
Concept explainers
Consider the following mRNA sequence:
- What amino acid sequence is coded for by this mRNA?
- What is the amino acid sequence ¡f a mutation converts ACC to ACU?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts UUA to UCA?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts CGA to AGA?
- What occurs if C is added to the beginning of the chain?
(a)
Interpretation:
Peptide synthesized by the 5' ACC UUA CGA 3' mRNA should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Answer to Problem 22.76P
Peptide − Thr-Leu-Arg
Explanation of Solution
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. There is a unique triplet representation for a particular amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
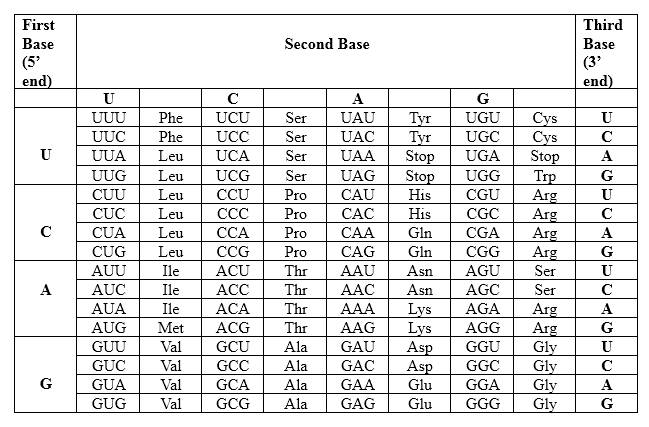
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. ACC triplet is unique for Threonine. UUA triplet is unique for Leucine. CGA triplet is unique for Arginine.
Therefore, Thr-Leu-Arg is the amino acid sequence for 5' ACC UUA CGA 3'.
(b)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA5' ACU UUA CGA3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.76P
Peptide − Thr-Leu-Arg
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
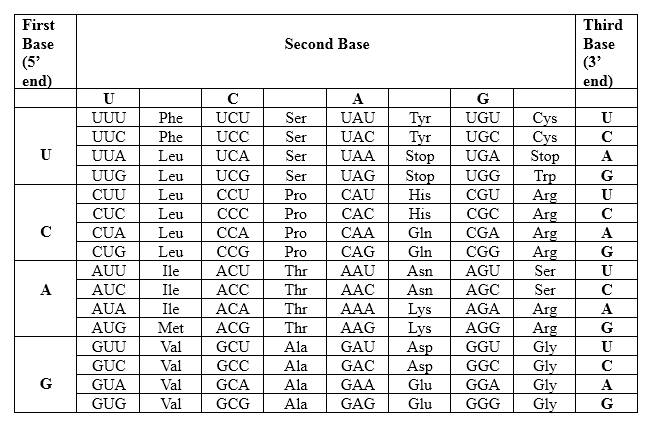
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. ACU triplet is unique for Threonine. UUA triplet is unique for Leucine. CGA triplet is unique for Arginine. Though there is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, in this example same peptide is generated as the non-mutated peptide. Therefore; this mutation has no effect with the generating peptide.
Therefore, Thr-Leu-Arg is the amino acid sequence for 5' ACU UUA CGA 3'.
(c)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' ACC UCA CGA 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.76P
Peptide − Thr-Ser-Arg.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
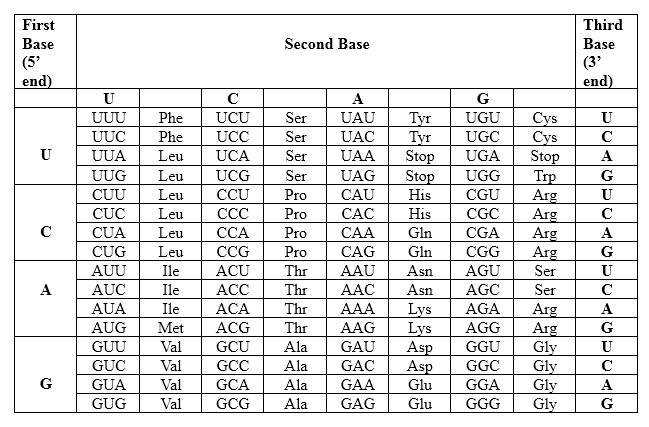
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. ACC triplet is unique for Threonine. UCA triplet is unique for Serine. CGA triplet is unique for Arginine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which UUA in the normal strand converts to UCA in the mutated strand. The resulting protein is different from the un-mutated one.
Therefore, Thr-Ser-Arg is the amino acid sequence for 5' ACC UCA CGA 3'.
(d)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' ACC UCA CGA 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.76P
Peptide − Thr-Leu-Arg
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
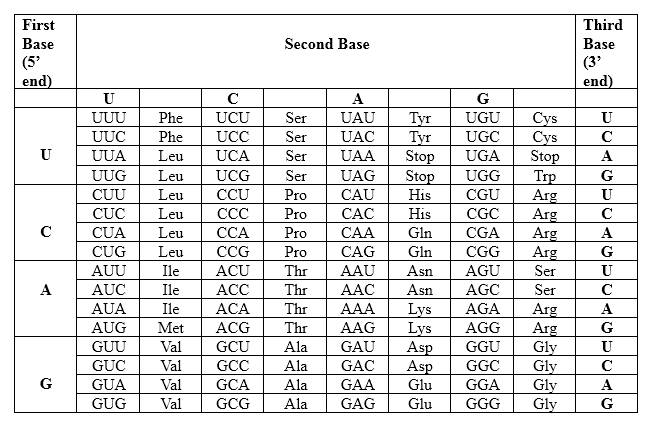
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. ACC triplet is unique for Threonine. UUA triplet is unique for Leucine. AGA triplet is unique for Arginine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which CGA in the normal strand converts to AGA in the mutated strand. Though there is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, in this example same peptide is generated as the non-mutated peptide. Therefore; this mutation has no effect with the generating peptide.
Therefore, Thr-Leu-Arg is the amino acid sequence for 5' ACC UUA AGA 3'.
(e)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' CACC UUA CGA 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.76P
Peptide − His-Leu-Thr
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
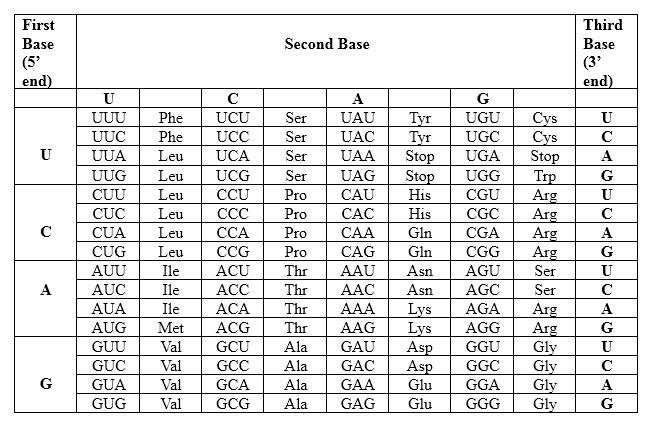
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA and read as triplets, because of the insertion mutation which occurred here because of additional C in the beginning of the mRNA, triplets are read as follows. CAC triplet is for Histidine, CUU is for Leucine and ACG is for Threonine. Furthermore, there is an additional A nucleotide, which is not involved into this peptide. This mutation generates totally different peptide and generated peptide is as follows; His-Leu-Thr is the amino acid sequence for 5' CAC CUU A AG A 3'.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forwardShown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forwardHi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forward
- Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





