
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Lock and key model of the enzymes needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
The biological catalyst is termed as enzymes. They are made up of different types of amino acids. They affect the speed of the biochemical reaction.
For the explanation of the action of the enzymes in the biochemical reaction, a famous theory is used that is the lock and key method.
Answer to Problem 7RQ
For the explanation of the catalytic nature of enzymes, a well know- method is the lock and key method. There are following two steps for this method-
Enzyme (E) + Substrate (S) = Enzyme Substrate Complex (ES)
Enzyme Substrate Complex (ES) = Enzyme (E) + Product (P).
Explanation of Solution
In the lock and key model the enzymes's activity shown by this diagram-
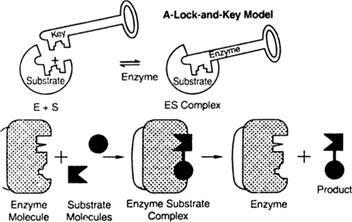
The enzymes attached to the substrate and formed the ES as enzymes substrate, the enzymes having the active site for the binding of the substrate just like a particular lock have a fixed key. A particular enzyme is fixed for a substrate. In the last step, the ES is converted into product and enzymes remain the same as staring at the reaction.
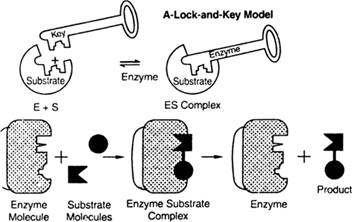
From the above diagram, the substrate is attached to a particularly active site of the enzyme for the formation of the product.
Chapter 21 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- 424 Repon Sheet Rates of Chemical Reactions : Rate and Order of 1,0, Deception B. Effect of Temperature BATH TEMPERATURE 35'c Yol of Oh نام Time 485 Buret rend ing(n) 12 194 16. 6 18 20 10 22 24 14 115 95 14738 2158235 8:26 CMS 40148 Total volume of 0, collected Barometric pressure 770-572 ml mm Hg Vapor pressure of water at bath temperature (see Appendix L) 42.2 Slope Compared with the rate found for solution 1, there is Using the ideal gas law, calculate the moles of O; collected (show calculations) times faster 10 Based on the moles of O, evolved, calculate the molar concentration of the original 3% 1,0, solution (sho calculations)arrow_forwardSteps and explanation pleasearrow_forwardSteps and explanation pleasearrow_forward
- can you please draw out and list step-by-step the synthetic strategy for this rxn? thank you sm in advancearrow_forwardSteps and explanations pleasearrow_forwardUse diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forward
- Draw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward15) Create Lewis structure Br Brarrow_forwardLIOT S How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate? View Rubricarrow_forward
- Steps and explantions pleasearrow_forwardMatch the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forwardCan you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





