
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion. For the molecules that have no lone pairs around the central atom the bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement is decided by the table as follows:
In order to determine the shape the steps to be followed are indicated as follows:
- 1. Lewis structure of molecule should be written.
- 2. The type electron arrangement around the central atom should be identified around the central atom. This essentially refers to determination of bond pairs and unshared or lone pairs around central atoms.
- 3. Then bonded-atom unshared -pair arrangement that can maximize the distance of electron pairs about central atom determines the shape.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone –lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.13E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 9 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the iodine atoms to satisfy their octet. Hence, the Lewis structure in
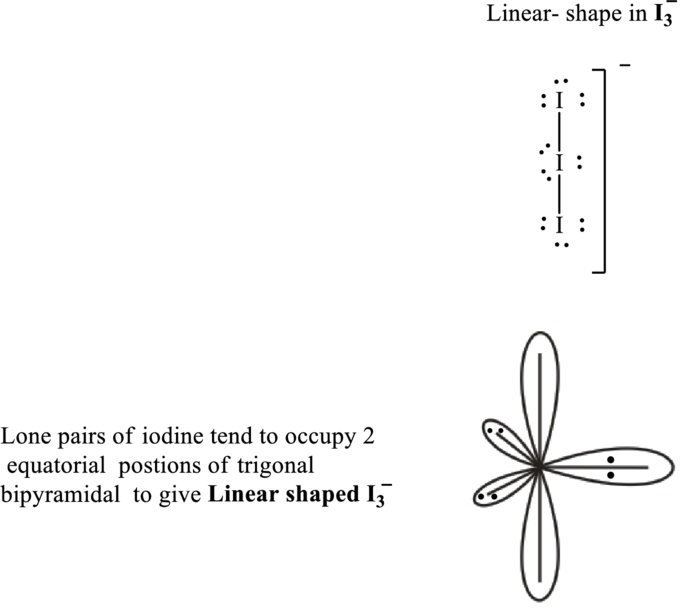
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any linear species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
(b)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for molecule has to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E.13E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 12 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs or multiple bonds to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure in
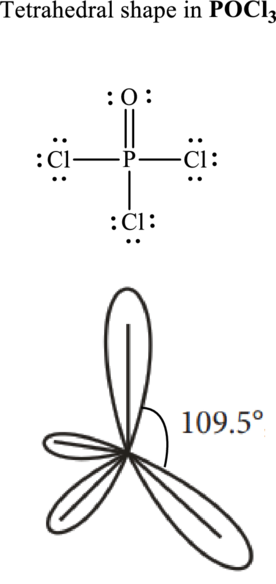
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any tetrahedral species the VSEPR formula is predicted to be
(c)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula and shape for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.13E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 10 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to each of the oxygen to satisfy its octet. Hence, the Lewis structure in
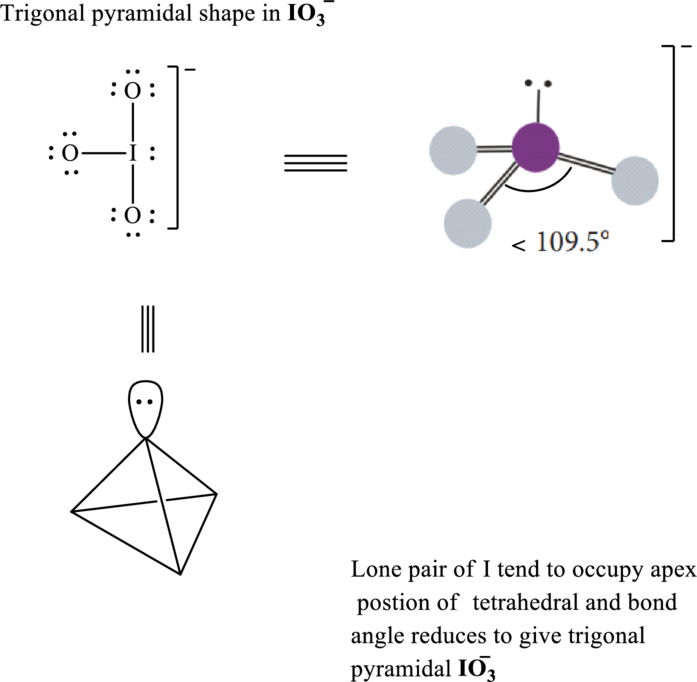
It is evident that in
Lone pairs tend to be localized on apical position while
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any trigonal pyramidal species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
(d)
Interpretation:
The VSEPR formula, shape for the Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.13E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 6 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs or double bonds on each of the atom in
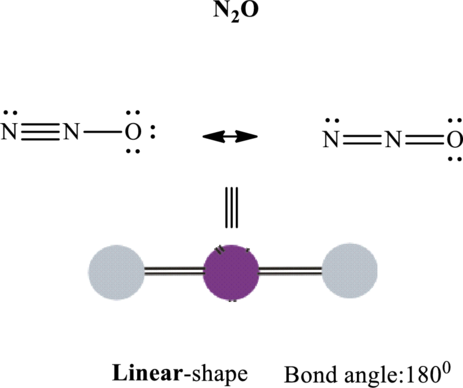
It is evident that in
If central atom is represented by A, and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any linear species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (LL) W/ACCESS
- H3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forward
- Is the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forward
- If CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward+ Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset H3C H H C CH3 CH-CH3 1-3-methylpent ene trans- cis- 5-6-3-1-2-4- tert- tri sec- di cyclo iso but pent hex meth prop eth yl ane ene yne ☑arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
