
a)
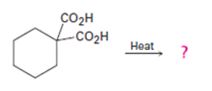
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Compounds having two carboxyl groups attached to a carbon readily undergo decarboxylation, when heated, to yield monocarboxylic acids.
To give:
The products of the reaction shown.
b)
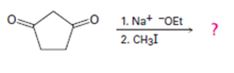
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the first reaction the base abstracts a proton to yield an enolate ion. In the second reaction alkylation takes place.
To give:
The product of the reaction shown.
c)
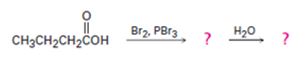
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
When carboxylic acids are treated with Br2 and PBr3, bromination occurs at the carbon α- to the carboxyl group and the acid group also is converted into an acyl bromide. When treated with water the acyl bromide gets hydrolyzed to yield the free acid.
To give:
The products of the reaction shown.
d)
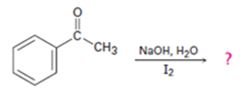
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction shown are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Methyl
To give:
The products of the reaction shown.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
