
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Sodiumborohydride is a metal reducing agent. It reduces
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
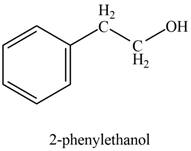
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of sodium borohydride and methanol, phenylacetaldehyde gets reduced to
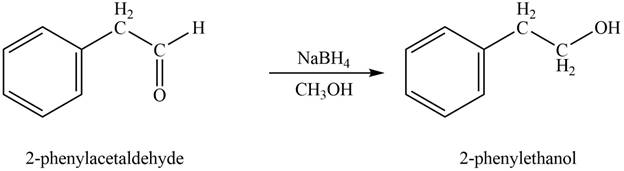
Figure 1
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Lithium aluminum hydride is a strong reducing agent. Treatment of carbonyl compounds with lithium aluminum hydride followed by water yields alcohols. It reduces aldehyde into primary alcohol.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
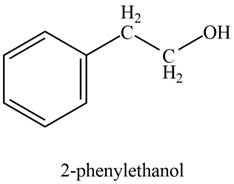
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of lithium aluminium hydride followed by hydrolysis, phenylacetaldehyde gets reduced to
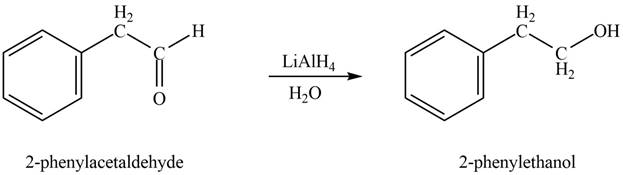
Figure 2
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
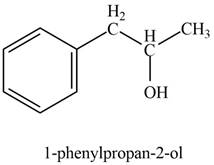
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis, phenylacetaldehyde forms primary alcohol. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
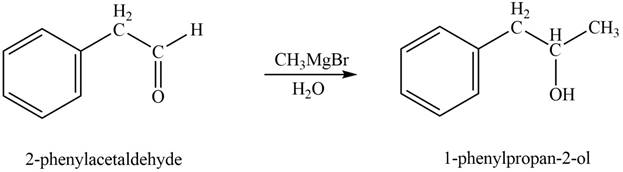
Figure 3
The product formed is
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic addition reaction is a type of organic reaction in which the nucleophile is added to an electrophilic site. In case of carbonyl compounds, the carbonyl carbon acts as an electrophilic site.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
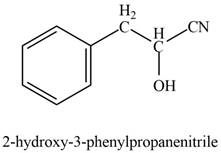
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with sodium cyanide followed by protonation to form
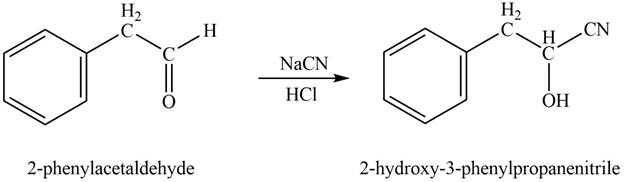
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In Wittig reaction, aldehyde can be directly converted to
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
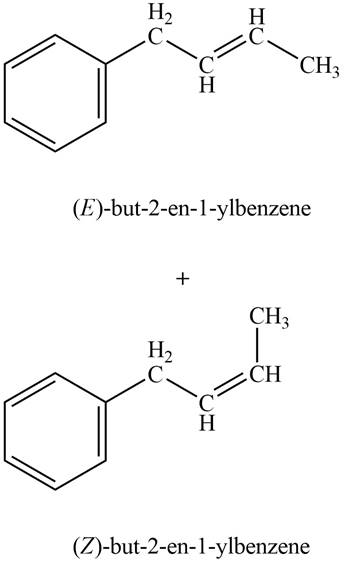
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde on reaction with Wittig reagent
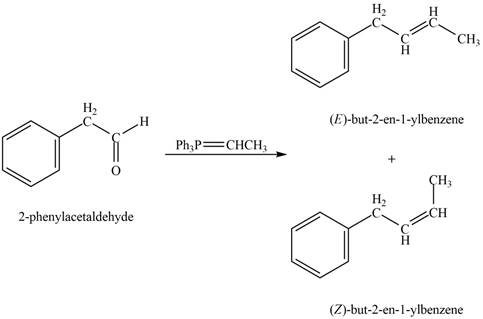
Figure 5
The products formed are
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Aldehyde or ketone on reaction with primary
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
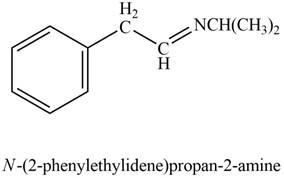
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with
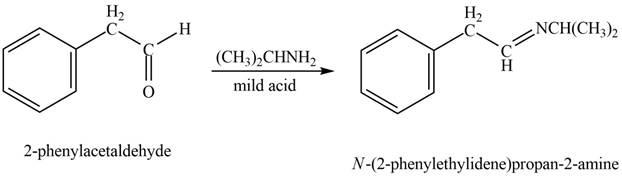
Figure 6
The product formed is
