
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118539293
Author: J. David Irwin, R. Mark Nelms
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 78P
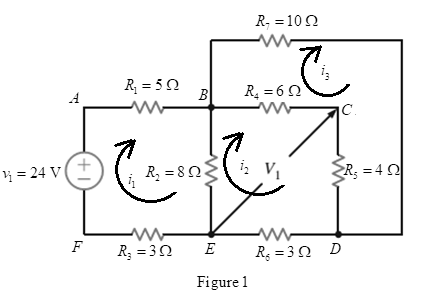
Find
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Chapter 2 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 2 - Determine the current and power dissipated in the...Ch. 2 - Determine the voltage across the resistor in Fig....Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.3, the power absorbed by...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.4, the power absorbed by...Ch. 2 - A model for a standard two D-cell flashlight is...Ch. 2 - An automobile uses two halogen headlights...Ch. 2 - Many years ago a string of Christmas tree lights...Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the network in Fig.P2.8.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig.P2.9.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig.P2.10.
Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the circuit in Fig.P2.11.Ch. 2 - Find I0 and I1 in the circuit in Fig.P2.12.Ch. 2 - Find Ix,Iy, and Iz in the network in Fig.P2.13.Ch. 2 - Find Ix in the circuit in Fig.P2.14.Ch. 2 - Find Ix in the network in Fig. P2.15.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig. P2.16.Ch. 2 - Find Vbd in the circuit in Fig. P2.17.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the circuit in Fig. P2.18.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the network in Fig. P2.19.Ch. 2 - Find Vfb and Vec in the circuit in Fig. P2.20.Ch. 2 - Given the circuit diagram in Fig. P2.21, find the...Ch. 2 - Find VBE and VDA in the circuit in Fig. P2.22.Ch. 2 - Find Vx and Vy in the circuit in Fig. P2.23.Ch. 2 - Find Vac in the circuit in Fig. P2.24.Ch. 2 - Find Vad and Vce in the circuit in Fig. P2.25.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.26.Ch. 2 - Find V1,V2, and V3 in the network in Fig. P2.27.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.28.Ch. 2 - Find V1,V2, and V3 in the network in Fig. P2.29.Ch. 2 - If Vo=3V in the circuit in Fig. P2.30, find Vs.Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by each source in the...Ch. 2 - The 10-V source absorbs 2.5-mW of power. Calculate...Ch. 2 - Find Vbd in the network in Fig. P2.33.Ch. 2 - Find V1 in the network in Fig. P2.34.Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the dependent source in...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.36, find Vx,VAE, and VBD...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.37, find VS if VEB=6V.Ch. 2 - Find VS in the circuit in Fig. P2.38, if VBE=18V.Ch. 2 - Find VA in the network in Fig. P2.39.Ch. 2 - If the 12-V source in the network in Fig. P2.40...Ch. 2 - If VX=12V in the network in Fig. P2.41, find VS...Ch. 2 - Calculate the power absorbed by the dependent...Ch. 2 - Find VA and VO in the circuit in Fig. P2.43.Ch. 2 - Find VO and the power absorbed by the 2k resistor...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed or supplied by the 12-V...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.46.Ch. 2 - Find I0 in the network in Fig. P2.47.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.48.Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by each source in the...Ch. 2 - Find the current IA in the circuit in Fig. P2.50.Ch. 2 - Find IS in the network in Fig. P2.51.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.52.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.53.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.54.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.55.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.56.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.57.Ch. 2 - Find IL in the circuit in Fig. P2.58.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.59.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.60.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.61.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.62.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.63.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.64.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.65.Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance Req in the network...Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.67.Ch. 2 - Given the resistor configuration shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the source in the...Ch. 2 - Find I1 and Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.73.Ch. 2 - Find I1 and Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.74.Ch. 2 - Find Vab and Vdc in the circuit in Fig. P2.75.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.76.