
(a)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The esters in acidic condition undergo hydrolysis and form the corresponding
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
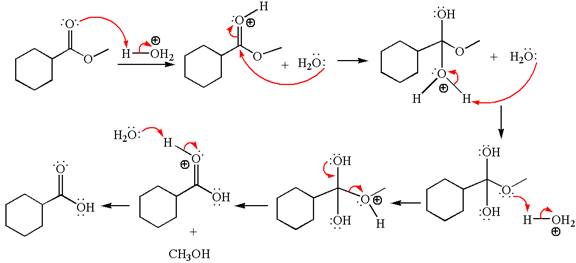
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:
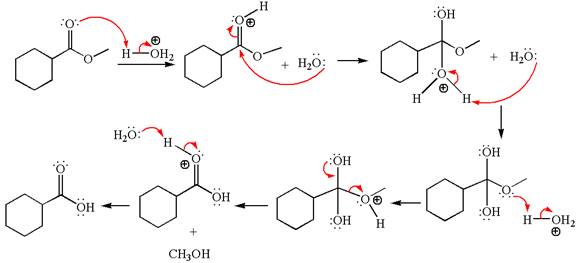
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in an acidic condition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester can be hydrolyzed in basic condition and forms corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol. As hydrolysis occurs in basic condition, it deprotonates carboxylic acid to carboxylate ion. Thus, to recover, it must then be treated with an acid.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
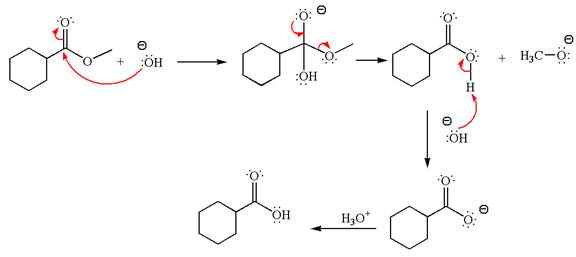
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in a basic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The hydroxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks ester carbonyl to form an intermediate having negatively charged oxygen. The intermediate undergoes elimination of methoxide by delocalization of lone pair of negatively charged oxygen and forms carboxylic acid. The carboxylic acid further undergoes deprotonated to carboxylate ion due to basic reaction condition. Therefore, the carboxylic acid is recovered by addition of
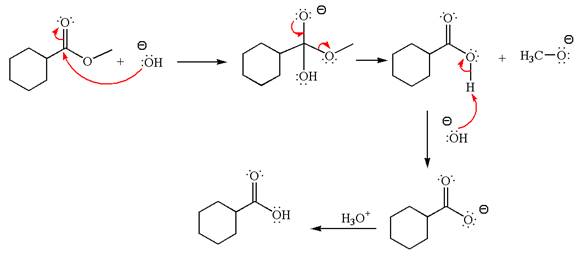
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in a basic condition.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles and thus cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, on addition of base, the alcohol is converted to alkoxide ion, which acts as a good nucleophile and undergoes transesterification when reacted with an ester.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
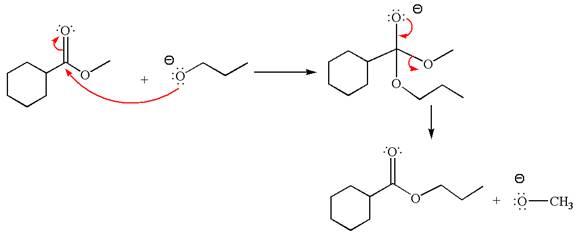
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with
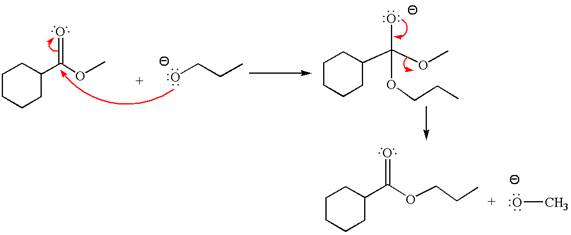
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alkoxide ion.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
Alcohols are weak nucleophiles and cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, for the reaction to carry out, it can be catalyzed by addition of an acid. The ester, on acid-catalyzed reaction with alcohol, undergoes transesterification, called acid-catalyzed transesterification.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
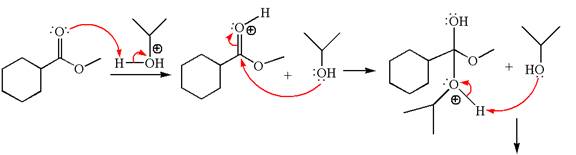
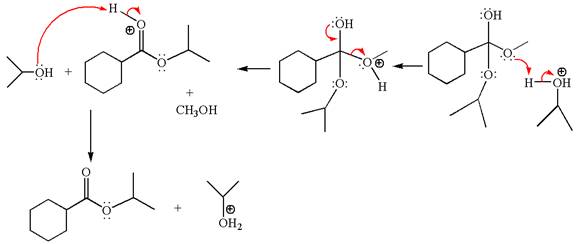
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
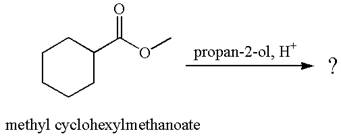
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with


The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alcohol in an acidic condition.
(e)
Interpretation:
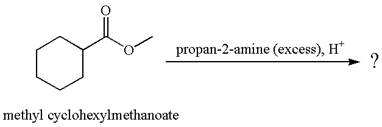
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester, on reaction with an excess of
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
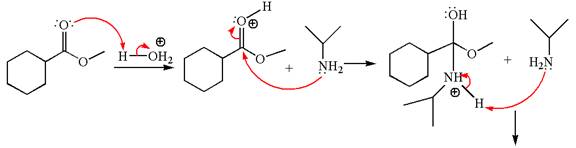
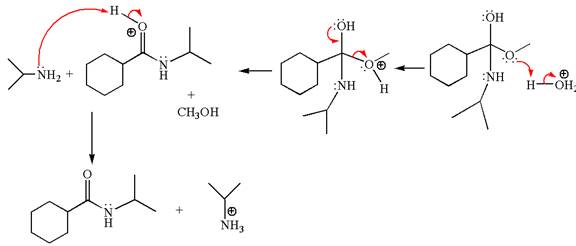
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes aminolysis to form amide and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The amine molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:

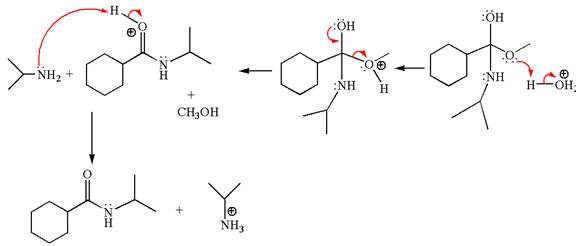
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with amine in an acidic condition.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles; in an acidic or basic condition, they undergo transesterification with an ester, but under normal condition, the reaction does not occur.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
No reaction takes place between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
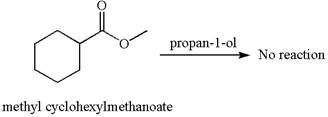
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
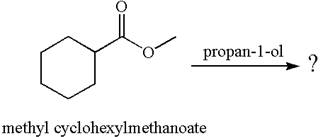
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester, and the given reagent
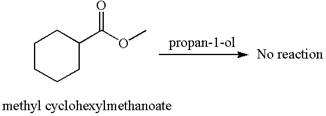
It is determined that there is no reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- 20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