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Aldehyde or ketone on reaction with secondary amine forms enamine. The nucleophilic attack of secondary amine on carbonyl carbon results in the formation of intermediate carbinolamine. This intermediate loses water to form an enamine. In this case, the elimination occurs across two adjacent carbon atoms to form new carbon-carbon double bond.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
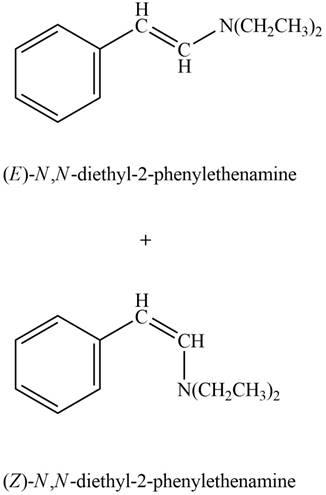
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with
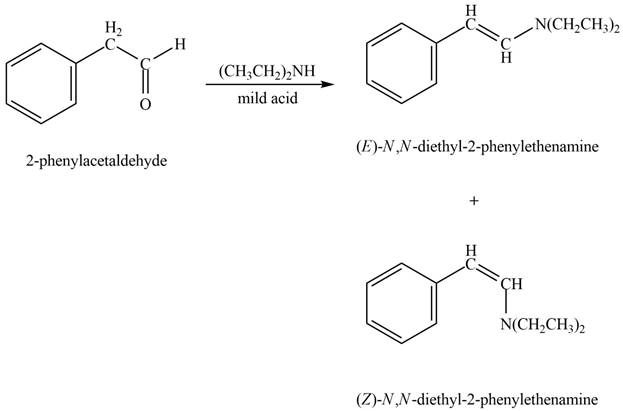
Figure 7
The products formed are
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes or ketones on reaction with one equivalent of alcohol form hemiacetal and on reaction with two equivalents of alcohol it forms acetals. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. These reactions take place in presence of acids.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
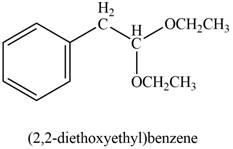
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with excess of ethanol in presence of acid to form acetal. The corresponding reaction is as follows,
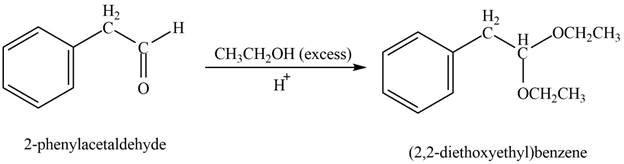
Figure 8
The product formed is (
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Aldehyde or ketone on reaction with secondary amine forms enamine. The nucleophilic attack of secondary amine on carbonyl carbon results in the formation of intermediate carbinolamine. This intermediate loses water to form an enamine. In this case the elimination occurs across two adjacent carbon atoms to form new carbon-carbon double bond.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
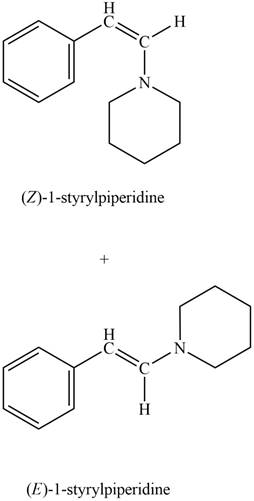
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with piperidine in presence of mild acid to form E and Z isomers of
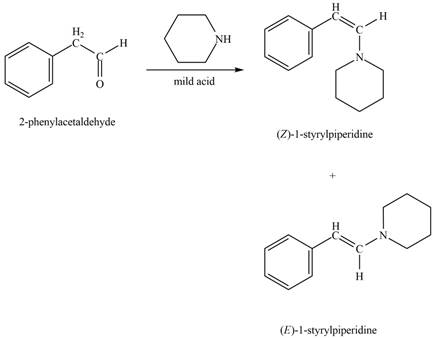
Figure 9
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation:
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes or ketones on reaction with one equivalent of alcohol form hemiacetal and on reaction with two equivalents of alcohol it forms acetals. This is nucleophilic addition reaction. These reactions take place in presence of acids.
Answer to Problem 21.45P
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is,
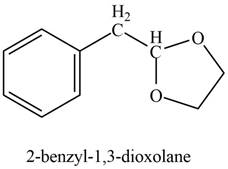
