
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781337571357
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 104P
3-120 Vinyl chloride is the starting material for the production of poly(vinyl chloride), abbreviated PVC. Its recycling code is “V”. The major use of PVC is for tubing in residential and commercial construction (Section 12-7).
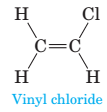
(a) Complete the Lewis structure for vinyl chloride by showing all unshared pairs of electrons.
(b) Predict the H−C−H, H−C−C, and Cl−C−H bond angles in this molecule.
(c) Does vinyl chloride have polar bonds? Is it a polar molecule? Does it have a dipole?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Topic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramolecules
Two cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 C
With the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
Ch. 3.1 - Problem 3-1 Show how the following chemical...Ch. 3.3 - Problem 3-2 Judging from their relative positions...Ch. 3.4 - Problem 3-3 Write the formulas for the ionic...Ch. 3.5 - Problem 3-4 Name these binary ionic compounds: (a)...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 3.5QCCh. 3.5 - Problem 3-6 Give each binary compound a systematic...Ch. 3.5 - Problem 3-7 Name these ionic compounds, each of...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 3.8QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.9QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.10QC
Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 3.11QCCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3.12QCCh. 3.8 - Prob. 3.13QCCh. 3.8 - Prob. 3.14QCCh. 3.9 - Problem 3-15 Predict all bond angles for these...Ch. 3.10 - Problem 3-16 Which of these molecules are polar?...Ch. 3 - 3-17 Answer true or false. (a) The octet rule...Ch. 3 - 3-18 How many electrons must each atom gain or...Ch. 3 - 3-19 Show how each chemical change obeys the octet...Ch. 3 - 3-20 Show how each chemical change obeys the octet...Ch. 3 - 3-21 Write the formula for the most stable ion...Ch. 3 - 3-22 Why is Li- not a stable ion?Ch. 3 - 3-23 Predict which ions are stable: (a) (b) (c)...Ch. 3 - 3-24 Predict which ions are stable: (a) Br2- (b)...Ch. 3 - 3-25 Why are carbon and silicon reluctant to form...Ch. 3 - 3-26 Table 3-2 shows the following ions of copper:...Ch. 3 - 3-27 Answer true or false. (a) For Group lA and...Ch. 3 - 3-28 Name each polyatomic ion. (a) HCO3- (b) NO2-...Ch. 3 - 3-29 Answer true or false. (a) According to the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14PCh. 3 - 3-31 Why does electronegativity generally increase...Ch. 3 - 3-32 Judging from their relative positions in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3 - 3-34 Which of these bonds is the most polar? The...Ch. 3 - 3-35 Classify each bond as nonpolar covalent,...Ch. 3 - 3-36 Classify each bond as nonpolar covalent,...Ch. 3 - 3-37 Answer true or false. (a) An ionic bond is...Ch. 3 - 3-38 Complete the chart by writing formulas for...Ch. 3 - 3-39 Write a formula for the ionic compound formed...Ch. 3 - Prob. 24PCh. 3 - 3-41 Describe the structure of sodium chloride in...Ch. 3 - 3-42 What is the charge on each ion in these...Ch. 3 - 3-43 Write the formula for the compound formed...Ch. 3 - 3-44 Write the formula for the ionic compound...Ch. 3 - 3-45 Which formulas are not correct? For each that...Ch. 3 - 3-46 Which formulas are not correct? For each that...Ch. 3 - 3-47 Answer true or false. (a) The name of a...Ch. 3 - 3-48 Potassium chloride and potassium bicarbonate...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33PCh. 3 - 3-50 Name the polyatomic ion(s) in each compound....Ch. 3 - 3-51 Write the formulas for the ions present in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 36PCh. 3 - 3-53 Write formulas for the following ionic...Ch. 3 - 3-54 Write formulas for the following ionic...Ch. 3 - Prob. 39PCh. 3 - 3-56 How many covalent bonds are normally formed...Ch. 3 - 3-57 What is: (a) A single bond? (b) A double...Ch. 3 - 3-58 In Section 2-3B, we saw that there are seven...Ch. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - Prob. 45PCh. 3 - Prob. 46PCh. 3 - 3-63 What is the difference between (a) a bromine...Ch. 3 - 3-64 Acetylene (C2H2), hydrogen cyanide (HCN), and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 49PCh. 3 - 3-66 Why can’t second-row elements have more than...Ch. 3 - 3-67 Why does nitrogen have three bonds and one...Ch. 3 - 3-68 Draw a Lewis structure of a covalent compound...Ch. 3 - Prob. 53PCh. 3 - 3-70 Draw a Lewis structure of a covalent compound...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Prob. 56PCh. 3 - Prob. 57PCh. 3 - 3-74 Answer true or false. (a) A binary covalent...Ch. 3 - Prob. 59PCh. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - 3-77 Ozone, O3, is an unstable blue gas with a...Ch. 3 - 3-78 Nitrous oxide, N20, laughing gas, is a...Ch. 3 - 3-79 Answer true or false. (a) The letters VSEPR...Ch. 3 - Prob. 64PCh. 3 - Prob. 65PCh. 3 - 3-82 Hydrogen and nitrogen combine in different...Ch. 3 - Prob. 67PCh. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - Prob. 69PCh. 3 - Prob. 70PCh. 3 - 3-87 Consider the molecule boron trffluoride, BF3....Ch. 3 - Prob. 72PCh. 3 - 3-89 Is it possible for a molecule to have no...Ch. 3 - Prob. 74PCh. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Prob. 76PCh. 3 - Prob. 77PCh. 3 - Prob. 78PCh. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Prob. 80PCh. 3 - Prob. 81PCh. 3 - Prob. 82PCh. 3 - 3-99 Knowing what you do about covalent bonding in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 84PCh. 3 - Prob. 85PCh. 3 - Prob. 86PCh. 3 - Prob. 87PCh. 3 - Prob. 88PCh. 3 - 3-105 Consider the structure of Vitamin E shown...Ch. 3 - 3-106 Consider the structure of Penicillin G shown...Ch. 3 - 3-107 Ephedrine, a molecule at one time found in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 92PCh. 3 - 3-109 Until several years ago, the two...Ch. 3 - 3-110 Name and write the formula for the fluorine...Ch. 3 - Prob. 95PCh. 3 - Prob. 96PCh. 3 - Prob. 97PCh. 3 - Prob. 98PCh. 3 - Prob. 99PCh. 3 - Prob. 100PCh. 3 - Prob. 101PCh. 3 - Prob. 102PCh. 3 - 3-119 Perchloroethylene, which is a liquid at room...Ch. 3 - 3-120 Vinyl chloride is the starting material for...Ch. 3 - 3-121 Tetrafluoroethylene is the starting material...Ch. 3 - 3-122 Some of the following structural formulas...Ch. 3 - 3-123 Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, has found wide...Ch. 3 - Prob. 108PCh. 3 - Prob. 109PCh. 3 - Prob. 110PCh. 3 - Prob. 111PCh. 3 - Prob. 112PCh. 3 - Consider the structure of Fluoxetine (or Prozac)...Ch. 3 - Consider the structure of lipoic acid shown below,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 115P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hi can you please help me solve this problem? thank youarrow_forwardAn electrode process takes place at a metal-solution interface. Indicate the current condition that must be met for Faradaic rectification to occur.arrow_forwardAt a metal-solution interface, an electron is exchanged, and the symmetry factor beta < 0.5 is found in the Butler-Volmer equation. What does this indicate?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY