
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given
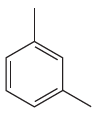
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two methyl groups attached. The alkyl groups are electron donating inductively, thus increases the electron density around the ring and activates it. As the ring is electron rich and activated it can undergo nitration on reaction with concentrated nitric acid and there is no need to add sulfuric acid.
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried out with concentrated nitric acid only and no need to add sulfuric acid based on the activation of aromatic ring.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound, it is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
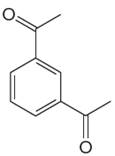
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two carbonyl groups attached. The carbonyl groups have electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreases the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, the sulfuric acid should be added to nitric acid to carry out the nitration.
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound, it is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
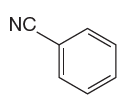
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has nitrile group attached. The nitrile group have electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreases the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, the sulfuric acid should be added to nitric acid to carry out the nitration.
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound, it is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration. The resonance effect is predominant over inductive effect due to actual delocalization of pi electrons.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
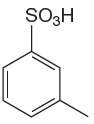
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound, it is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
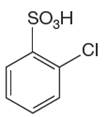
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound, it is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The nitration is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with nitric acid or with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene, this is called nitration. The selection of reagent either nitric acid or mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivates it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo nitration on reaction with nitric acid. The deactivated ring required addition of sulfuric acid to nitric acid to undergo nitration.
Answer to Problem 23.49P
The sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated nitric acid to carry out a nitration on given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
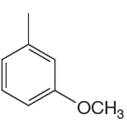
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has one methyl and one methoxy groups attached. The alkyl groups are electron donating inductively and methoxy group has electron donating resonance effect, thus increases the electron density around the ring and activates it. As the ring is electron rich and activated it can undergo nitration on reaction with concentrated nitric acid and there is no need to add sulfuric acid.
It is determined that the nitration of a given compound can be carried out with concentrated nitric acid only and no need to add sulfuric acid based on the activation of aromatic ring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
- Please provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