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with ethane-
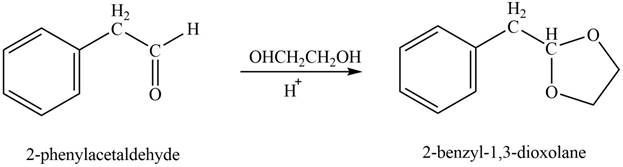
Figure 10
The product formed is
The product formed on treatment of phenylacetaldehyde with given reagent is shown in figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Help me answer this practice sheet I found for an answer guidearrow_forwardshow the retrosynthesis of this molecule step by step starting with 1,3-dimethoxy benzene H3CO OH OH OCH 3arrow_forwardConsider the reaction of a propanoate ester with hydroxide ion shown below. A series of four alcohol leaving groups were tested to determine which would be the best leaving group. Based on the pKa values of the alcohols, predict which alcohol would produce the fastest hydrolysis reaction. HO FOR A Alcohol I, pKa =16.0 B Alcohol II, pKa =10.0 C Alcohol III, pKa = 7.2 + ROH D Alcohol IV, pKa = 6.6arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: NaOH, H₂O 00:4 Na O heat NaO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows :0: Na a NaOH, H2O :0: NaOH, H2O heat heat Na ONH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H CH3NH3+ :0: :0: HO CH3NH2 HH iSelect to Add Arrows i Select to Add Arrows i HH CH3NH3+ CH3NH2 Select to Add Arrows i CH3NH3 CH3NH2 ايكدا HH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardThe reaction is carried out with gases: A → B + C at 300 K. The total pressure is measured as a function of time (table). If the reaction order is 2, calculate the rate or kinetic constant k (in mol-1 L s¹) Ptotal (atm) 492 676 760 808 861 t(s) 0 600 1200 1800 3000arrow_forward
- can someone give a description of this NMR including whether its a triplt singlet doublet where the peak is around at ppm and what functional group it representsarrow_forward1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6 points, 2 points each). OH OH OH A-A OH HOT HO- ACHN and HO- ACHN OH HO HO ° OH and OH OH SH and ...SHarrow_forward20,0 Complete the electron pushing mechanism to y drawing the necomery unicaciones and carved on for Step 1: Add curved arms for the tint step, traiment with NalilĻ. The Nation 458 Step 2: Added for the second step, inalment with), how the "counterion bar Step 3: Daw the products of the last simplom organic and one incoganic spacient, including all nonbondingarrow_forward
- please provide the structure for this problem, thank you!arrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
