
EBK MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY BODY...-
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134608242
Author: BAUMAN
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 1CM
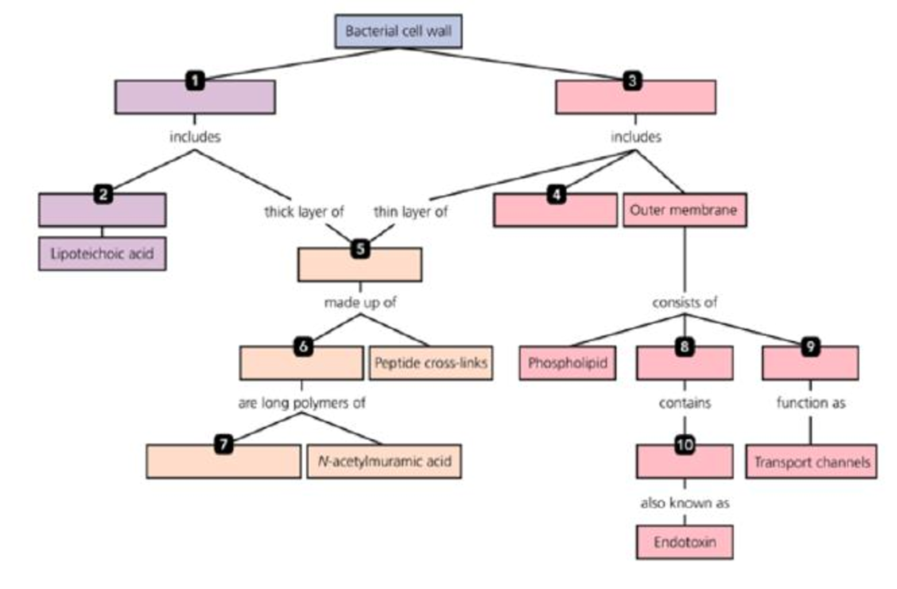
Using the following terms, fill in the following concept map that describes the bacterial cell wall. You can also complete this and other concept maps online by going to the MasteringMicrobiology Study Area.
Glycan chains
Gram-negative cell wall
Gram-positive cell wall
Lipid A
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
N-acetylglucosamine
Peptidoglycan
Periplasm
Porins
Teichoic acids
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the dental formula and enter it in the following format:
I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format)
Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).
Answer i
Answer
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY BODY...-
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1TMWCh. 3 - In 1985, an Israeli scientist discovered the...Ch. 3 - Why is a pilus a type of fimbria, but a flagellum...Ch. 3 - Why is the microbe illustrated in Figure 3.2 more...Ch. 3 - The Big Game College sophomore Nadia is a star...Ch. 3 - When the bacterium Escherichia coli is grown in a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6TMWCh. 3 - Why do scientists consider bacterial and archaeal...Ch. 3 - Why did scientists in the 19th and early 20th...Ch. 3 - Why do some scientists consider archaea, which are...
Ch. 3 - Why are eukaryotic glycocalyces covalently bound...Ch. 3 - Many antimicrobial drugs target bacterial cell...Ch. 3 - Colchicine is a drug that inhibits microtubule...Ch. 3 - A cell may allow a large or charged chemical to...Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements concerning...Ch. 3 - A 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules is seen in...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is most associated with...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is not associated with...Ch. 3 - Which of the following is true of Svedbergs? a....Ch. 3 - Which of the following statements is true? a. The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 8MCCh. 3 - Bacterial flagella are ______________. a. anchored...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10MCCh. 3 - A Gram-negative cell is moving uric acid across...Ch. 3 - Gram-positive bacteria _______________. a. have a...Ch. 3 - Endospores ________________. a. are reproductive...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14MCCh. 3 - Dipicolinic acid is an important component of...Ch. 3 - Match the structures on the left with the...Ch. 3 - Match the term on the left with its description on...Ch. 3 - Label the structures of the following prokaryotic...Ch. 3 - Label each type of flagellar arrangement.Ch. 3 - A scientist who is studying passive movement of...Ch. 3 - Describe (or draw) an example of diffusion down a...Ch. 3 - Sketch, name, and describe three flagellar...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3SACh. 3 - The term fluid mosaic has been used in describing...Ch. 3 - A local newspaper writer has contacted you, an...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6SACh. 3 - Compare bacterial cells and algal cells, giving at...Ch. 3 - Contrast a cell of Streptococcus pyogenes (a...Ch. 3 - Differentiate among pili, fimbriae, and cilia,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10SACh. 3 - Prob. 11SACh. 3 - Prob. 12SACh. 3 - What is the function of glycocalyces and fimbriae...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14SACh. 3 - Compare and contrast three types of passive...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16SACh. 3 - Prob. 17SACh. 3 - Prob. 18SACh. 3 - Prob. 1CTCh. 3 - Methylene blue binds to DNA. What structures in a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3CTCh. 3 - Prob. 4CTCh. 3 - A researcher carefully inserts an electrode into...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6CTCh. 3 - An electron micrograph of a newly discovered cell...Ch. 3 - An entry in a recent scientific journal reports...Ch. 3 - Prob. 9CTCh. 3 - Prob. 10CTCh. 3 - Prob. 11CTCh. 3 - Prob. 12CTCh. 3 - Prob. 13CTCh. 3 - Prob. 14CTCh. 3 - Using the following terms, fill in the following...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 For the following pedigree, assume that the mode of inheritance is X-linked recessive, and that the trait has full penetrance and expressivity and occurs at a very low frequency in the hum population. Using XA for the dominant allele and Xa for the recessive allele, assign genotypes for the following individuals (if it is not possible to figure out the second allele of a genotype, that with an underscore): 2 m 1 2 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 IV 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 CO 9 10 12 13 V 1, 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a. Il-1: b. 11-2: c. III-3: d. III-4: e. If individuals IV-11 and IV-12 have another child, what is the probability that they will have a boy with the disorder?arrow_forwardAnswerrarrow_forward
- please,show workings ahd solutions calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQuestion about consensus and the relationship to transcriptional activityarrow_forwardQuestion about archaea and eukaryotic general transcription homologsarrow_forward
- Question about general transcription factors and their relationship to polymerasesarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forwardHow does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College- Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...
Nursing
ISBN:9781305964792
Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...
Nursing
ISBN:9781285244662
Author:White
Publisher:Cengage


Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Bacterial Structure and Functions; Author: Osmosis;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b15Hy3jCPDs;License: Standard youtube license