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.77.Ch. 2 - Find V1 in the network in Fig. P2.78.Ch. 2 - Find Vab in the circuit in Fig. P2.79.Ch. 2 - Find Vab in the network in Fig. P2.80.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and V1 in the circuit in Fig. P2.81.Ch. 2 - Determine Vo in the network in Fig. P2.82.Ch. 2 - Calculate VAB in Fig. P2.83.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.84 if all...Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.85.Ch. 2 - Determine the power supplied by the 36-V source in...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the current source in...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.88, V1=12V. Find VS.Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. P2.89, Vo=2V. Find IS.Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.90, V1=14V. Find VS.Ch. 2 - If VR=15V, find VX in Fig. P2.91.Ch. 2 - Find the value of IA in the network in Fig. P2.92.Ch. 2 - If V1=5V in the circuit in Fig. P2.93, find IS.Ch. 2 - Given that Vo=4V in the network in Fig. P2.94,...Ch. 2 - Find the value of VS in the network in Fig. P2.95...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.96, VO=6V. Find IS.Ch. 2 - Find the value of V1 in the network in Fig. P2.97...Ch. 2 - Find the value of IA in the circuit in Fig. P2.98.Ch. 2 - If the power supplied by the 2-A current source is...Ch. 2 - The 40-V source in the circuit in Fig. P2.100 is...Ch. 2 - Find the value of the current source IA in the...Ch. 2 - Given Io=2mA in the network in Fig. P2.102, find...Ch. 2 - Find the value of Vx in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Given Ia=2mA in the circuit in Fig. P2.104, find...Ch. 2 - Given Va in the network in Fig. 2.105, find IA.Ch. 2 - Find the value of Vx in the circuit in Fig. P2.106...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the value of g in the network in Fig. P2.108...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 24-V source in the...Ch. 2 - Find Io in circuit in Fig. P2.110.Ch. 2 - Find Io in circuit in Fig. P2.111.Ch. 2 - Determine the value of Vo in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - If Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.113 is 24 V, find...Ch. 2 - Find the value of VS in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 6-mA source in the...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.116.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.117.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig. P2.118.Ch. 2 - A single-stage transistor amplifier is modeled as...Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.120.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.121.Ch. 2 - A typical transistor amplifier is shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find VX in the network in Fig. P2.123.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.124.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the circuit in Fig. P2.125.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.126.Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the 12-k resistor on...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the 12-k resistor in...Ch. 2 - Find the value of k in the network in Fig. P2.129...Ch. 2 - If the power absorbed by the 10-V source in Fig....Ch. 2 - If the power supplied by the 2-A current source in...Ch. 2 - What is the power generated by the source in the...Ch. 2 - Find v ah in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-2. a. 5V c....Ch. 2 - If Req=10.8 in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-3, what is...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit in...Ch. 2 - The 100-V source is absorbing 50W of power in the...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 40-V source in the...Ch. 2 - What is the current I0 in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the voltage Vo in the network in Fig. 2PFE-8....Ch. 2 - What is the voltage Vo in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the current Ix in Fig. 2PFE-10. a. 1/2Ac....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A(n) _____ is a specialized routine that performs a specific operation and then returns a value.
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Determine the components of reaction at the fixed support A. Neglect the thickness of the beam. Prob. F5-4
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
If a value in an array of base type int occurs twicefor example, both b[0] and b[5] are 7and you sort the array...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
A method in a subclass that has the same signature as a method in the superclass is an example of __________. a...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Computer programs typically perform what three steps?
