
(a)
Interpretation: Soap property in a polar solvent and for non-polar molecules needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
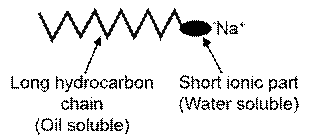
Soap is the chemical compounds that are made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9STP
The soap contains hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic groups. The soaps non-polar ends cover the non-polar molecules and the polar end dissolves in water.
Explanation of Solution
Soap is made with two types of groups one is polar and another one is non-polar. So the polar end is dissolved with a polar solvent, same as like dissolve like. On the other hand, non-polar groups or hydrophobic groups interact with non-polar molecules and dissolve them.
(b)
Interpretation: A diagram showing a soap solution able to dissolve the grease needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Soap is the chemical compounds that are made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9STP
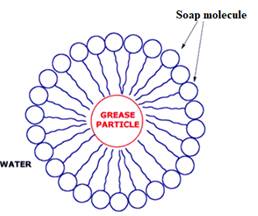
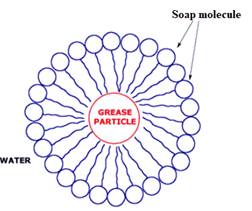
The diagram showing the soap action on grease
Explanation of Solution
The soap contains hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic groups. The non-polar ends of soaps cover grease molecules which is a non-polar molecule, and the polar end of soap dissolves in water. The polar end of soap contains the hydrophilic group, which is dissolved in water.
(c)
Interpretation: Hard water needs to be explained. The reason for the soap solution to be less effective in it needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Hard water is a less effective water type. In hard water, a large number of minerals are dissolved, the minerals are mainly calcium and magnesium.
Soap is the chemical compound that is made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(c)
Answer to Problem 9STP
A large quantity of minerals containing water is hard water. The insoluble substances are formed when soap is mixed with hard water. So the activity of soap is decreased.
Explanation of Solution
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium minerals. Soaps contain hydrophilic groups that are replaced by hard water minerals and the activity of soap is decreased.
So the hard water is not suitable for the cleaning action of soap.
Chapter 21 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- identify the relationship between the structures and H- OH HO H H- OH and HO H H -ОН HO H Br and Brarrow_forwardThe right-hand side of this reaction shows the product of an aldol condensation. What are the reactants missing from the left-hand side? Draw them below. ? NaOH Δ If there aren't any reactants that would lead to these products under the reaction conditions given, just check the box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: don't worry if the reactants you propose might also make some other products under these reaction conditions. Just make sure the product above is one of the major products.arrow_forwardPlease help! I need to identify four labeled unknown bottles based off of their colors doing titration using phenlphtalein. I've included my answers, but I wanted to make sure they were correct and if not, what will be correct thank you in advance.arrow_forward
- An organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area. NaOH ?arrow_forwardA student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single molecule that doesn't have a ring. If the student is correct, draw the starting material below, otherwise, check the box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ + NaOH टेarrow_forwardRate = k [I]1.7303[S2O82-]0.8502, Based on your rate, write down a mechanism consistent with your results and indicate which step is the rate determining step.arrow_forward
- 36. Give the major product(s) of each of the following reactions. Aqueous work-up steps (when necessary) have been omitted. a. CH3CH=CHCH3 b. CH3CH2CH2CCH3 H,PO₂, H₂O, A (Hint: See Section 2-2.) 1. LIAIH. (CH,CH,),O 2. H', H₂O H NaBH, CH,CH₂OH d. Br LIAIH. (CH,CH,)₂O f. CH3 NaBH, CH,CH,OH (CH3)2CH H NaBH, CH,CH₂OH Harrow_forwardPredict the major products of this reaction: + H excess NaOH Δ ? Note that the second reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the second reactant than the first. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead.arrow_forwardAn organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area. 1. NaOMe CH3O N. OCH3 ? 2. H3O+arrow_forward
- Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. + More... ☐ ☐ : ☐ + G 1. NaOMe Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward6. Ammonia reacts with nitrogen monoxide and oxygen to form nitrogen and water vapor. If the rate of consumption of NO is 4.5 mollitermin) (a) Find the rate of reaction (b) Find the rate of formations of N; and HO (c) Find the rate of consumption of NH, and O 4NH: 4NO 0:4: +60arrow_forward34. Give the expected major product of each of the following reactions. Conc. HI a. CH3CH2CH2OH b. (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH Conc. HBr H Conc. HI C. OH Conc.HCI d. (CH3CH2)3COHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





