
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring, on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid (
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given
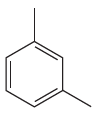
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two methyl groups attached. The alkyl groups are electron inductively donating and activate the ring. The ring can then undergo sulfonation on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, and there is no need to add fuming sulfuric acid.
It is determined that sulfonation of the given compound can be carried out with concentrated sulfuric acid only and no need to add fuming sulfuric acid based on the activation of the aromatic ring.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring, on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid, undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
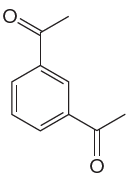
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two carbonyl groups attached. The carbonyl groups have electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreasing the electron density around the ring and deactivating it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation.
It is determined that sulfonation of the given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of the aromatic ring.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
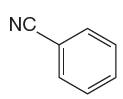
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has a nitrile group attached. The nitrile group has electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreasing the electron density around the ring and deactivating it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation.
It is determined that sulfonation of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation. The resonance effect is predominant over inductive effect due to actual delocalization of pi electrons.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
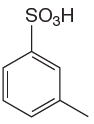
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that sulfonation of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
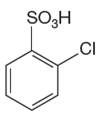
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that the sulfonation of a given compound can be carried out by the addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The fuming sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out a sulfonation on given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
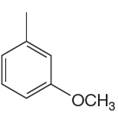
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has one methyl and one methoxy group attached. The alkyl groups are electron donating inductively, and methoxy group has electron donating resonance effect, thus increasing the electron density around the ring and activating it. As the ring is electron rich and activated, it can undergo sulfonation on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, and there is no need to add sulfuric acid.
It is determined that the sulfonation of a given compound can be carried out with concentrated sulfuric acid only and no need to add fuming sulfuric acid based on the activation of aromatic ring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





