
Concept explainers
Name the following
(a) CH3CH2CH2NH2
(b) (CH3)3N
(c) (CH3)(C2H5)NH
(d) C6H13NH2
(a)
Interpretation: The name of the following amine has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
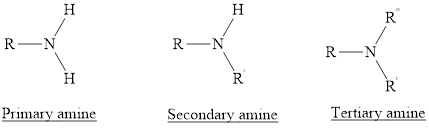
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The systematic name of the given amine,
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine is
It is a primary amine
One propyl
Therefore, the name of the given amine is propylamine.
(b)
Interpretation: The name of the following amine has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The systematic name of the given amine,
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine is
Three methyl
It is a tertiary amine
Therefore,
The name of the given amine is N,N-trimethylamine.
(c)
Interpretation: The name of the following amine has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The systematic name of the given amine,
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine is
One methyl
It is a secondary amine
Therefore, the name of the given amine is N-ethylmethylamine.
(d)
Interpretation: The name of the following amine has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Answer to Problem 40PS
The systematic name of the given amine,
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the given amine is
It is a primary amine
One hexyl
Therefore the name of the given amine is hexylamine.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card
- Please see photoarrow_forward=Naming benzene derivatives Name these organic compounds: structure C1 CH3 name ☐ CH3 ப C1 × ☐arrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see image **NOTE: The compound on the left is the starting point, and the compound on the right is the final product. Please show the steps in between to get from start to final, please. These are not two different compounds that need to be worked.arrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attachedarrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





