
Concept explainers
Give the structure corresponding to each name.
a.
b. dipropyl
c.
d.
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
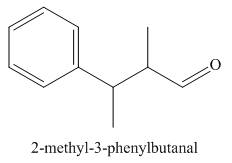
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 1
The structure corresponding to
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to dipropyl ketone is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to dipropyl ketone is shown below.
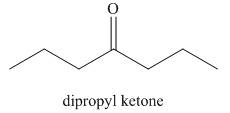
Explanation of Solution
The given name is dipropyl ketone. The word root used in this is diprop. It means structure contains two propyl groups. The hydrocarbons that are attached to the longest chain are called substituents and they are written as prefix in alphabetical order. The functional group present in the given compound is ketone
The structure corresponding to dipropyl ketone is shown below.

Figure 2
The structure corresponding to dipropyl ketone is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
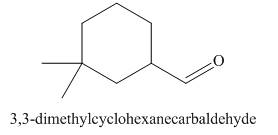
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 3
The structure corresponding to
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
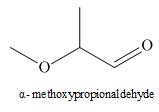
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 4
The structure corresponding to is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
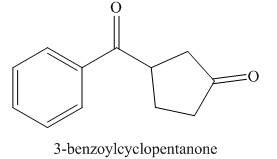
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 5
The structure corresponding to
(f)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
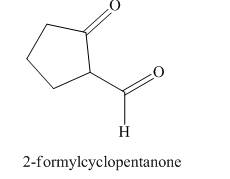
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 6
The structure corresponding to
(g)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
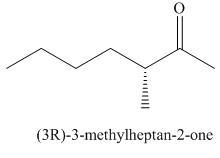
Explanation of Solution
The given name is -3-
The structure corresponding to

Figure 7
The structure corresponding to
(h)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
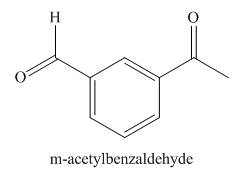
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 8
The structure corresponding to
(i)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
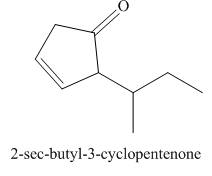
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
In the given compound, one benzaldehyde group is present. The functional group present in the given compound is ketone.
The structure corresponding to

Figure 9
The structure corresponding to
(j)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
• First identify the word root for the given compound.
• The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
• Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 21.43P
The structure corresponding to
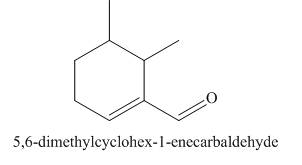
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
The structure corresponding to

Figure 10
The structure corresponding to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- a. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forwardhelp draw any straightchain moleculearrow_forward
- How to do the mechanism drawn for the reactionarrow_forwardPlease provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forward
- Question 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forwardA. Add Water to below compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H₂C CH₂ CH, + H₂O-> ? Major product? Minor product? B. Add Bromine to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + Br₂→ ? Major product and Minor product both are same in this? C. Add Hydrogen Bromide to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H,C CH₂ CH₂ + HBr Major product? Minor product? D. Add Hydrogen to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + H₂ Major product and Minor product both are same in this?arrow_forward36) Complete the following multi-step reactions showing applications of enolate ions arising from ketones, esters, malonic ester, and keto ester, etc. (30 pts) (1) A NaOH, H₂O+ heat A NaOEt EtO OEt (11) EOH, H+ H. B LDA, H₂O+ -78°C B (i) NaOMe, Et-Br (ii) H₂O+, heat EtOOC (III) COOEt B A (i) NaOEt LiAlH 4-bromo-2-butene H₂O+ (ii) H3O+, heat Write the mechanism for Aldol Condensation (I A or B), and Claisen Condensation (II A).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





