
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model predicts shape by inclusion of bond angles and most distant arrangement of atoms that leads to minimum repulsion.
For molecules that have lone pairs around central atom, lone pairs influence shape, because there are no atoms at the positions occupied by these lone pairs. The key rule that governs the molecular shape, in this case, is the extent of lone pair–lone pair repulsions are far greater than lone bond pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsions. The table that summarized the molecular shapes possible for various combinations of bonded and lone pairs are given as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E.14E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 12 electron pairs are assigned as lone pairs of each of the
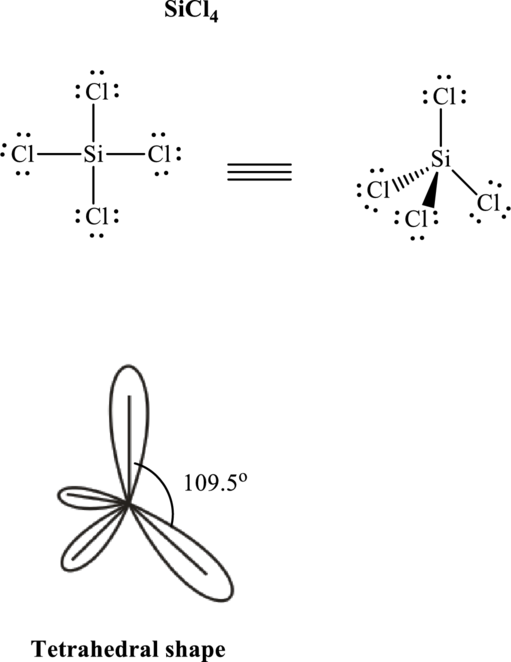
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bon pairs by X, then for any see-saw species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
It is evident that in
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.14E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
The skeleton structure in
These 15 electron pairs are assigned as lone pairs of each of the
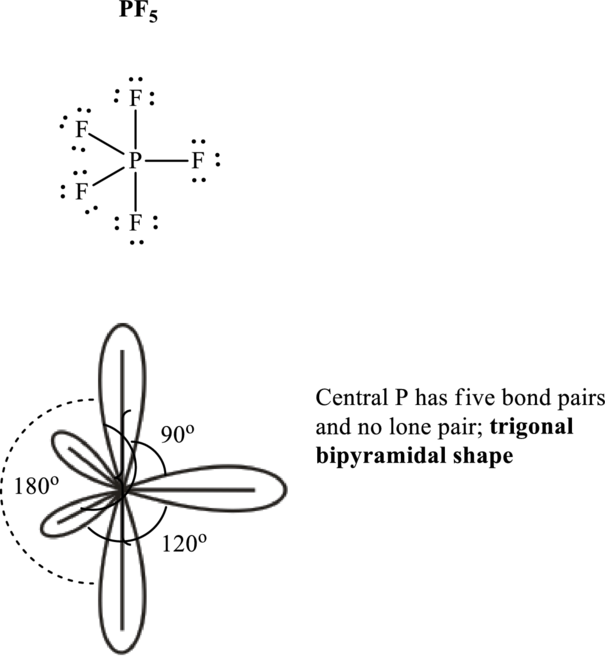
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any trigonal pyramidal geometry the VSEPR formula is predicted as
It is evident that in
The bond angles are
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E.14E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each chlorine and central iodine in
The skeleton structure in
These 8 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs to each of the bromine atoms and central sulfur to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSPER geometry in
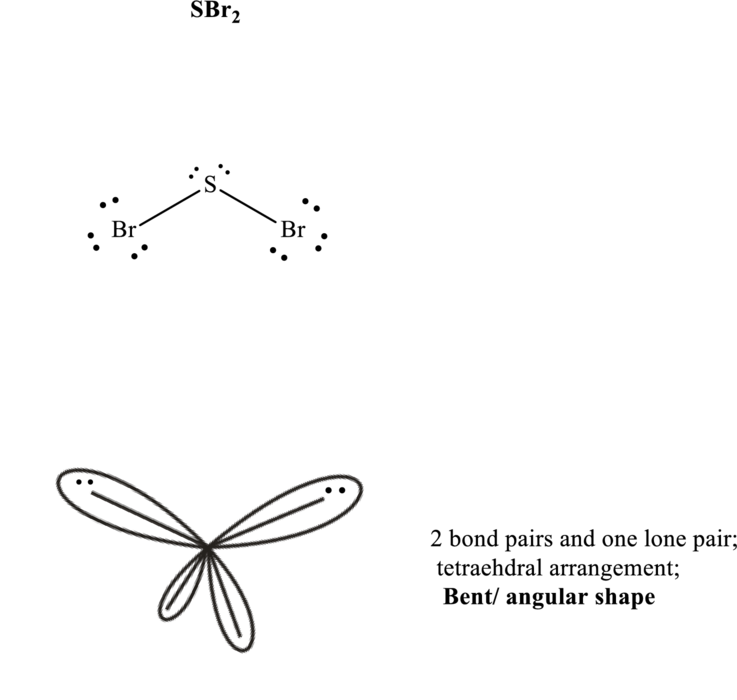
It is evident that in
If lone pairs are represented by E, central atom with A and other attached bond pairs by X, then for any see-saw species the VSEPR formula is predicted as
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E.14E
The shape for
Explanation of Solution
Total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons on each chlorine and central iodine in
The skeleton structure in
These 8 electron pairs are allotted as lone pairs of each of the chlorine atoms and central iodine to satisfy respective octets. Hence, the Lewis structure and corresponding VSPER geometry in
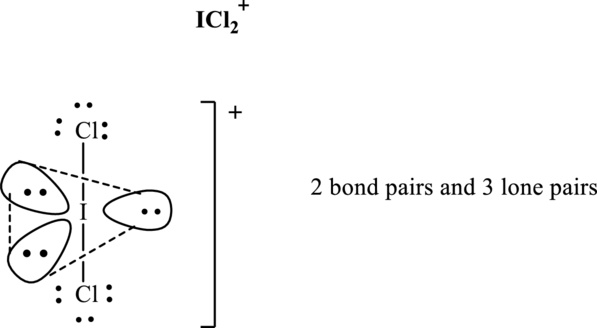
It is evident that in
Lone pairs tend to occupy the equatorial locations of trigonal plane so that they are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (LL) W/ACCESS
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





