
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 32P
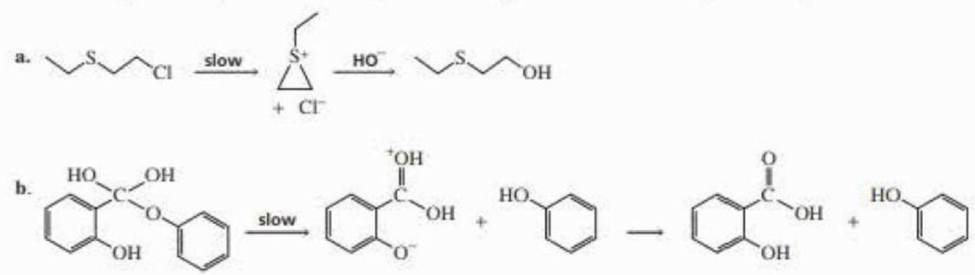
Indicate the type of catalysis that is occurring in the slow step in each of the following reaction sequences:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you please explain this problem to me and expand it so I can understand the full Lewis dot structure? Thanks!
Can you please explain this problem to me and expand it so I can understand the full Lewis dot structure? Thanks!
Please answer the questions in the photos and please revise any wrong answers. Thank you
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 22.2 - Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with...Ch. 22.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 22.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 22.3 - a. Draw the mechanism for the following reaction...Ch. 22.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 22.5 - Propose a mechanism for the Co2+ catalyzed...Ch. 22.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 10PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 22.7 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following amino acid side chains can...Ch. 22.9 - Which of the following C-terminal peptide bonds is...Ch. 22.9 - Carboxypeptidase A has esterase activity as well...Ch. 22.10 - Arginine and lysine side chains fit into trypsins...Ch. 22.10 - Explain why serine proteases do not catalyze...Ch. 22.11 - If H2 18O is used in the hydrolysis reaction...Ch. 22.11 - Draw the pH-activity profile for an enzyme that...Ch. 22.12 - The pHactivity profile for glucose-6-phosphate...Ch. 22.12 - Prob. 23PCh. 22.13 - Draw the mechanism for the hydroxide ion-catalyzed...Ch. 22.13 - What advantage does the enzyme gain by forming an...Ch. 22.13 - Prob. 26PCh. 22.13 - Prob. 27PCh. 22.13 - Aldolase shows no activity if it is incubated with...Ch. 22 - Which of the following parameters would be...Ch. 22 - Prob. 29PCh. 22 - Prob. 30PCh. 22 - Prob. 31PCh. 22 - Indicate the type of catalysis that is occurring...Ch. 22 - The deuterium kinetic isotope effect (KH2O/KD2O)...Ch. 22 - Prob. 34PCh. 22 - Co2+ catalyzes the hydrolysis of the lactam shown...Ch. 22 - there are two kinds of aldolases. Class I...Ch. 22 - Prob. 37PCh. 22 - The hydrolysis of the ester shown here is...Ch. 22 - Prob. 39PCh. 22 - At pH = 12, the rate of hydrolysis of ester A is...Ch. 22 - 2-Acetoxycyclohexyl tosylate reacts with acetate...Ch. 22 - Proof that an imine was formed between aldolase...Ch. 22 - Prob. 43PCh. 22 - a. Explain why the alkyl halide shown here reacts...Ch. 22 - Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzes the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Please be sure that 7 carbons are available in the structure )Based on the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT 135 NMR and DEPT 90 NMR, provide a reasoning step and arrive at the final structure of an unknown organic compound containing 7 carbons. Dept 135 shows peak to be positive at 128.62 and 13.63 Dept 135 shows peak to be negative at 130.28, 64.32, 30.62 and 19.10.arrow_forward-lease help me answer the questions in the photo.arrow_forwardDefine electronegativity.arrow_forward
- Why do only the immediately adjacent H's show up in the number of peaks? Are there normally peaks for the H's that are 2-3 carbons away?arrow_forwardPlease help me understand this question. Thank you. Organic Chem 1arrow_forwardFor the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.50 M, [0] = 0.45 M, and [SO3] = 1.7 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forward
- scratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forwardA compound has the molecular formula CH40, and shows a strong IR absorption at 2850-3150 cm. The following signals appear in the 'H NMR spectrum: 1.4 ppm (triplet, 6H), 4.0 ppm (quartet, 4H), 6.8 ppm (broad singlet, 4H). Which of the following structures is consistent with these data? Select the single best answer. OCH CH₂ x OCH2CH3 CH₂OCH3 OH CH₂OCH OH CH, OCH₁ CH₂OCH, CH₂OCH HO OH ° CH₂OCH3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License