
a)
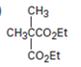
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
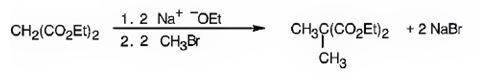
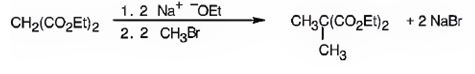
Explanation of Solution
The compound shown is a derivative of carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The acid has two methyl groups attached to the carbon adjacent to ester groups. It can be prepared by replacing the two hydrogens on the active methylene group of malonic ester by two methyl groups. This is achieved by treating the ester with two equivalents of sodium ethoxide and two equivalents of methyl bromide.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
b)
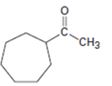
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
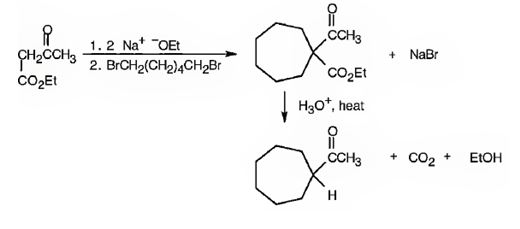
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
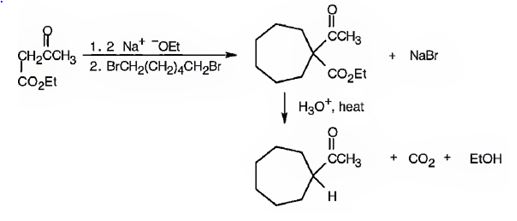
Explanation of Solution
: The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,6- dibromohexane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted acetoacetic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield methyl cycloheptyl ketone.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
c)
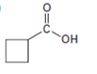
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
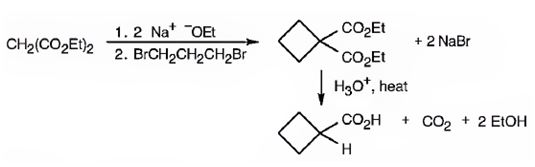
Explanation of Solution
The compound shown is a carboxylic acid. Hence it can be prepared using malonic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of malonic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on 1,3- dibromopropane displaces the bromide ion to produce a α- substituted malonic ester. The second acidic hydrogen of the ester is then removed by another ethoxide ion which is followed by the nucleophilic attack of the anion on the other carbon bearing bromine to produce a cyclic diester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester groups get hydrolyzed to give a dicarboxylic acid. The dicarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield cyclobutylcarboxylic acid.
The compound shown can be prepared by using malonic ester synthesis.
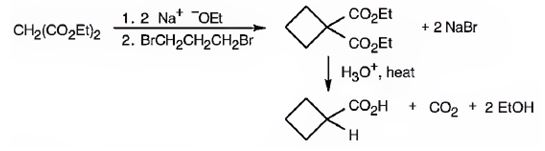
d)
Interpretation:
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Acetoacetic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide in to a methyl ketone having three more carbons. The methyl ketone part comes from acetoacetic eater while the remaining carbon comes from the primary alkyl halide. Malonic ester synthesis converts an alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid having two more carbon atoms.
Both reactions involve the same steps such as i) enolate ion formation ii) SN2 attack of the enolate anion on the alkyl halide iii) hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
To show
How to prepare the compound shown using either an acetoacetic ester synthesis or malonic ester synthesis.
Answer to Problem 46AP
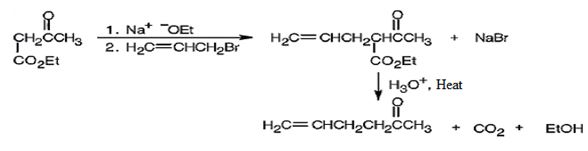
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
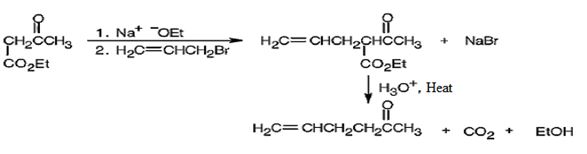
Explanation of Solution
The compound is a methyl ketone. Hence it can be prepared using aceto acetic ester synthesis. The base ethoxide ion abstracts a proton from the active methylene group of acetoacetic ester to yield the enolate anion. The nucleophilic attack of the anion on allyl bromide displaces the bromide ion to produce α- allylsubstituted acetoacetic ester. Upon treating with aqueous acids the ester group gets hydrolyzed to give a β- ketocarboxylic acid. The ketocarboxylic acid eliminates a CO2 molecule on heating to yield hex-5-ene-2-one.
The compound shown can be prepared by using an acetoacetic ester synthesis as shown below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + H CH3CH2OH HCI Drawingarrow_forwardplease explain this in simple termsarrow_forward
- K Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward(2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic trisulfide anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. с [ ] - Garrow_forward1. Calculate the accurate monoisotopic mass (using all 1H, 12C, 14N, 160 and 35CI) for your product using the table in your lab manual. Don't include the Cl, since you should only have [M+H]*. Compare this to the value you see on the LC-MS printout. How much different are they? 2. There are four isotopic peaks for the [M+H]* ion at m/z 240, 241, 242 and 243. For one point of extra credit, explain what each of these is and why they are present. 3. There is a fragment ion at m/z 184. For one point of extra credit, identify this fragment and confirm by calculating the accurate monoisotopic mass. 4. The UV spectrum is also at the bottom of your printout. For one point of extra credit, look up the UV spectrum of bupropion on Google Images and compare to your spectrum. Do they match? Cite your source. 5. For most of you, there will be a second chromatographic peak whose m/z is 74 (to a round number). For one point of extra credit, see if you can identify this molecule as well and confirm by…arrow_forward
- Please draw, not just describe!arrow_forwardcan you draw each step on a piece of a paper please this is very confusing to mearrow_forward> Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? esc ? A O O •If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. olo 18 Ar Explanation Check BB Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


