
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures represent covalent bonds and describe valence electrons configuration of atoms. The covalent bonds are depicted by lines, and unshared electron pairs by pairs of dots. The sequence to write Lewis structure of some molecule is given as follows:
- The central atom is identified and various other atoms are arranged around it. This central atom so chosen is often the least electronegative.
- Total valence electrons is estimated.
- single bond is first placed between each atom pair.
- The electrons left can be allocated as unshared electron pairs or as multiple bonds around the right
symbol of the element to satisfy the octet (or duplet) for each atom. - Add charge on the overall structure in case of polyatomic cation or anion.
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Here,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure possible for
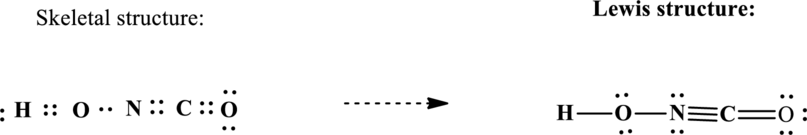
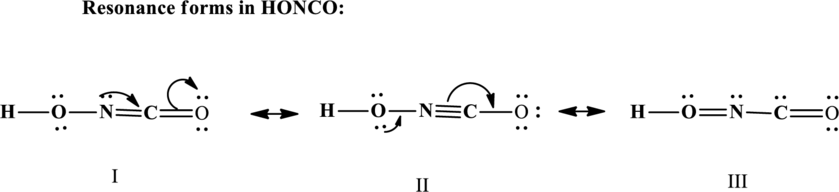
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in various equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the non-zero formal charges can be assigned as follows:
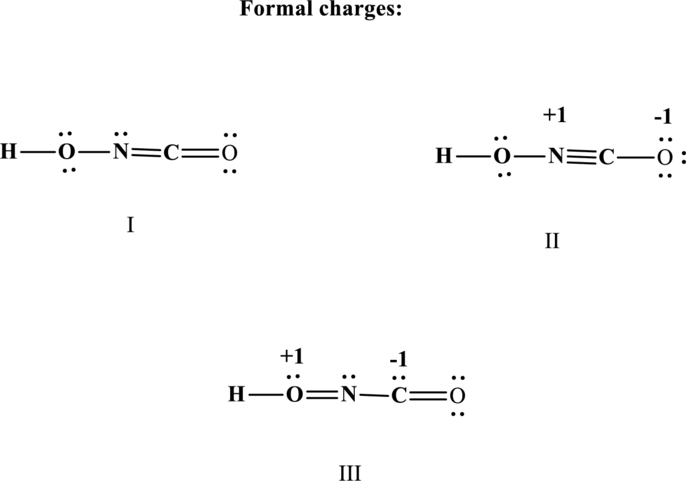
(b)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure possible for
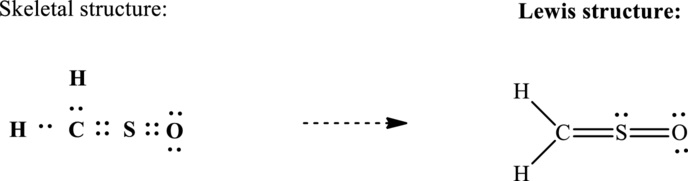
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in various equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
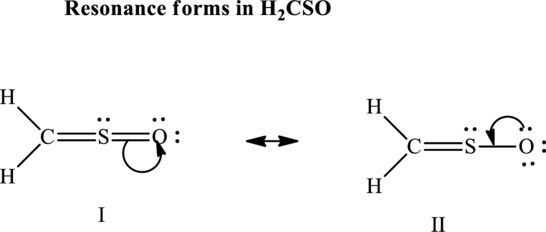
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 6 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the formal charges can be assigned as follows:
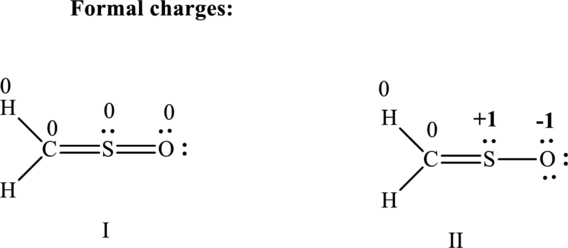
(c)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
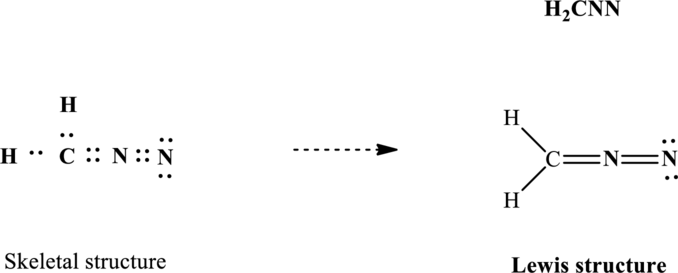
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in two equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
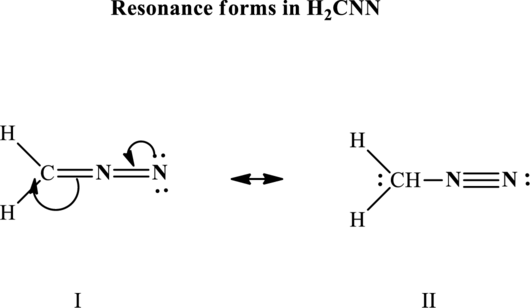
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 1 for
Therefore the formal charges in
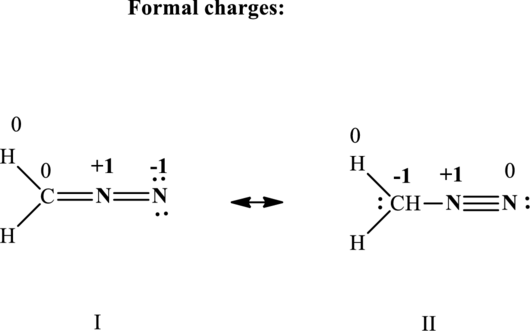
(d)
Interpretation:
The most important Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
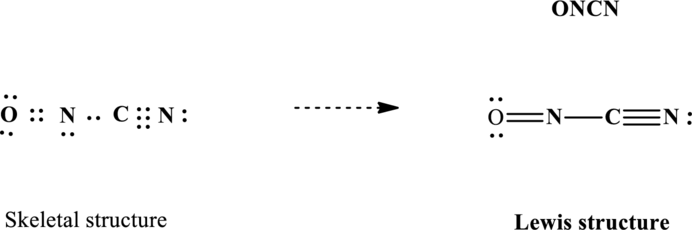
Since the double and triple bonds can conjugate therefore delocalization occurs that results in two equivalent resonance structures as indicated below:
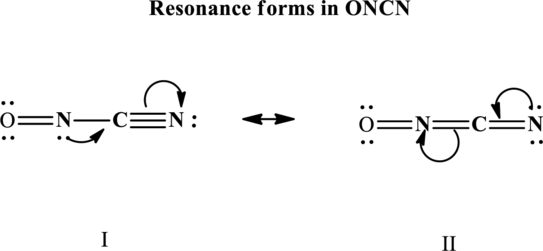
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure is calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5 for
Substitute 5 for
Therefore the non-zero formal charges in
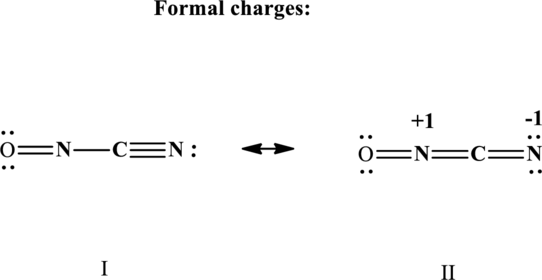
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (LL) W/ACCESS
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning


