
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of
Concept introduction:
Activating groups speed up an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction because they stabilize the arenium ion intermediate that is produced. Deactivating groups destabilize the arenium ion intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
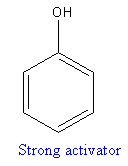
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
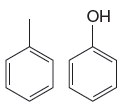
By using table 23-3, the –OH group is strongly activating than

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as a weak, moderate, or strong activator or deactivator.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl groups have electron donating inductive effect, thus stabilizing the positive charge on the adjacent carbon. The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with the increase in electron density around the ring. The groups which donate electrons, activates the aromatic ring. Electron-withdrawing group withdraws electron density from the ring, so the driving force for the aromatic ring to attack the electrophile is diminished relative to benzene; thus the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution decreases.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
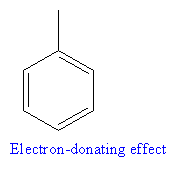
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
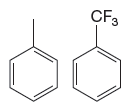
In the given compounds, the

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as a weak, moderate, or strong activator or deactivator.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Activating groups speed up an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction because they stabilize the arenium ion intermediate that is produced. Deactivating groups destabilize the arenium ion intermediate. Activating groups stabilize the arenium ion intermediate by participation of lone pair on the atom of the substituent in resonance.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
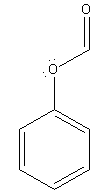
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
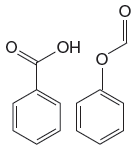
In the given pair of compounds, the

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as activator or deactivator.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron-withdrawing group withdraws electron density from the ring, so the driving force for the aromatic ring to attack the electrophile is diminished relative to hydrogen; thus, the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution decreases. Electron-withdrawing group is a deactivator.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
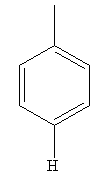
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
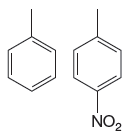
In the given pair of compounds, the

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as activator or deactivator.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron-withdrawing group withdraws electron density from the ring, so the driving force for the aromatic ring to attack the electrophile is diminished; thus the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution decreases. Electron-withdrawing group is a deactivator.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
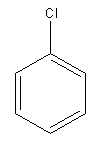
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
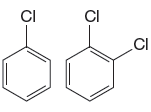
The Cl is a deactivating group. In the compound having two Cl atoms, the reaction is slower than the reaction in that with one atom. Therefore, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is as shown below:

Presence of two deactivating groups decreases the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution than that of one group.
(f)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Activating groups speed up an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction because they stabilize the arenium ion intermediate that is produced. Activating groups stabilize the arenium ion intermediate by participation of lone pair on the atom of the substituent in resonance. Deactivating groups destabilize the arenium ion intermediate.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
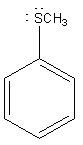
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
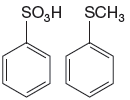
The

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as activator or deactivator.
(g)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Activating groups speed up an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction because they stabilize the arenium ion intermediate that is produced. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is increased by strong activating group.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
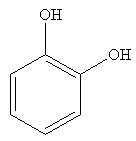
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
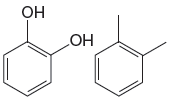
The compound on the left has OH groups that are strong activating groups. The CH3 group is a weak activator. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is increased by strong activating group. Therefore, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is as shown below:

The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is determined by identifying substituents as a weak, moderate, or strong activator or deactivator.
(h)
Interpretation:
For the given pair of aromatic compounds, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Activating groups speed up an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction because they stabilize the arenium ion intermediate that is produced. As the number of activating group to the ring increases, the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction increases.
Answer to Problem 23.43P
The compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is shown below:
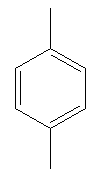
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is
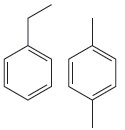
Both compounds above have activating groups. The compound on the right has two activating groups. Two activating groups to the benzene ring increase the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Therefore, the compound that will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution faster is as shown below:

Presence of two deactivating groups decreases the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution than that of one group.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- What is the molar mass of a gas that takes three times longer to effuse than helium?arrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forwardwhat is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forward
- One step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardWhy does the following reaction lead to poor yields? Correct the reaction. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





