
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 25, Problem 47P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The possible structure of A and B should be identified from the given reaction sequence.
Concept introduction:
Ozonolysis:
Ozonolysis is a oxidising agent when
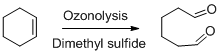
Dimethyl sulphide is used as reducing work up in the reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons.
Using the provided structures, draw the curved arrows that
epict the mechanistic steps for the proton transfer between
a hydronium ion and a pi bond.
Draw any missing organic structures in the empty boxes.
Be sure to account for all lone-pairs and charges as well as
bond-breaking and bond-making steps.
2 56°F
Mostly cloudy
F1
Drawing Arrows
>
Q Search
F2
F3
F4
▷11
H.
H
: CI:
H
+
Undo
Reset
Done
DELL
Calculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbons. Draw out the benzene ring structure when doing it
1) Calculate the longest and shortest wavelengths in the Lyman and Paschen series.
2) Calculate the ionization energy of He* and L2+ ions in their ground states.
3) Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron emitted upon irradiation of a H-atom in ground state by a 50-nm radiation.
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 25.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 25.3 - Which has a higher melting point, glyceryl...Ch. 25.3 - Draw the structure of an optically inactive fat...Ch. 25.3 - Draw the structure of an optically active fat...Ch. 25.5 - Do the identities of R1 and R2 in phosphatidic...Ch. 25.5 - Membranes contain proteins, Integral membrane...Ch. 25.5 - Prob. 8PCh. 25.5 - The membrane phospholipids in deer have a higher...Ch. 25.6 - Treating PGC2 with a strong base such as sodium...Ch. 25.7 - Mark off the isoprene units in menthol, -selinene,...
Ch. 25.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 25.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 25.8 - Propose mechanisms for the Claisen condensation...Ch. 25.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the conversion of...Ch. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the biosynthesis of...Ch. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the conversion of the E...Ch. 25.8 - The fluoro-substitued geranyl pyrophosphate shown...Ch. 25.8 - Prob. 22PCh. 25.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 25.9 - Draw the individual 1,2-hydride and 1,2-methyl...Ch. 25.10 - Prob. 26PCh. 25.10 - Prob. 27PCh. 25.10 - The acid component of a cholesterol ester is a...Ch. 25.10 - Prob. 29PCh. 25.10 - Prob. 30PCh. 25 - Prob. 31PCh. 25 - An optically active fat, when completely...Ch. 25 - Prob. 33PCh. 25 - a. How many different triacylglycerols are there...Ch. 25 - Cardiolipins are found in heart muscles. Draw the...Ch. 25 - Nutmeg contains a simple, fully saturated...Ch. 25 - Draw the product that is obtained from the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 39PCh. 25 - Prob. 40PCh. 25 - Propose a mechanism for the biosynthesis of...Ch. 25 - 5-Androstene-3.17-dione is isomerized to...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PCh. 25 - Eudesmol is a sesquiterpene found in eucalyptus....Ch. 25 - Prob. 46PCh. 25 - Prob. 47PCh. 25 - Diethylstilbestrol (DES) was given to pregnant...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the ionization energy of He+ and Li²+ ions in their ground states. Thannnxxxxx sirrr Ahehehehehejh27278283-4;*; shebehebbw $+$;$-;$-28283773838 hahhehdvaarrow_forwardPlleeaasseee solllveeee question 3 andd thankss sirr, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee don't use AIarrow_forwardCalculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forward
- 4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward
- 3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY