
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
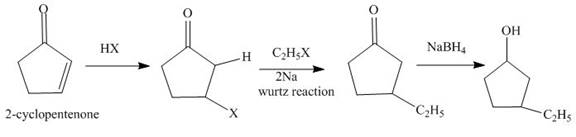
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
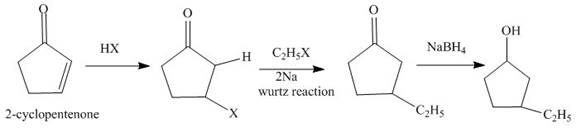
Figure 1
The synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the class of functional group which is derived from conjugated diene by replacing one double bond with a carbonyl group. The dienone compound is in conjugation to each other.
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
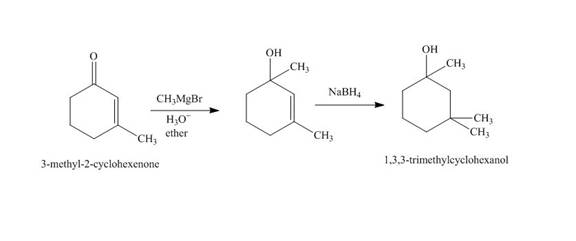
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
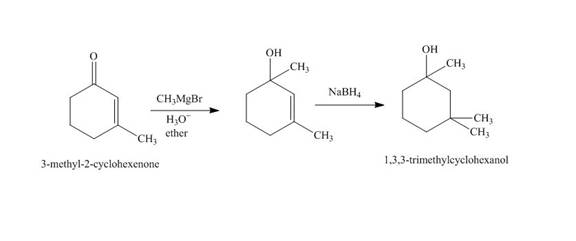
Figure 2
The synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
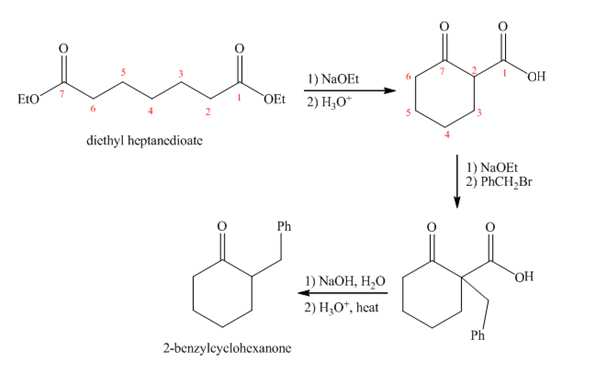
Explanation of Solution
Diethyl heptanedioate in presence of

Figure 3
The synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
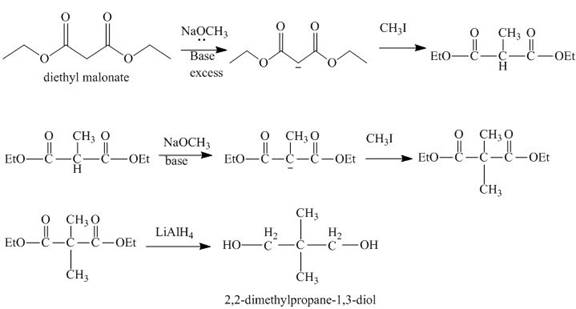
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of diethyl malonate in presence of base and then

Figure 4
The synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
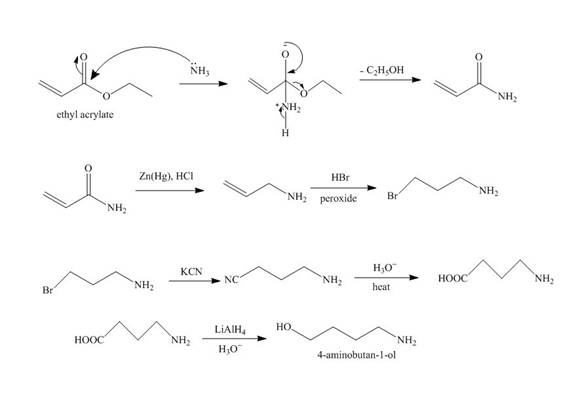
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethyl acrylate with ammonia forms amide derivative. It undergoes reduction reaction with

Figure 5
The synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the compound with the molecular formula
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
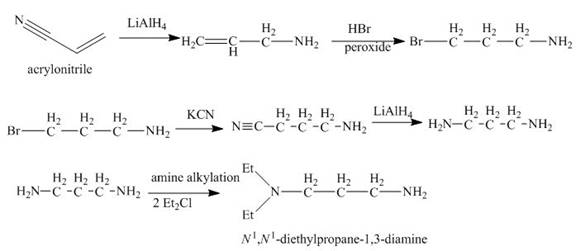
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acrylonitrile with
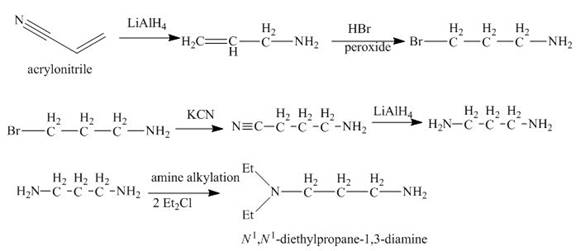
Figure 6
The synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
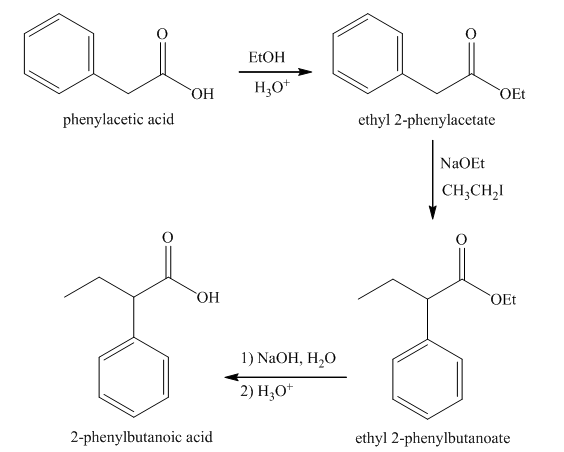
Explanation of Solution
Esterification of phenylacetic acid forms ethyl

