
(a)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increases the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decrease electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
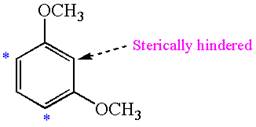
The most likely site(s) electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule is:
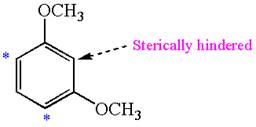
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
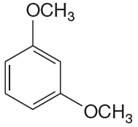
In the given molecule, benzene has two methoxy substituents. These are activating groups, thus ortho-para directors. Each methoxy group activates their two ortho and one para positions. The activated sites are same for both groups, thus overall there are three activated sites. But the position between two methoxy groups is sterically hindered. Thus, the molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(b)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activate whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivate the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increase the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decreases electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
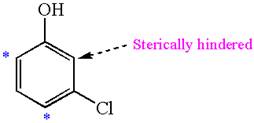
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
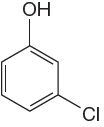
In the given molecule, benzene has one hydroxyl and one chloride substituent. Both these are activating groups, thus ortho-para directors. Each of the susbtituents activates their two ortho and one para positions. The activated sites are same for both groups thus overall there are three activated sites. But the position between these two substituents is sterically hindered. Thus, molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk
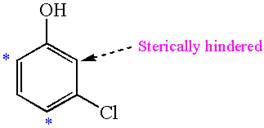
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(c)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increase the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decrease electron density at ortho/para and have comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
Explanation of Solution
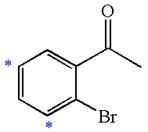
The given molecule is:
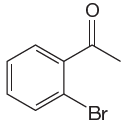
In the given molecule, benzene has one acetyl and one bromide substituent. Acetyl is carbonyl group which is deactivating thus it is meta director. The bromine atom is activating group thus it is ortho/para director. The acetyl group activates its two meta positions and bromine activates its one ortho and one para positions. The meta positions of acetyl group are same as the ortho/para position of bromine atom. Thus the molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk
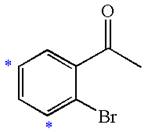
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(d)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increases the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decreases electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
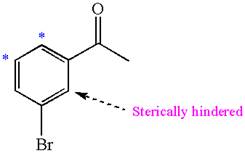
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
In the given molecule, benzene has one acetyl and one bromide substituent. Acetyl is carbonyl group which is deactivating thus it is meta director. The bromine atom is activating group thus it is ortho/para director.
The acetyl group activates its one meta positions and bromine activates two ortho and one para positions. The activating sites of both groups are different, thus overall there are three activated sites. But the position between these two substituents is sterically hindered. Thus, molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk

The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(e)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increases the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decreases electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
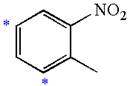
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
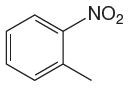
In the given molecule, benzene has one nitro and one methyl substituent. Nitro group is deactivating thus it is meta director. The methyl group is activating group thus it is ortho/para director. The nitro group activates its two meta positions and methyl group activates its one ortho and one para positions. The meta positions of nitro group are same as the ortho/para positions of methyl groups. Thus, the molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk

The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(f)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increases the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decreases electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
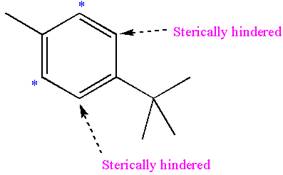
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
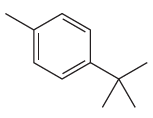
In the given molecule, benzene has one methyl and one

The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
(g)
Interpretation:
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are to be indicated.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction rate increases with increase in electron density around the ring. The electron donating groups activates whereas the electron withdrawing groups deactivates the aromatic ring. The electron donating groups increases the electron density at ortho-para position and thus they are ortho-para directing. The electron withdrawing groups decreases electron density at ortho/para and has comparatively greater electron density at meta position, thus they are meta directing.
Answer to Problem 23.53P
The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution in the given molecule are:
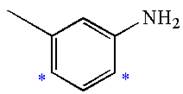
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
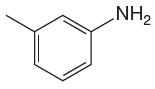
In the given molecule, benzene has one methyl and one amino substituent. They both are activating groups, thus they are ortho/para positions. Each of the susbtituents activates their two ortho and one para positions. The some activated sites are not same for both groups so, overall there are three activated sites. But the position between two groups is sterically hindered. Thus, molecules have only two possible sites of electrophilic aromatic substitution which are indicated by an asterisk

The most likely site(s) of electrophilic aromatic substitution are determined by identifying positions activated by the substituents attached.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density × NO2 ○ donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O electron-rich electron-deficient no inductive effects O no resonance effects O similar to benzene E [ CI O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Explanation Check ○ donating withdrawing no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardUnderstanding how substituents activate Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation HN NH2 Check X (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Aarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects on benzene For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density Molecule CF3 O donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene CH3 O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects O donating O withdrawing Ono resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Explanation Check Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- * Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules. Follow Up Questions for Part B 12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts) a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts) b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts) ofarrow_forwardDraw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers Draw 1 chemical reaction of an etherarrow_forwardPlease help me with the following questions for chemistry.arrow_forward
- + C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





