
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25.8, Problem 21P
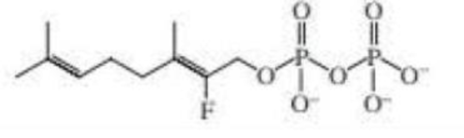
The fluoro-substitued geranyl pyrophosphate shown here reacts with isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form fluoro-substitued farnesyl pyrophosphate. The
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.
If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.
When propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 25.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 25.3 - Which has a higher melting point, glyceryl...Ch. 25.3 - Draw the structure of an optically inactive fat...Ch. 25.3 - Draw the structure of an optically active fat...Ch. 25.5 - Do the identities of R1 and R2 in phosphatidic...Ch. 25.5 - Membranes contain proteins, Integral membrane...Ch. 25.5 - Prob. 8PCh. 25.5 - The membrane phospholipids in deer have a higher...Ch. 25.6 - Treating PGC2 with a strong base such as sodium...Ch. 25.7 - Mark off the isoprene units in menthol, -selinene,...
Ch. 25.7 - Prob. 13PCh. 25.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 25.8 - Propose mechanisms for the Claisen condensation...Ch. 25.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the conversion of...Ch. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the biosynthesis of...Ch. 25.8 - Propose a mechanism for the conversion of the E...Ch. 25.8 - The fluoro-substitued geranyl pyrophosphate shown...Ch. 25.8 - Prob. 22PCh. 25.8 - Prob. 23PCh. 25.9 - Draw the individual 1,2-hydride and 1,2-methyl...Ch. 25.10 - Prob. 26PCh. 25.10 - Prob. 27PCh. 25.10 - The acid component of a cholesterol ester is a...Ch. 25.10 - Prob. 29PCh. 25.10 - Prob. 30PCh. 25 - Prob. 31PCh. 25 - An optically active fat, when completely...Ch. 25 - Prob. 33PCh. 25 - a. How many different triacylglycerols are there...Ch. 25 - Cardiolipins are found in heart muscles. Draw the...Ch. 25 - Nutmeg contains a simple, fully saturated...Ch. 25 - Draw the product that is obtained from the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 39PCh. 25 - Prob. 40PCh. 25 - Propose a mechanism for the biosynthesis of...Ch. 25 - 5-Androstene-3.17-dione is isomerized to...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PCh. 25 - Eudesmol is a sesquiterpene found in eucalyptus....Ch. 25 - Prob. 46PCh. 25 - Prob. 47PCh. 25 - Diethylstilbestrol (DES) was given to pregnant...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forwardIndicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forward
- A unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alanine and histidine write the amididation reaction mechanism using arrows then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction and the one letter code for the product of the reaction.arrow_forwardWrite the amididation reaction mechanism of p-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophen please use arrows.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning


EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305446021
Author:Lampman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License