Figure 7
The synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
In Aldol condensation reaction, the base abstracts an acidic proton from the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
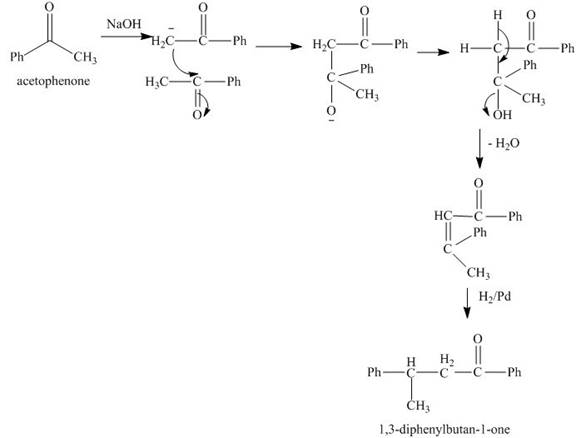
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acetophenone in presence of base abstracts a

Figure 8
The synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of deuterium substituted diphenylethanol from phenylacetic acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid is a class of organic compound that contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of di-deuterium substituted diphenyl ethanol from phenylacetic acid is shown below.
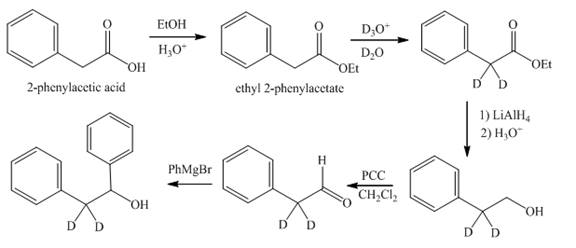
Explanation of Solution
Reaction of

Figure 9
The synthesis of deuterium substituted diphenyl ethanol from phenylacetic acid is shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted product from cyclohexanone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In organic chemistry, the carbonyl compound is a class of functional group which contains a
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted product from cyclohexanone is shown below.
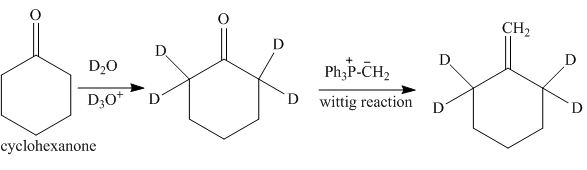
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of cyclohexanone with

Figure 10
The synthesis of tetra-deuterium substituted from cyclohexanone is shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
Friedel Craft acylation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the synthesis of the monoacylated product takes place from the reaction between aromatic rings and acyl chlorides. The organic reaction in which an organohalide is reacted with alcohols or phenols to form ethers is Willamson synthesis reaction.
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
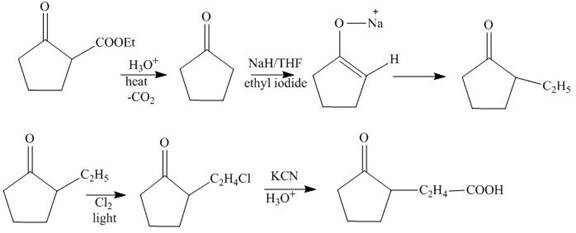
The synthesis of
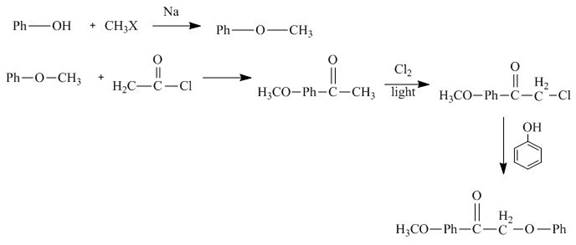
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of phenol with methyl halide forms methylphenyl ether. It reacts with acetyl chloride followed by chlorination in sunlight. Then it reacts with phenol to give the desired product. The synthesis of

Figure 11
The synthesis of
(l)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
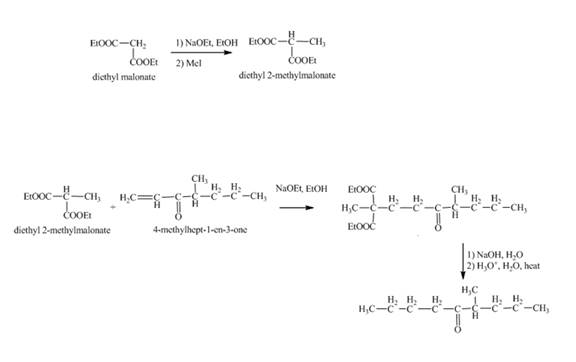
Explanation of Solution
Methylation of diethyl malonate in the presence of sodium ethoxide and

Figure 12
The synthesis of
(m)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
An ester is a derivative of carboxylic which is obtained by replacing the
Answer to Problem 22.82AP
The synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis reaction of

Figure13
The synthesis of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
- Question 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forwardA. Add Water to below compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H₂C CH₂ CH, + H₂O-> ? Major product? Minor product? B. Add Bromine to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + Br₂→ ? Major product and Minor product both are same in this? C. Add Hydrogen Bromide to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H,C CH₂ CH₂ + HBr Major product? Minor product? D. Add Hydrogen to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + H₂ Major product and Minor product both are same in this?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

