
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic
Answer to Problem 23.1P
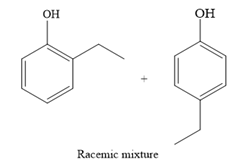
The major product for the given reaction is
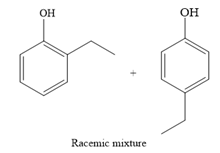
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
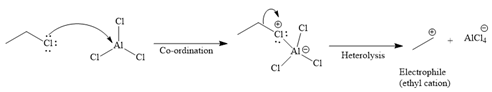
Formation of the electrophile:
Formation of the product (a racemic mixture of ortho and para isomer):
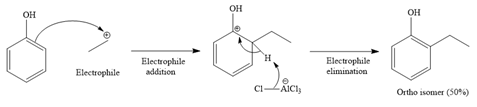
For ortho isomer:
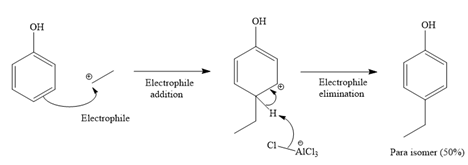
For para isomer:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
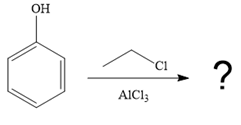
It is noticed that the given substrate, phenol, is treated with ethyl chloride in the presence of
The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, the electron-rich chlorine of the ethyl chloride is coordinated with an electron-deficient aluminum of
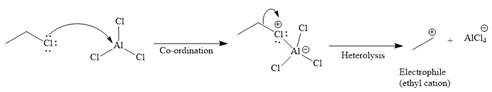
The formed electrophile, ethyl cation (
For ortho isomer:
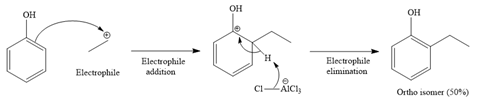
For para isomer:
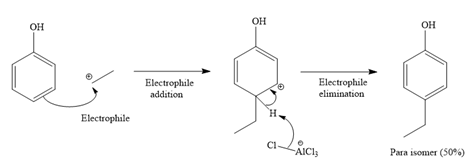
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
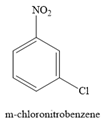
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
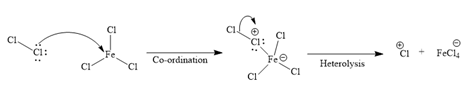
Formation of the electrophile:
Formation of the product:
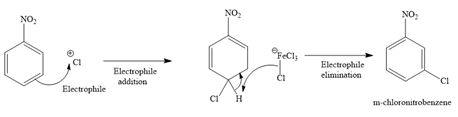
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
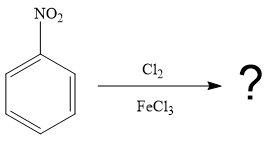
It is noticed that the given substrate is treated with

The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, one of the electron-rich chlorine atoms of

The formed electrophile (

The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
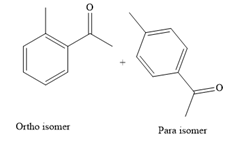
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Formation of the electrophile:
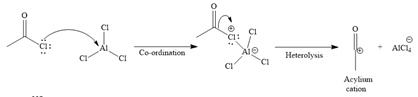
Formation of the product (a racemic mixture of ortho and para isomer):
For ortho isomer:
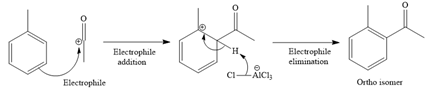
For para isomer:
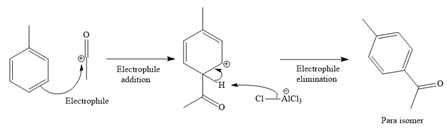
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
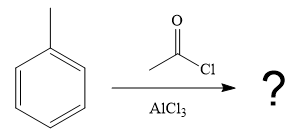
It is noticed that the given substrate, toluene, is treated with an acyl chloride in the presence of

From the Table 23-1, the product is a mixture of o+p isomer more than 95%.
The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, electron-rich chlorine of the ethyl chloride is coordinated with an electron-deficient aluminum of

The formed electrophile, acylium cation, then undergoes electrophilic addition to the benzene ring, followed by electrophilic elimination mechanism, to form the ortho and para isomers shown below:
For ortho isomer:

