
Concept explainers
Effects of Dietary Fats on Lipoprotein Levels
Cholesterol that is made by the liver or that enters the body from food cannot dissolve in blood, so it is carried through the bloodstream in clumps called lipoprotein particles. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles carry cholesterol to body tissues such as artery walls, where they can form deposits associated with cardiovascular disease. Thus, LDL is often called “bad” cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles carry cholesterol away from tissues to the liver for disposal, so HDL is often called “good” cholesterol. In 1990, Ronald Mensink and Martijn Katan published a study that tested the effects of different dietary fats on blood lipoprotein levels. Their results are shown in FIGURE 3.2.
FIGURE 3.2 Effect of diet on lipoprotein levels. Researchers placed 59 men and women on a diet in which 10 percent of their daily energy intake consisted of cis fatty acids, trans fatty acids, or saturated fats.
The amounts of LDL and HDL in the blood were measured after three weeks on the diet; averaged results are shown in mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter of blood). All subjects were tested on each of the diets. The ratio of LDL to HDL is also shown.
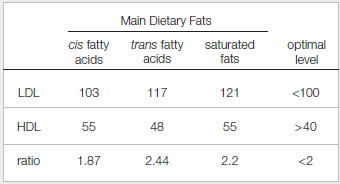
In which group was the level of LDL (“bad” cholesterol) highest?
To explain: The group that had the highest level of LDL (“bad” cholesterol).
Concept introduction: Lipoproteins are carriers of hydrophobic molecules in the extracellular matrix and the blood. The lipoproteins are made of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. The proteins are made of amino acids. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports fat, essentially cholesterol molecules in aqueous medium. LDL can get oxidized with arterial walls and forms plaque. Saturated fatty acids have fatty acid chains lacking double bonds between their carbon atoms.
Explanation of Solution
In the experiment, the amount of LDL was checked in three groups of main dietary fats: cis fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and saturated fats. Their optimal levels were also checked. The optimal level of LDL is lesser than 100. The amount of LDL in cis fatty acids is 103, trans fatty acids is 117, and saturated fats is 121.
The saturated fats had the highest level of LDL also known as bad cholesterol among the three groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
HUMAN ANATOMY
Physical Science
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- 4.arrow_forward2arrow_forward1. 2. 3. Marine fish cells are hypotonic compared to their seawater environment; their cells lose water by osmosis and gain solutes. If you add heterotrophic respiration and autotrophic respiration together and then subtract that value from gross primary productivity, then you have a more refined estimate of ecosystem carbon storage than NEE. Differential heating due to the earth's tilt generates the global wind AND oceanic circulation patternsarrow_forward
- KD 200- 116- 66- Vec ATF6 (670) ATF6 (402) ATF6 (373) ATF6 (366) I I 45- 1 2 3 4 5 ATFG (360) (e/c) 9V ATFG (402) g ant- ATF anti-KDEL DAPI barrow_forwardWestern blot results: what information can you get? Presence of proteins of your interest Levels of protein expression Levels of protein activation (must use activation state-specific antibody) Decreased function of the ATM kinase in aging mice. A C57BL/6 female 6 month Con IR 20 month C57BL/6 male 6 month 28 month Con IR Con IR Con IR p-ATM (S1981) ATM P-p53 (ser18) Actinarrow_forwardDoes it show the level of proteins? What about the amount? Levels of protein activation? How can you tell? Does the thickness tell you anything? What about the number of the lines?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





