can be accelerated to speeds near that of light in particle accelerators. Estimate the... Problem 3.59QP Problem 3.60QP Problem 3.61QP Problem 3.62QP Problem 3.63QP: What are the inadequacies of Bohrs theory? Problem 3.64QP: What is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle? What is the Schrdinger equation? Problem 3.65QP Problem 3.66QP Problem 3.67QP Problem 3.68QP: The speed of a thermal neutron (see Problem 3.57) is known to within 2.0 km/s. What is the minimum... Problem 3.69QP: Alveoli are tiny sacs of air in the lungs. Their average diameter is 5.0 105 m. Calculate the... Problem 3.70QP: In the beginning of the twentieth century, some scientists thought that a nucleus may contain both... Problem 3.71QP: Suppose that photons of blue light (430 nm) are used to locate the position of a 2.80-g Ping-Pong... Problem 3.72QP Problem 3.73QP Problem 3.74QP: Which of the four quantum numbers (n, , m, ms) determine (a) the energy of an electron in a hydrogen... Problem 3.75QP Problem 3.76QP Problem 3.77QP Problem 3.78QP Problem 3.79QP: Describe the shapes of s, p, and d orbitals. How are these orbitals related to the quantum numbers... Problem 3.80QP Problem 3.81QP: Describe the characteristics of an s orbital, p orbital, and d orbital. Which of the following... Problem 3.82QP: Why is a boundary surface diagram useful in representing an atomic orbital? Problem 3.83QP Problem 3.84QP: Give the values of the four quantum numbers of an electron in the following orbitals: (a) 3s, (b)... Problem 3.85QP: Describe how a 1s orbital and a 2s orbital are similar. Describe how they are different. Problem 3.86QP Problem 3.87QP Problem 3.88QP: Make a chart of all allowable orbitals in the first four principal energy levels of the hydrogen... Problem 3.89QP Problem 3.90QP Problem 3.91QP: A 3s orbital is illustrated here. Using this as a reference to show the relative size of the other... Problem 3.92QP Problem 3.93QP Problem 3.94QP: State the Aufbau principle, and explain the role it plays in classifying the elements periodic... Problem 3.95QP: Indicate the total number of (a) p electrons in N (Z = 7); (b) s electrons in Si (Z = 14); and (c)... Problem 3.96QP: Calculate the total number of electrons that can occupy (a) one s orbital, (b) three p orbitals, (c)... Problem 3.97QP: Determine the total number of electrons that can be held in all orbitals having the same principal... Problem 3.98QP: Determine the maximum number of electrons that can be found in each of the following subshells: 3s,... Problem 3.99QP Problem 3.100QP: The electron configuration of an atom in the ground state is 1s22s22p63s2. Write a complete set of... Problem 3.101QP: List the following atoms in order of increasing number of unpaired electrons: B, C, N, O, F. Problem 3.102QP: Determine the number of unpaired electrons in each atom: K, Ca, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn. Problem 3.103QP: Determine the number of impaired electrons in each of the following atoms in the ground state and... Problem 3.104QP: Determine the number of unpaired electrons in each of the following atoms in the ground state and... Problem 3.105QP Problem 3.106QP: Portions of orbital diagrams representing the ground-state electron configurations of certain... Problem 3.107QP Problem 3.108QP Problem 3.109QP Problem 3.110QP: Define the following terms and give an example of each: lanthanides, actinides. Problem 3.111QP: Explain why the ground-state electron configurations of Cr and Cu are different from what we might... Problem 3.112QP: Write the election configuration of a xenon core. Problem 3.113QP: Comment on the correctness of the following statement: The probability of finding two electrons with... Problem 3.114QP Problem 3.115QP Problem 3.116QP: Write the ground-state electron configurations for the following elements: B, V, C, As, I, Au. Problem 3.117QP: Write the ground-state electron configurations for the following elements: Ge, Fe, Zn, Ni, W, Tl. Problem 3.118QP: What is the symbol of the element with the following ground-state electron configurations? (a)... Problem 3.119QP Problem 3.120QP Problem 3.121QP: Discuss the current view of the correctness of the following statements, (a) The electron in the... Problem 3.122QP: Distinguish carefully between the following terms: (a) wavelength and frequency, (b) wave properties... Problem 3.123QP: What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following quantum numbers?... Problem 3.124QP Problem 3.125QP Problem 3.126QP: A baseball pitchers fastball has been clocked at 101 mph. (a) Calculate the wavelength of a 0.141-kg... Problem 3.127QP: A ruby laser produces radiation of wavelength 633 nm in pulses with a duration of 1.00 109 s. (a)... Problem 3.128QP: Four atomic energy levels of an atom are shown here. When an electron in an excited atom moves from... Problem 3.129QP Problem 3.130QP: Spectral lines of the Lyman and Balmer series do not overlap. Verify this statement by calculating... Problem 3.131QP: Only a fraction of the electric energy supplied to a tungsten lightbulb is converted to visible... Problem 3.132QP: The figure here illustrates a series of transitions that occur in a hydrogen atom. (a) Which... Problem 3.133QP: When one of heliums electrons is removed, the resulting species is the helium ion. He+. The He+ ion... Problem 3.134QP: The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 1017... Problem 3.135QP: An electron in an excited state in a hydrogen atom can return to the ground state in two different... Problem 3.136QP Problem 3.137QP: The election configurations described in this chapter all refer to gaseous atoms in their ground... Problem 3.138QP: Draw the shapes (boundary surfaces) of the following orbitals: (a) 2py, (b) 3dz2, (c). (Show... Problem 3.139QP Problem 3.140QP: Consider the graph here. (a) Calculate the binding energy (W) of each metal. Which metal has the... Problem 3.141QP: Scientists have found interstellar hydrogen atoms with quantum number n in the hundreds. Calculate... Problem 3.142QP: Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It is usually... Problem 3.143QP Problem 3.144QP Problem 3.145QP: The cone cells of the human eye are sensitive to three wavelength ranges, which the eye interprets... Problem 3.146QP: (a) An electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom moves at an average speed of 5 106 m/s. If... Problem 3.147QP Problem 3.148QP Problem 3.149QP: When an election makes a transition between energy levels of a hydrogen atom, there are no... Problem 3.150QP: Blackbody radiation is the term used to describe the dependence of the radiation energy emitted by... Problem 3.151QP: Suppose that photons of red light (675 nm) are used to locate the position of a 2.80-g Ping-Pong... Problem 3.152QP: In an election microscope, electrons are accelerated by passing them through a voltage difference.... Problem 3.153QP: According to Einsteins special theory of relativity, the mass of a moving panicle. mmoving, is... Problem 3.154QP: The mathematical equation for studying the photoelectric effect is hv=W+12meu2 where v is the... format_list_bulleted



 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY