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
In Exercises 39 through 44, write a program to carry out the stated task. Cost of Electricity The cost of the e...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Chose the correct answer: 1- A squirrel cage induction motor is not selected when (A) initial cost is the main consideration (B) maintenance cost is to be kept low (C) higher starting torque is the main consideration (D) all above considerations are involved 2- The torque of an induction motor is .............. (A) directly proportional to slip (B) inversely proportional to slip... (C) proportional to the square of the slip (D) none of the above 3- Insertion of resistance in the stator of an induction motor. (A) increases the load torque (B) decreases the starting torque (C) increases the starting torque (D) none of above tool to slip 10 or of the above 4- Increase in the length of air-gap in the induction motor results in the increasing of its (A) air-gap flux (B) magnetizing current (C) speed (D) power factor 5- In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and PB is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the set…arrow_forwardChose the correct answer: 1- The resultant flux in stator winding of three-phase induction motor is equal to (A) Maximum value of flux due to any phase (B) Twice of the maximum value of flux due to any phase. (C) 0.5 times the maximum value of flux due to any phase (D) 1.5 times the maximum value of flux due to any phase 2- Which one of the following starters cannot be used for 3-phase, star - connected, slip-ring induction motor? (A) Auto-transformer starter (B) Star-delta starter (C) Direct-on-line starter (D) Rotor resistance starter 3- The crawling in the induction motor is caused by.............. (A) low voltage supply (B) high loads (D) improper design of the machine (C) harmonics developed in the motor 4- The 'cogging' of an induction motor can be avoided by........... (A) good ventilation (B) using DOL starter (C) star-connecting of stator winding (D) having number of rotor slots more or less than the number of stator slots 5- The method which can be used for the speed control…arrow_forwardManual solution only, no Al usedarrow_forward
- Choose the correct answer: 1- The stator core of a 3- phase induction motor is laminated in order to reduce the Eddy current loss ) Weight of the stator (B) Hysteresis loss (C) Both eddy current and hysteresis loss - In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling of a 3-phase induction motor, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and P, is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the motor B is given by Ⓐ120f/ PA + PB CO (B) 120f/PA-Ps (C) 120f/PA (D) 120f/ Ps 3-Direct online starter is used for 3- phase induction motors having capacity COOOO ⑭Ⓐ Less than 5 h.p. (B) Less than 10 h.p. (C) Greater than 10 h.p. (D) For any capacity motor 4-Crawling of a 3- phase induction motor is a phenomena mainly associated with (B) 5th harmonics Ⓒ) 7 th harmonics (D) 2nd harmonics (A) 3rd harmonics 5-Cogging in a 3- phase induction motor is caused --------- (Ⓐ) If the number of stator slots are equal to number of rotor slots (B) If the motor is running at fraction of its…arrow_forwardChoose the correct answer: 1-We avoid line starting of induction motor and use starter because... (A) It will run in reverse direction (B) It will pick up very high speed and may go out of step Motor takes five to seven times its full load current (D) Starting torque is very high 2-DOL starting of induction motors is usually restricted to........... A Low horsepower motors (D) High speed motors (B) Variable speed motors (C) High horsepower motors 3- The method which can be used for the speed control of induction motor from stator side is......... (A) V/f control (B) Controlling number of stator poles to control Ns (C) Adding rheostats in stator circuit All of these 4-In cumulatively cascade method for speed controlling, if PA is the number of poles of main motor and PB is the number of poles of auxiliary motor. Then the speed of the rotor B is given by 120f/PA + PB (B) 120f/PA-PB (C) 120f/PA 5-The crawling in the induction motor is caused by.............. (A) low voltage supply (B)…arrow_forwardFor the picture attached below the parameters are the following: f1 = 400 Hz m(t) = sin(2 fmt), where fm = 300 Hz. Assume ideal LPFs with a cut-o frequency of f1. What would be the value of frequency f2 be so that the carrier frequency is 2.5kHz? What modification of this system is required to generate USSB (at the same carrier frequency)? ( Note: this does not involbe changing the oscillator frequencies)arrow_forward
- Determine (analytically) the signals at points A-Garrow_forwardSolve without using alarrow_forwardA Si step junction maintained at room temperature under equilibrium conditions has a p-side doping of NA 2X1015/cm³ and an n-side doping of ND=1015/cm³. Compare a) Vbi b) Xp, Xn, and W c) ɛ at x=0 d) V at x=0 Make sketches that are roughly to scale of the charge density, electric field, and electrostatic potential as a function of position.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY