
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118539293
Author: J. David Irwin, R. Mark Nelms
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 40P
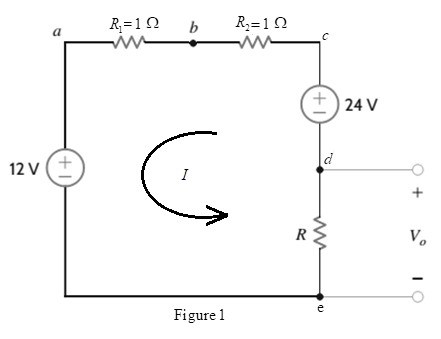
If the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the integral for
ezz
Cz-i
ezz
Zdz and $c (z-i)³
dz
Determine the voltage across A and B in the circuit given below:
An inductive coil having negligible resistance and 0.1H inductance is connected a supply of 220V, 50 Hz. Calculate (a) Inductive reactance, (b) RMS value of Current, (c) Power consumed, (d) Power factor, (e) Write down the equations for voltage and current.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 2 - Determine the current and power dissipated in the...Ch. 2 - Determine the voltage across the resistor in Fig....Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.3, the power absorbed by...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.4, the power absorbed by...Ch. 2 - A model for a standard two D-cell flashlight is...Ch. 2 - An automobile uses two halogen headlights...Ch. 2 - Many years ago a string of Christmas tree lights...Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the network in Fig.P2.8.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig.P2.9.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig.P2.10.
Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the circuit in Fig.P2.11.Ch. 2 - Find I0 and I1 in the circuit in Fig.P2.12.Ch. 2 - Find Ix,Iy, and Iz in the network in Fig.P2.13.Ch. 2 - Find Ix in the circuit in Fig.P2.14.Ch. 2 - Find Ix in the network in Fig. P2.15.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig. P2.16.Ch. 2 - Find Vbd in the circuit in Fig. P2.17.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the circuit in Fig. P2.18.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the network in Fig. P2.19.Ch. 2 - Find Vfb and Vec in the circuit in Fig. P2.20.Ch. 2 - Given the circuit diagram in Fig. P2.21, find the...Ch. 2 - Find VBE and VDA in the circuit in Fig. P2.22.Ch. 2 - Find Vx and Vy in the circuit in Fig. P2.23.Ch. 2 - Find Vac in the circuit in Fig. P2.24.Ch. 2 - Find Vad and Vce in the circuit in Fig. P2.25.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.26.Ch. 2 - Find V1,V2, and V3 in the network in Fig. P2.27.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.28.Ch. 2 - Find V1,V2, and V3 in the network in Fig. P2.29.Ch. 2 - If Vo=3V in the circuit in Fig. P2.30, find Vs.Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by each source in the...Ch. 2 - The 10-V source absorbs 2.5-mW of power. Calculate...Ch. 2 - Find Vbd in the network in Fig. P2.33.Ch. 2 - Find V1 in the network in Fig. P2.34.Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the dependent source in...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.36, find Vx,VAE, and VBD...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.37, find VS if VEB=6V.Ch. 2 - Find VS in the circuit in Fig. P2.38, if VBE=18V.Ch. 2 - Find VA in the network in Fig. P2.39.Ch. 2 - If the 12-V source in the network in Fig. P2.40...Ch. 2 - If VX=12V in the network in Fig. P2.41, find VS...Ch. 2 - Calculate the power absorbed by the dependent...Ch. 2 - Find VA and VO in the circuit in Fig. P2.43.Ch. 2 - Find VO and the power absorbed by the 2k resistor...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed or supplied by the 12-V...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.46.Ch. 2 - Find I0 in the network in Fig. P2.47.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.48.Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by each source in the...Ch. 2 - Find the current IA in the circuit in Fig. P2.50.Ch. 2 - Find IS in the network in Fig. P2.51.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.52.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.53.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.54.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.55.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.56.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.57.Ch. 2 - Find IL in the circuit in Fig. P2.58.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.59.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.60.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.61.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.62.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.63.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.64.Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the circuit in Fig. P2.65.Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance Req in the network...Ch. 2 - Find RAB in the network in Fig. P2.67.Ch. 2 - Given the resistor configuration shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Determine the total resistance, RT, in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the source in the...Ch. 2 - Find I1 and Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.73.Ch. 2 - Find I1 and Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.74.Ch. 2 - Find Vab and Vdc in the circuit in Fig. P2.75.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.76.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.77.Ch. 2 - Find V1 in the network in Fig. P2.78.Ch. 2 - Find Vab in the circuit in Fig. P2.79.Ch. 2 - Find Vab in the network in Fig. P2.80.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and V1 in the circuit in Fig. P2.81.Ch. 2 - Determine Vo in the network in Fig. P2.82.Ch. 2 - Calculate VAB in Fig. P2.83.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.84 if all...Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.85.Ch. 2 - Determine the power supplied by the 36-V source in...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the current source in...