
Concept explainers
The stress-strain curve.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial area is
The final area is
The original length is
Formula used:
The true strain is given as,
Here,
The Actual area is given as,
The actual are for the initial load is given as,
The final length is given as,
Here,
The stress is given as,
Here, P is the applied load.
Calculation:
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,\
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
For
The final length can be calculated as,
The strain can be calculated as,
The actual area can be calculated as,
The stress can be calculated as,
The stress-strain curve from the above calculation is given as,
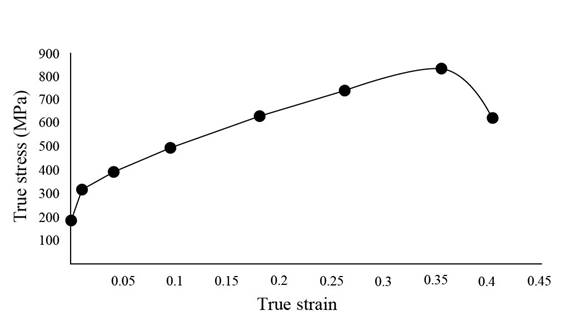
Figure 1.1
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MANUFACTURING PROCESSES FOR ENGINEE
- varrow_forward13.64 The shaft shown in Sketch h transfers power between the two pulleys. The tension on the slack side (right pul- ley) is 30% of that on the tight side. The shaft rotates at 900 rpm and is supported uniformly by a radial ball bearing at points 0 and B. Select a pair of radial ball bear- ings with 99% reliability and 40,000 hr of life. Assume Eq. (13.83) can be used to account for lubricant clean- liness. All length dimensions are in millimeters. Ans. Cmin = 42,400 N.arrow_forwardA 4 inch wide, 12 inch tall cross section beam is subjected to an internal shear of 5.5 kips. What is the maximum transverse shear stress in the beam in psi if this bending is about the x axis?arrow_forward
- A Brayton cycle produces 14 MW with an inlet state of 17°C, 100 kPa, and a compression ratio of 16:1. The heat added in the combustion is 960 kJ/kg. 0.7 MW of heat transferred from the turbine to the environment. What are the highest temperature and the mass flow rate of air? Assume cold air properties.arrow_forward. A gas turbine with air enters the compressor at 300 K, 1 bar, and exits from the turbine at 750 K, 1 bar. The thermal efficiency of the cycle is 40.1% and the back work ratio (BWR) is 0.4. Find the pressure ratio of the cycle. Assume variable specific heat.arrow_forwardA regenerative gas turbine power plant is shown in Fig. below. Air enters the compressor at 1 bar, 27°C with a mass flow rate of 0.562 kg/s and is compressed to 4 bar. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 80%, and the regenerator effectiveness is 90%. All the power developed by the high-pressure turbine is used to run the compressor. The low-pressure turbine provides the net power output. Each turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 87% and the temperature at the inlet to the highpressure turbine is 1200 K. Assume cold air properties, determine: a. The net power output, in kW. b. The thermal efficiency of the cycle.arrow_forward
- For tixed inlet state and exit pressure, use a cold-air standard analysis to show that the pressure ratio across the two compressor stages that gives nunimum work input is:=)) k/(k-1) when Ta Ti, where Ta is the temperature of the air entering the second stage compressor and Pi is the intercooler pressure. Put the suitable assumptionsarrow_forwardDerive the equation below ah ap ax 12μ ax, +( ah ap ay 12μ ay Where P P (x, y) is the oil film pressure. 1..ah 2 axarrow_forwardCan you determine the eignevalues by hand?arrow_forward
- Monthly exam 13 2021-2022 Power plant Time: 1.5 Hrs Q1. A The gas-turbine cycle shown in Fig. is used as an automotive engine. In the first turbine, the gas expands to pressure Ps, just low enough for this turbine to drive the compressor. The gas is then expanded through the second turbine connected to the drive wheels. The data for the engine are shown in the figure, and assume that all processes are ideal. Determine the intermediate pressure Ps, the net specific work output of the engine, and the mass flow rate through the engine. Find also the air temperature entering the burner T3 and the thermal efficiency of the engine. Exhaust Air intake Φ www Regenerator www Bumer Compressor Turbine Power turbine et 150 kW Wompressor P₁ = 100 kPa T₁ = 300 K PP₁ =60 P-100 kPa T₁ = 1600 K Q2. On the basis of a cold air-standard analysis, show that the thermal efficiency of an ideal regenerative gas turbine can be expressed as 77 = 1- where - () () гp is the compressor pressure ratio, and T₁ and…arrow_forwardI need to find m in R = mD from the image given. Do you really need to know what R and D is to find R. I was thinking geometrically we can find a relationship between R and D. D = R*cos(30). Then R = mD becomes m = R/D = 1/cos(30) = 1.1547. Is that correct?arrow_forwardQ1] B/ (16 Marks) To produce a lightweight epoxy part to provide thermal insulation. The available material are hollow glass beads for which the outside diameter is 1.6 mm and the wall thickness is 0.04 mm. Determine the weight and number of beads that must be added to the epoxy to produce a 0.5 kg of composite with a density of 0.65 g/cm³. The density of the glass is 2.5 g/cm³ and that of the epoxy is 1.25 g/cm³.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





