
a.
Create a table of f(x) and g(x) values for x=−4 to x=4 .
a.
Answer to Problem 39PPS
xf(x)−40−3−1−2−2−1−30−41−32−23−140 , xg(x)−412−39−26−1300132639412
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the following absolute value functions.
f(x)=|x|−4
g(x)=|3x|
Create a table of f(x) and g(x) values for x=−4 to x=4 .
Calculation:
Consider the function
f(x)=|x|−4
Calculate the function values using TI83 calculator for x=−4 to x=4
Press Y= and enter the equation. To enter the absolute function press MATH and select NUM and then press 1 to select abs function
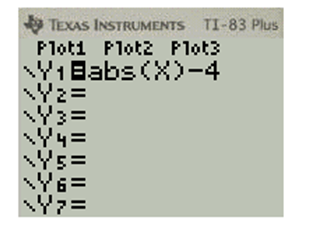
Press 2nd
GRAPH to see the tabular values
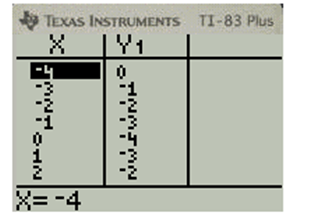
Scroll the table and to view the values for different
xf(x)−40−3−1−2−2−1−30−41−32−23−140
Consider the function
g(x)=|3x|
Calculate the function values using TI83 calculator for x=−4 to x=4
Press Y= and enter the equation. To enter the absolute function press MATH and select NUM and then press 1 to select abs function
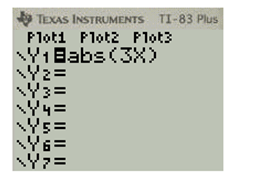
Press 2nd
GRAPH to see the tabular values
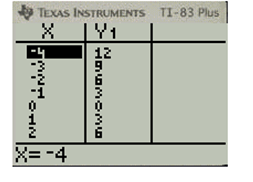
Scroll the table and to view the values for different x
xg(x)−412−39−26−1300132639412
b.
Graph the functions on separate graphs.
b.
Answer to Problem 39PPS
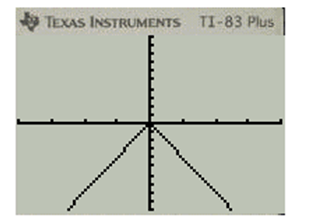
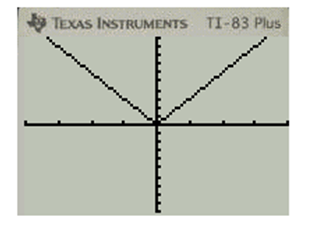
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the following absolute value functions.
f(x)=|x|−4
g(x)=|3x|
Graph the functions on separate graphs.
Calculation:
Press GRAPH for plotting for the graph of the function f(x)=|x|−4
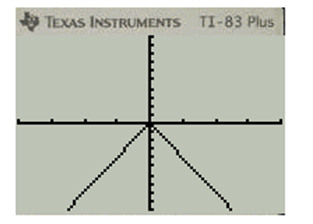
Press GRAPH for plotting for the graph of the function g(x)=|3x|
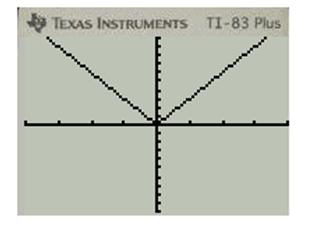
c.
Determine the slope between each two consecutive points in the table.
c.
Answer to Problem 39PPS
xf(x)slope−of−f(x)g(x)slope−of−g(x)−4012−3−1−19−3−2−2−16−3−1−3−13−30−4−10−31−31332−21633−1193401123
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the following absolute value functions.
f(x)=|x|−4
g(x)=|3x|
Determine the slope between each two consecutive points in the table.
Calculation:
Consider the slope of the line joining two points (x1y1),(x2y2) is m=y2−y1x2−x1
Hence, the slope between two consecutive points for f(x) and g(x)
xf(x)slope−of−f(x)g(x)slope−of−g(x)−4012−3−1−19−3−2−2−16−3−1−3−13−30−4−10−31−31332−21633−1193401123
d.
Describe how the slopes of the two sections of an absolute value graph are related.
d.
Answer to Problem 39PPS
The slope is constant for each sections of the graph.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the following absolute value functions.
f(x)=|x|−4
g(x)=|3x|
Describe how the slopes of the two sections of an absolute value graph are related.
Calculation:
The two sections of an absolute value graph have opposite slopes.
Hence, the slope is constant for each sections of the graph.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Algebra 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
- 1) Given matrix A below, answer the following questions: a) What is the order of the matrix? b) What is the element a13? c) What is the element a₁₁? 4 -1arrow_forward[25 points] Given the vector let v = ER² and the collection of vectors ε = E-{)·()}-{☹) (9)} = {(A)·(9)}· B: = and C = · {(6)·(})}· answer the following question. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) verify Verify is a basis for R² and find the coordinate [] of under ε. Verify B is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []B of ʊ Verify C is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []c of under ε. under ε. Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]+B from basis B to basis ε, and EE+BUB Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]B+ε from basis Ɛ to basis B, and verify [U]B= [] B+EVEarrow_forwardExplain the following terms | (a) linear span (b) dimension of vector space (c) linearly independent (d) linearly dependent (e) rank of matrix Aarrow_forward
- 3. Let u = 3/5 √ = and = -4/5 -() Define V span{ū, }. (a) (b) (c) Show that {u, } is orthonormal and forms a basis for V. Explicitly compute Projy w. Explicitly give a non-zero vector in V+.arrow_forwardIs 1.1 0.65 -3.4 0.23 0.4 -0.44 a basis for R3? You must explain your answer 0arrow_forwardFind the values of x and y in the following scalar multiplication. 8 2 x 1 3 || y = 9 LY_ Show Calculatorarrow_forward
- A professor gives two types of quizzes, objective and recall. He plans to give at least 15 quizzes this quarter. The student preparation time for an objective quiz is 15 minutes and for a recall quiz 30 minutes. The professor would like a student to spend at least 5 hours total (300 minutes) preparing for these quizzes. It takes the professor 1 minute to grade an objective quiz, and 1.5 minutes to grade a recall type quiz. How many of each type of quiz should the professor give in order to minimize his grading time (why still meeting the other requirements outlined)?arrow_forwardTable 15-21 shows the relative frequencies of the scores of a group of students on a philosophy quiz.Table 15-21 Score45678 Relative frequency7%11%19%24%39%arrow_forwardInstructions: Answer each question showing all work. 1. Out of 30 animals at a veterinarian clinic, 8 cats and 4 dogs have been vaccinated. 6 cats and 12 dogs are not yet vaccinated. Create a two-way frequency table to represent the data. 2. Convert the table from number 1 into a two-way relative frequency table. Instructions: Based on the tables created in questions 1 and 2 above, answer questions 3-7. 3. What percentage of cats from the total animals are vaccinated? 4. What is the relative frequency of dogs from the total animals that are not yet vaccinated? 5. What is the conditional frequency of cats that have not been vaccinated? 6. What is the marginal frequency of the total number of animals vaccinated? 7. What is the joint frequency of the cats that are vaccinated?arrow_forward
- The the high 3000arrow_forwardHow long will it take you to double your money if you invest it at a rate of 8% compounded annually?arrow_forwardOne hundred dollars is invested at 7.2% interest compounded annually. Determine how much the investment is worth after: a. I year b. 5 years c. 10 years d. 20 years e. Use your answers to parts (a)-(d) to estimate the doubling time for the investment.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