For para isomer:
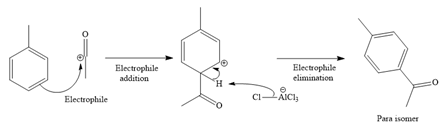
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
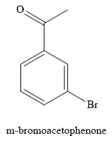
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Formation of the electrophile:
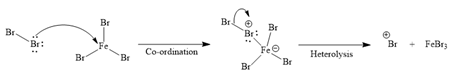
Formation of the product:
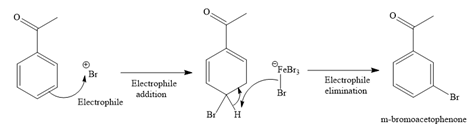
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
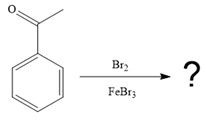
It is noticed that the given substrate is treated with

The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, one of the electron-rich bromine atoms of
The formed electrophile (
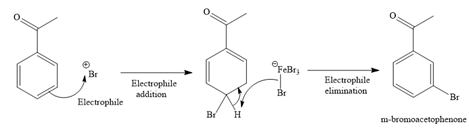
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- A certain inorganic cation has an electrophoretic mobility of 5.27 x 10-4 cm2s-1V-1. The same ion has a diffusion coefficient of 9.5 x 10-6cm2s-1. If this ion is separated from cations by CZE with a 75cm capillary, what is the expected plate count, N, at an applied voltage of 15.0kV? Under these separation conditions, the electroosmotic flow rate was 0.85mm s-1 toward the cathode. If the detector was 50.0cm from the injection end of the capillary, how long would it take in minutes for the analyte cation to reach the detector after the field was applied?arrow_forward2.arrow_forwardPlease solve for the following Electrochemistry that occursarrow_forward
- Commercial bleach contains either chlorine or oxygen as an active ingredient. A commercial oxygenated bleach is much safer to handle and less likely to ruin your clothes. It is possible to determine the amount of active ingredient in an oxygenated bleach product by performing a redox titration. The balance reaction for such a titration is: 6H+ +5H2O2 +2MnO4- à 5O2 + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O If you performed the following procedure: “First, dilute the Seventh Generation Non-Chlorine Bleach by pipetting 10 mL of bleach in a 100 mL volumetric flask and filling the flask to the mark with distilled water. Next, pipet 10 mL of the diluted bleach solution into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask and add 20 mL of 1.0 M H2SO4 to the flask. This solution should be titrated with 0.0100 M KMnO4 solution.” It took 18.47mL of the KMnO4 to reach the endpoint on average. What was the concentration of H2O2 in the original bleach solution in weight % assuming the density of bleach is 1g/mL?arrow_forward10.arrow_forwardProper care of pH electrodes: Why can you not store a pH electrode in distilled water? What must you instead store it in? Why?arrow_forward
- Write the electron configuration of an atom of the element highlighted in this outline of the Periodic Table: 1 23 4 569 7 He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Hint: you do not need to know the name or symbol of the highlighted element! §arrow_forwardIdentify the amino acids by name. Illustrate a titration curve for this tetrapeptide indicating the pKa's for each ionizable groups and identify the pI for this tetrapeptide. please helparrow_forward↓ ina xSign x Sign X labs X Intro X Cop Xa chat X My Cx Grac X Laur x Laur xash learning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db2 +949 pts /3400 K Question 16 of 34 > © Macmillan Learning Draw the major E2 reaction product formed when cis-1-chloro-2-ethylcyclohexane (shown) reacts with hydroxide ion in DMSO. H CH2CH3 H H HO- H H H Cl DMSO H H C Select Draw Templates More C H 0 2 Erasearrow_forward
- A common buffer for stabilizing antibodies is 100 mM Histidine at pH 7.0. Describe the preparation of this buffer beginning with L-Histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate and 1 M NaOH. Be certain to show the buffering reaction that includes the conjugate acid and base.arrow_forwardFina x | Sign X Sign X lab: X Intro X Cop) X a chat x My x Grad xLaur x Laur x a sheg X S Shoj XS SHE X acmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db27d6b4ee?actualCourseld=d591b3f2- 5 © Macmillan Learning Organic Chemistry Maxwell presented by Macmillan Learning For the dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction shown, draw the Zaitsev product, showing the stereochemistry clearly. H H KOH Br EtOH Heat Select Draw Templates More Erase // C H Q Search hp Q2 Q Δ קו Resouarrow_forwardIs the structural form shown possible given the pKa constraints of the side chains?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





