
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The intermediate generated in the first cycle of the lipogenesis pathway that has a carbon chain that is derived from a C4 hydroxy monoacid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The cyclic process occurs in the enzyme fatty acid synthase. The one turn of this cyclic process constitutes four reactions. The various intermediates formed in the process are associated with a carrier protein known as ACP.
Hydroxy monoacid is the compound that has a hydroxy group and
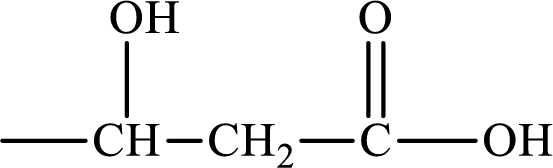
(b)
Interpretation:
The intermediate generated in the first cycle of the lipogenesis pathway that has a carbon chain that is derived from a C4 saturated monoacid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The cyclic process occurs in the enzyme fatty acid synthase. The one turn of this cyclic process constitutes four reactions. The various intermediates formed in the process are associated with a carrier protein known as ACP.
Saturated monoacid is the compound that has no double bond or triple bond but consists of the carboxylic acid group in its structure. The structure of saturated monoacid is:
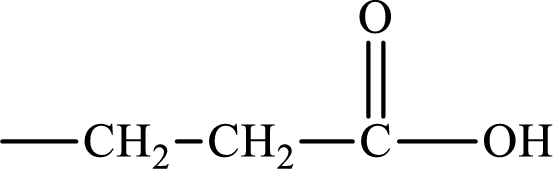
(c)
Interpretation:
The intermediate generated in the first cycle of the lipogenesis pathway that undergoes a dehydration reaction has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The cyclic process occurs in the enzyme fatty acid synthase. The one turn of this cyclic process constitutes four reactions. The various intermediates formed in the process are associated with a carrier protein known as ACP.
Dehydration reaction is the reaction in which water molecule is eliminated with the formation of the product.
(d)
Interpretation:
The intermediate generated in the first cycle of the lipogenesis pathway that is produced by a condensation reaction has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. The fatty acid is synthesized in two parts. In the first part, there is citrate-malate shuttle system and in the second part, there is a cyclic process to synthesize saturated fatty acid.
The cyclic process occurs in the enzyme fatty acid synthase. The one turn of this cyclic process constitutes four reactions. The various intermediates formed in the process are associated with a carrier protein known as ACP.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



