
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures represent covalent bonds and describe valence electrons configuration of atoms. The covalent bonds are depicted by lines and unshared electron pairs by pairs of dots. The sequence to write Lewis structure of some molecule is given as follows:
- The central atom is identified and various other atoms are arranged around it. This central atom so chosen is often the least electronegative.
- Total valence electrons are estimated for each atoms.
- single bond is first placed between each atom pair.
- The electrons left can be allocated as unshared electron pairs or as multiple bonds around
symbol of element to satisfy the octet (or duplet) for each atom. - Add charge on overall structure in case of polytatomic cation or anion.
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Here,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electrons is sum of the valence electrons for each atom along with uni-positive in
Hence, 5 pairs are allocated to form Lewis structure of
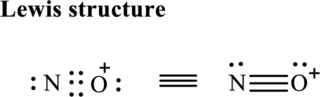
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation as follows:
Substitute 5for
Substitute 6for
Hence
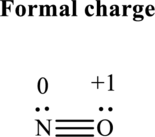
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electrons is sum of the valence electrons on each atom in
Hence, of these five pairs two are allocated as lone pairs and three pairs are added so as to form triple bond to obtain Lewis structure of
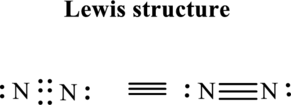
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Substitute 5for
Hence each
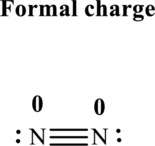
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electron is sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 5 pairs are allocated to form Lewis structure of
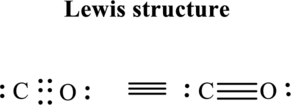
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Substitute 4for
Substitute 6 for
Hence
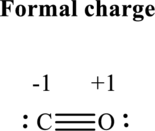
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electron is sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 5 pairs are arranged to form Lewis structure of
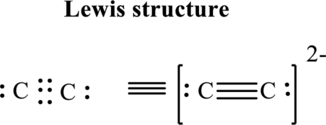
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Substitute 4 for
Hence each
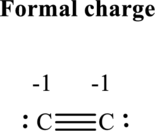
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Thus total valence electron is sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
Hence, 5 pairs are arranged to form Lewis structure of
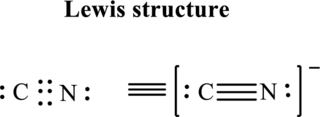
The formal charge on each atom in the Lewis structure can be calculated from the equation written as follows:
Substitute 4 for
Substitute 5 for
Hence formal charge on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (LL) W/ACCESS
- 1. Part 1: Naming Organic Compounds он H₁C-C-CH3 CH3 Br CI CI 2. Br-CH-CH-CH₂ H₂C-CH-C= -CH-CH2-CH3 3. HC-CH-CH-C-OH 5. H₂C-CH-CH₂-OH 7. OH 4. CH CH₂-CH₂ 6. сно CH-CH-CH-CH₂-CH₂ H₁₂C-CH-CH-CH-CH₁₂-CH₁₂ 8. OHarrow_forward11 Organic Chemistry Organic Nomenclature Practice Name/Functional Group n-butane Formula Structural Formula (1) C4tt10 H3C C- (2) CH3CH2CH2 CH 3 H₂ -CH3 Н2 name & functional group (1) and (2) OH H₁₂C Н2 name only (1) and (2) name only (1) and (2) H₁C - = - CH₂ Н2 HC=C-C CH3arrow_forwardUnder aqueous basic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2: NC H₂O он- H₂O 1 2 OH Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Assign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forwardAssign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward
- 个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