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.88, V1=12V. Find VS.Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Fig. P2.89, Vo=2V. Find IS.Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.90, V1=14V. Find VS.Ch. 2 - If VR=15V, find VX in Fig. P2.91.Ch. 2 - Find the value of IA in the network in Fig. P2.92.Ch. 2 - If V1=5V in the circuit in Fig. P2.93, find IS.Ch. 2 - Given that Vo=4V in the network in Fig. P2.94,...Ch. 2 - Find the value of VS in the network in Fig. P2.95...Ch. 2 - In the network in Fig. P2.96, VO=6V. Find IS.Ch. 2 - Find the value of V1 in the network in Fig. P2.97...Ch. 2 - Find the value of IA in the circuit in Fig. P2.98.Ch. 2 - If the power supplied by the 2-A current source is...Ch. 2 - The 40-V source in the circuit in Fig. P2.100 is...Ch. 2 - Find the value of the current source IA in the...Ch. 2 - Given Io=2mA in the network in Fig. P2.102, find...Ch. 2 - Find the value of Vx in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Given Ia=2mA in the circuit in Fig. P2.104, find...Ch. 2 - Given Va in the network in Fig. 2.105, find IA.Ch. 2 - Find the value of Vx in the circuit in Fig. P2.106...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the value of g in the network in Fig. P2.108...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 24-V source in the...Ch. 2 - Find Io in circuit in Fig. P2.110.Ch. 2 - Find Io in circuit in Fig. P2.111.Ch. 2 - Determine the value of Vo in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - If Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.113 is 24 V, find...Ch. 2 - Find the value of VS in the network in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 6-mA source in the...Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.116.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.117.Ch. 2 - Find I1 in the network in Fig. P2.118.Ch. 2 - A single-stage transistor amplifier is modeled as...Ch. 2 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P2.120.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P2.121.Ch. 2 - A typical transistor amplifier is shown in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find VX in the network in Fig. P2.123.Ch. 2 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P2.124.Ch. 2 - Find I1,I2, and I3 in the circuit in Fig. P2.125.Ch. 2 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P2.126.Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the 12-k resistor on...Ch. 2 - Find the power absorbed by the 12-k resistor in...Ch. 2 - Find the value of k in the network in Fig. P2.129...Ch. 2 - If the power absorbed by the 10-V source in Fig....Ch. 2 - If the power supplied by the 2-A current source in...Ch. 2 - What is the power generated by the source in the...Ch. 2 - Find v ah in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-2. a. 5V c....Ch. 2 - If Req=10.8 in the circuit in Fig. 2PFE-3, what is...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit in...Ch. 2 - The 100-V source is absorbing 50W of power in the...Ch. 2 - Find the power supplied by the 40-V source in the...Ch. 2 - What is the current I0 in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the voltage Vo in the network in Fig. 2PFE-8....Ch. 2 - What is the voltage Vo in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 2 - Find the current Ix in Fig. 2PFE-10. a. 1/2Ac....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why are the relational operators called relational?
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
12. Consider the following strange, but true, units:
1 arroba =11.5 kilograms [kg] 1 peck = 9 liters [L]
A bask...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
The process of input validation works as follows: when the user of a program enters invalid data, the program s...
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Distinguish among data definition commands, data manipulation commands, and data control commands.
Modern Database Management
Write a program that demonstrates type casting of double values by performing the following tasks: Use scanner ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
A file that contains a Flash animation uses the __________ file extension. a. .class b. .swf c. .mp3 d. .flash
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If Fourier transform of f(t) is F(w) find Fourier transform of g(t) using only properties. d g(t) = f(2t)+8(3-1)+ ej(t-1)f(t) dtarrow_forward3z²+7z+1 dz (b) If C is the circle |z+i|=1. What is the value of S (a) If C is the circle |z+1|=1. z+1 (c) If C is the ellipse x²+y2=8.arrow_forward= Find the residues of all the poles of f(z) = 3z (z+2)²(z²-1)arrow_forward
- find the inverse Laplace transform of X(s)= i) Re[s]> 3 ii) Re[s]<1 s+5 for (s-1)(s-2)(s-3) iii) 1arrow_forwardFor R1, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R1, what the current in mA? For R1, what is the voltage in V? For R1, what is the power in W? For R2, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R2, what the current in mA? For R2, what is the voltage in V? For R2, what is the power in W? For R3, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R3, what the current in mA? For R3, what is the voltage in V? For R3, what is the power in W? For R4, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R4, what the current in mA? For R4, what is the voltage in V? For R4, what is the power in W? For R5, what is the resistance in kΩ? For R5, what the current in mA? For R5, what is the voltage in V? For R5, what is the power in W? What is the total resistance in Ω? What is the total current in mA? What is the total voltage in V? What is the total power in W?arrow_forwardPlease answer allarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY