
Concept explainers
a. Rank the following alcohols from strongest to weakest acid:
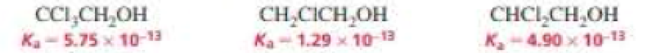
b. Explain the relative acidities.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given alcohols have to be ranked from strongest to weakest acid.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Answer to Problem 47P
The given alcohols are ranked from strongest to weakest acid as follows,
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The conjugated base of a weak acid is very strong. As the electronegativity of substituent increases, the greater will be the inductive electron withdrawal of the substituent making it a strong acid.
Therefore, the acidity order is:
The compound with three chlorine atoms near to the
(b)
Interpretation:
The relative acidities of the given alcohol compounds have to be explained briefly.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The electron density near
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
