
The Big Game
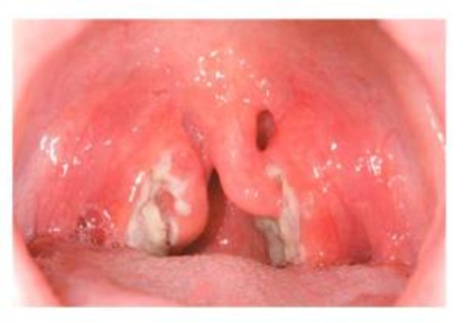
College sophomore Nadia is a star point guard for her school’s basketball team. She is excited about the divisional finals Friday night-she’s even heard rumors that a professional scout will be in the stands. On Thursday morning, she wakes up with a sore throa1. Her forehead doesn’t feel warm, so she forces herself to attend her Thursday classes; but when she wakes up on Friday morning, her throat is noticeably worse. Still, she forces herself to attend Friday morning class but feels tired and much worse by noon. It is downright painful to swallow, and she skips lunch.
Nearly crying, she heads back to the dorm and checks her temperature—101°F. Desperate, she walks to the student health center, where a nurse practitioner notices white spots on the back of Nadia's throat and on her tonsils. The divisional basketball game starts in six hours, but it only takes a few minutes for the nurse practitioner to perform a rapid streptococcal antigen test and determine that Nadia has streptococcal pharyngitis—strep throat. She will miss the big game.
Strep throat is caused by an encapsulated, Gram-positive bacterium, Streptococcus pyogenes. The only good news is that by taking the prescribed penicillin, Nadia should be ready for her next big game-hopefully, the quarterfinals.
- 1. How does the capsule of Streptococcus contribute to the bacterium's ability to cause disease?
- 2. What bacterial structures, besides the capsule, may be allowing Streptococcus to infect Nadia’s throat?
- 3. Penicillin works by interrupting the formation of peptidoglycan. What bacterial structure contains peptidoglycan? In a Gram-positive organism such as Streptococcus, is this structure typically thicker or thinner than ii would be in a Gram-negative bacterium?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY BODY...-
- Temporal flexibility (the ability to change over time) of actin structures within a cell is maintained by… A. The growth/shrinkage cycle B. Periodic catastrophe C. GTP hydrolysis D. Treadmilling E. None of the abovearrow_forwardDuring in vitro polymerization of actin and microtubule filaments from their subunits, what causes the initial delay in filament growth? A.Nucleation B.Reaching homeostasis C.Nucleotide exchange D.ATP or GTP hydrolysis E.Treadmillingarrow_forwardYou expect to find which of the following in the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)...(mark all that apply) A. Gamma tubulin B. XMAP215 C. Centrioles D. Kinesin-13arrow_forward
- The actin-nucleating protein formin has flexible “arms” containing binding sites that help recruit subunits in order to enhance microfilament polymerization. What protein binds these sites? A.Thymosin B.Profilin C.Cofilin D.Actin E.Tropomodulinarrow_forwardWhile investigating an unidentified motor protein, you discover that it has two heads that bind to actin. Based on this information, you could confidently determine that it is NOT... (mark all that apply) A. A myosin I motor B. A dynein motor C. A myosin VI motor D. A kinesin motorarrow_forwardYou isolate the plasma membrane of cells and find that . . . A. it contains regions with different lipid compositions B. it has different lipid types on the outer and cytosolic leaflets of the membrane C. neither are possible D. A and B both occurarrow_forward
- You are studying the mobility of a transmembrane protein that contains extracellular domains, one transmembrane domain, and a large cytosolic domain. Under normal conditions, this protein is confined to a particular region of the membrane due to the cortical actin cytoskeletal network. Which of the following changes is most likely to increase mobility of this protein beyond the normal restricted region of the membrane? A. Increased temperature B. Protease cleavage of the extracellular domain of the protein C. Binding to a free-floating extracellular ligand, such as a hormone D. Protease cleavage of the cytosolic domain of the protein E. Aggregation of the protein with other transmembrane proteinsarrow_forwardTopic: Benthic invertebrates as an indicator species for climate change, mapping changes in ecosystems (Historical Analysis & GIS) What objects or events has the team chosen to analyze? How does your team wish to delineate the domain or scale in which these objects or events operate? How does that limited domain facilitate a more feasible research project? What is your understanding of their relationships to other objects and events? Are you excluding other things from consideration which may influence the phenomena you seek to understand? Examples of such exclusions might include certain air-born pollutants; a general class of water bodies near Ottawa, or measurements recorded at other months of the year; interview participants from other organizations that are involved in the development of your central topic or issue. In what ways do your research questions follow as the most appropriate and/or most practical questions (given the circumstances) to pursue to better understand…arrow_forwardThe Esp gene encodes a protein that alters the structure of the insulin receptor on osteoblasts and interferes with the binding of insulin to the receptor. A researcher created a group of osteoblasts with an Esp mutation that prevented the production of a functional Esp product (mutant). The researcher then exposed the mutant strain and a normal strain that expresses Esp to glucose and compared the levels of insulin in the blood near the osteoblasts (Figure 2). Which of the following claims is most consistent with the data shown in Figure 2 ? A Esp expression is necessary to prevent the overproduction of insulin. B Esp protein does not regulate blood-sarrow_forward
- Predict the per capita rate of change (r) for a population of ruil trees in the presence of the novel symbiont when the soil moisture is 29%. The formula I am given is y= -0.00012x^2 + 0.0088x -0.1372. Do I use this formula and plug in 29 for each x variable?arrow_forwardPlease answer the following chart so I can understand how to do it.arrow_forwardDigoxin: Intravenous Bolus - Two Compartment Model Drug Digoxin Route: IV Bolus Dose: 0.750 mg Plasma Concentration Time Profile Beta Alpha Time (hrs) Conc (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN 0.00 #NUM! #NUM! #NUM! 0.10 12.290 2.509 #NUM! #NUMI 0.60 6.975 1.942 #NUM! #NUMI 1.00 4.649 1.537 #NUM! #NUMI 2.00 2.201 0.789 #NUM! #NUM! 3.00 1.536 0.429 #NUM! #NUM! 4.00 1.342 0.294 #NUM! #NUM! 5.00 1.273 0.241 #NUM! #NUMI 6.00 1.238 0.213 #NUM! #NUM! 7.00 1.212 0.192 #NUM! #NUM! 8.00 1.188 0.172 #NUMI #NUM! 9.00 1.165 0.153 #NUM! #NUMI 10.00 1.143 0.134 #NUMI #NUM! 11.00 1.122 0.115 #NUM! 12.00 1.101 0.096 #NUMI 13.00 1.080 0.077 #NUMI 16.00 1.020 0.020 #NUMI 24.00 0.876 -0.132 #NUMI Pharmacokinetic Parameters Parameter Value Alpha B Beta Units ng/ml hr-1 ng/ml hr-1 CO ng/ml H.C AUC ng x hr/ml Vc Vbeta Vss C L/hr TK (alpha) hr TX (beta) days 5+ F3 F4 F5 0+ F6 F7 % 6 95 14 #3 29 & t F8 F9 FW EWarrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage LearningUnderstanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage LearningUnderstanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage





