
Concept explainers
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
a. 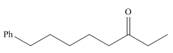 d.
d. 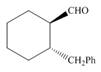 g.
g. 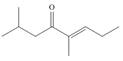
b. 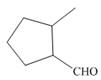 e.
e. 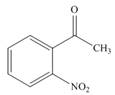 h.
h. 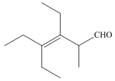
c. 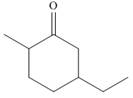 f.
f. 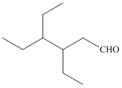
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl carbon. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is a ketone.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of eight
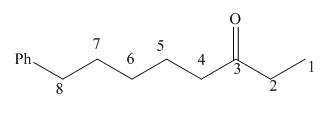
Figure 1
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl carbon. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is an aldehyde.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of the aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of five
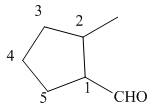
Figure 2
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl carbon. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is a ketone.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of six
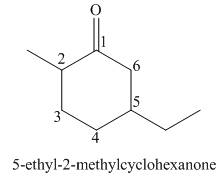
Figure 3
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(d)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is an aldehyde.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given structure shows the presence of six
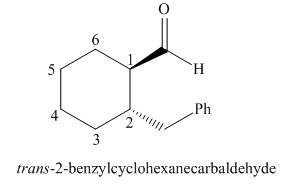
Figure 4
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(e)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl carbon. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is a ketone.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of six
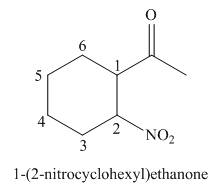
Figure 5
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(f)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is an aldehyde.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given structure shows the presence of six
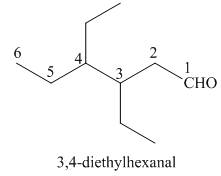
Figure 6
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(g)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl carbon. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is a ketone.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of a ketone. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains a carbonyl group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -one. The third step is numbering of chain to give the least number to carbonyl carbon, and using the general rules of nomenclature.
The given structure shows the presence of eight
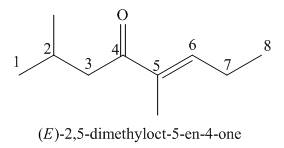
Figure 7
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(h)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be stated.
Concept introduction: One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
Answer to Problem 21.42P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is an aldehyde.
One should follow the given steps to give the IUPAC name of an aldehyde. The first step is finding of longest parent chain that contains an aldehyde group. The second step is changing of -e ending of the parent alkane to the suffix -al. However, when an aldehyde
The given structure shows the presence of six
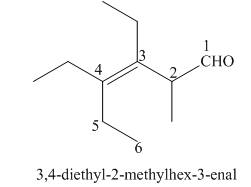
Figure 8
Thus, the IUPAC name for the given compound is
(a) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(b) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(c) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(d) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(e) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(f) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(g) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
(h) The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning



