
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The theoretical yield of
Concept introduction:
Number of moles of a substance,
From its given mass is,
Theoretical yield is the maximum product yield that can be expected based on the masses of the reactants and the reaction stoichiometry.
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
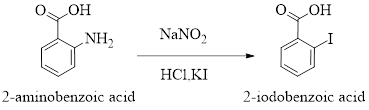
(a)
Answer to Problem 104IL
Theoretical yield of benzoic acid is
Explanation of Solution
From the given data,
Let’s calculate the number of moles of 2-amino benzoic acid:
From the given:
Let’s calculate the number of moles of
From the given:
Let’s calculate the number of moles of
From the equation , we can see that 1 mole of 2- amino benzoic acid gives 1 mole of 1-iodo benzoic acid .
For this conversion required 1 mole of
Theoretically produced
Molar mass of 2-iodobenzoic acid =
Therefore, theoretical yield of 2-iodobenzoic acid is
(b)
Interpretation: To Check the possibilty of isomers for 2-iodobenzoic acid
Concept introduction:
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
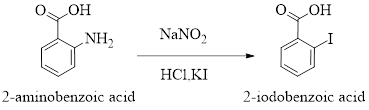
Two compounds that have the same molecular formula, but have different structural formulas are called isomers.
(b)
Answer to Problem 104IL
No other possible isomers for 2-Iodobenzoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
No other isomers of 2-iodo benzoic acid are possible in this reaction because the
(c)
Interpretation: The molar mass of the product formed in the given reaction has to be determined. And check whether the calculated molar mass is in reasonable agreement with the theoretical molar mass or not.
Concept introduction:
2-Iodobenzoic acid is a crystaline solid and it can be prepared from 2-aminobenzoic acid treated with
The reaction can be represnted as follows,
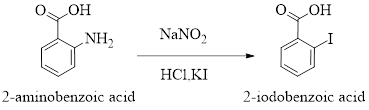
Concentration of solutions can be expressed in various terms; molarity is one such concentration expressing term.
Molarity (M) of a solution is the number of gram moles of a solute present in one liter of the solution.
A solution containing one gram mole or
Amount of substance (mol) can be determined by using the equation,
The molar mass of an element or compound is the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance, and it is expressed in the unit of grams per mol (g/mol).
Theoretical yield is the maximum product yield that can be expected based on the masses of the reactants and the reaction stoichiometry.
(c)
Answer to Problem 104IL
Molar mass of 2-Iodobenzoic acid
There is only
Explanation of Solution
From the given,
Let’s calculate the number of mole of
Let’s calculate molar mass of 2-iodo benzoic acid.
Theoretical mass 2-Iodobenzoic acid is
Therefore, there is only
We can say that it is in reasonable agreement with theoretical molar mass.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



