
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The result of treating compound 1 with
Concept introduction:
Reduction reaction: The reaction in which addition of hydrogen takes place is known as reduction reaction.
The reduction of a
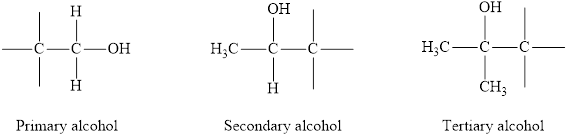
Alcohols are the hydrocarbons which have
Alcohols can be of three types on the basis of degree of carbon atom to which the
Primary alcohol: The
Secondary alcohol: The
Tertiary alcohol: The
(a)
Answer to Problem 62PS
The product obtained from the reaction of given compound
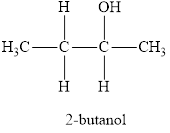
The systematic name of the product is 2-butanol and functional group is alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
Compound 1 s,
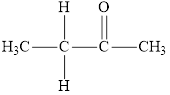
It is a ketone
The reaction between compound
The reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol in presence of
The reaction is in which the compound

The product has same number of carbon atoms as in compound
The parent chain name will be butane and suffix will be “-ol” as there is one
Therefore, name of the product is 2-butanol and functional group is alcohol.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of the reaction product from comounds 2 and 4 has to be drawn. The functional group of the product has to be identified
Concept introduction:
Ester: One
The name for an ester molecule can be written by using alkyl chain
Esterification reaction: Esters are prepared by the reaction of a
Here, the
(b)
Answer to Problem 62PS
The structure of the product is,
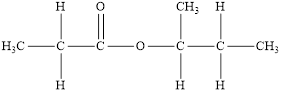
The functional group is an ester
Explanation of Solution
Compound 2 is,
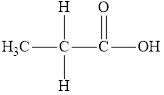
It is a carboxylic acid
Compound 4 is,
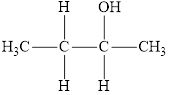
It is a secondary alcohol
Esters are prepared by the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol molecule with the elimination of water molecule
The reaction is written below in which the compound
Here, the
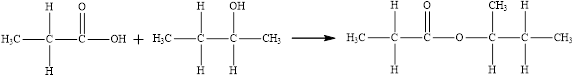
The product has
(c)
Interpretation: The compound that results from the addition of
Concept introduction:
Hydrogenation: The addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds to convert into saturated compounds in the presence of catalyst.
An
Alcohols are the hydrocarbons which have
Alcohols can be of three types on the basis of degree of carbon atom to which the
(c)
Answer to Problem 62PS
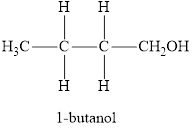
The product obtained from the reaction of given compound
Explanation of Solution
Compound 3 is,
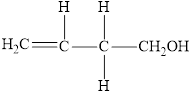
It is an alkene
The reaction between compound
In this reaction, the compound
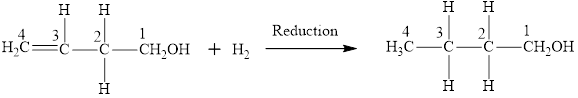
The product has same number of carbon atoms as in compound
The parent chain name will be butane
The suffix will be “-ol” as there is one
Therefore, name of the product is 1-butanol and functional group is alcohol.
(d)
Interpretation: The compound that results from the addition of
Concept introduction:
The reaction of carboxylic acid with
(d)
Answer to Problem 62PS
The product obtained from the reaction of given compound
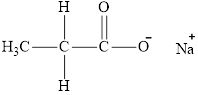
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of carboxylic acid with
The product obtained is the sodium salt of the acid and water.
The reaction of compound
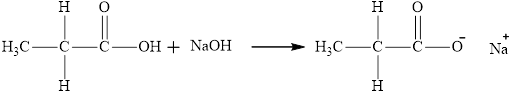
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card
- Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions: 847 Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. H₁C 0 H 0 IL 유 || OCH2CH3 1. NaOEt, EtOH C 2. H₂O H3C CH₂ Cold not tobizmo. S OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. ou OELarrow_forwardA. What is the correct structure for a-D-glucopyranose? CH₂OH a HO HO- OH b HO HO- OH HOH₂C OH OH OH CH₂OH HO C. HO HO- OH OH CH₂OH OH OH B. Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of B-D-galactopyranose with each of the following reagents. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry. [FOUR only] A. CH, Ag₂O B. warm dilute HNO3 C. (CH3CO)20, pryridine D. NaBH in H₂O E. CH₂OH, HCI F. Br₂, H₂O HO CH₂OH HO- OH OH B-D-galactopyranosearrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or reaction sequences. CH₂CN 5% NaOEt, EIOH سجد سی . بلی H 1. NaOCH, CH,OH CH3 OCH3 2 H₂O*arrow_forward
- Draw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. 004 HNO F HO CHCO) D Dydre R.SO. 1.1 NO fe HO H.SO. 2. CC1 NOH HO MCL HNO, H.50.arrow_forward. Each of the following compounds can be prepared by a mixed aldol condensation reaction. Give the Cructures of the aldehyde and/or ketone precursors for each aldol product and formulate the reaction. 0 CH=CHCCH 3. Ph 1arrow_forward. Consider the reaction below to answer the following question: H NaOEt H BOH بلی H + H₂O A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the reaction above. Show all intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows. B. This reaction is an example of: an intramolecular aldol condensation a. an intramolecular Claisen condensation b. C. d. a Robinson annulation a Michael reaction C. The product of this reaction is: a. b. C. d. a ẞ. y-unsaturated aldehyde an a, B-unsaturated ketone an a, B-unsaturated aldehyde an enolarrow_forward
- Classify each of the following nitrogen atoms in the following compounds as primary, secondary, tiary, or quaternary. A. B. C. CH3 HO-CHCHNHCH3 ephedrine CH CHCH3 amphetamine NH₂ D. CF H3C CH3 mapiquat chloride HO fexofenadine OH H3C CH3 CO₂Harrow_forward.. Name each of the following compounds by IUPAC rules. [three Only] A. 0 B. C. Cl NH₂ OCH N CH3 NHCH2CH3 D. CH O₁₂N NH₂arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the aldol self condensation product for each of the following compounds if a compound does not under go aldol self condensation explain whyarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



