
Concept explainers
The current waveform depicted in Fig. 2.29 is characterized by a period of 4 s. (a) What is the average value of the current over a single period? (b) Compute the average current over the interval 1 < t < 3 s. (c) If q(0) = 1C, sketch q(t), 0 < t < 4 s.
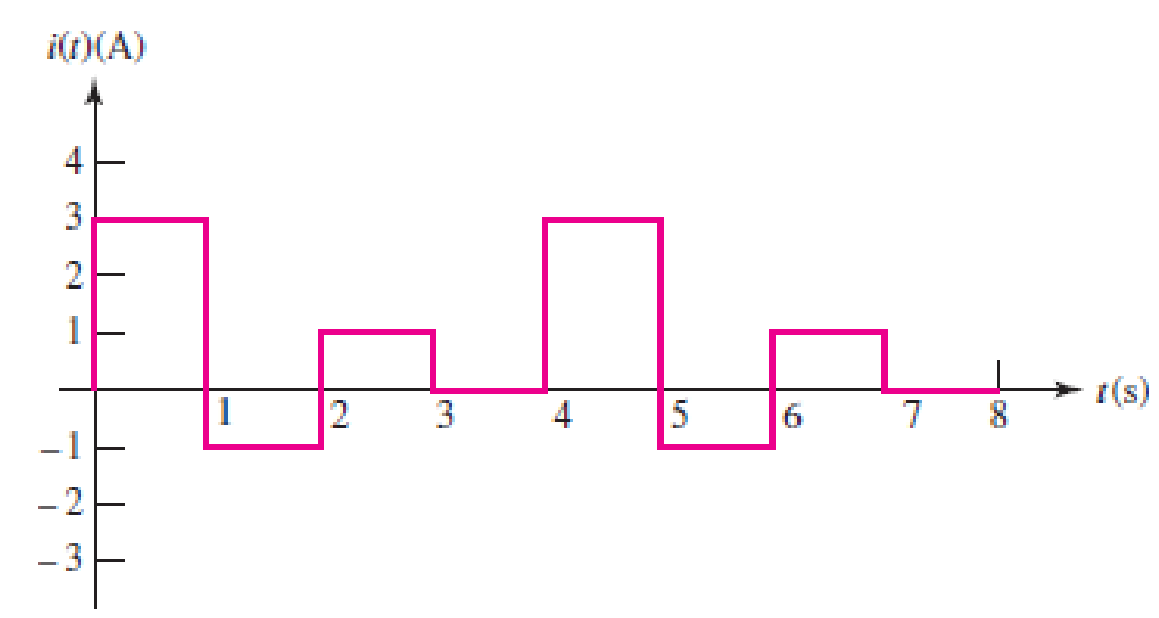
FIGURE 2.29 An example of a time-varying current.
(a)
Find the average value of the given current waveform in Figure 2.29 over the period of 4 s.
Answer to Problem 21E
The average value of the given current waveform over the period of 4 s is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 2.29 in textbook for the time-varying current with the period of 4 s.
Formula used:
Write the formula to find the average value of a function of current over a period as,
Here,
T is the time period.
Calculation:
From the given current waveform in Figure 2.29, the function of current
For the period of
For the period of
For the period of
For the period of
Therefore, the final function of current
The average value of current
Reduce the equation as follows.
Conclusion:
Thus, the average value of the given current waveform over the period of 4 s is
(b)
Find the average current of the waveform over the period of
Answer to Problem 21E
The average current of the waveform over the period of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to part (a).
Formula used:
Write the formula to find the average value of a function of current over a period of
Here,
Calculation:
Write the function of current
Now, the average current of
Conclusion:
Thus, the average current of the waveform over the period of
(c)
Sketch the waveform for the charge
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to part (a).
The initial charge
Formula used:
Write the expression for the relation between charge
Integrate the above equation on both sides.
Calculation:
Using the function of
For
Substitute 3 A for
Substitute 1 C for
Substitute 1 for
For
For the period of
Substitute –1 A for
Substitute 4 C for
Substitute 2 for
For
For the period of
Substitute 1 A for
Substitute 3 C for
Substitute 3 for
For
For the period of
Substitute 0 A for
Substitute 4 C for
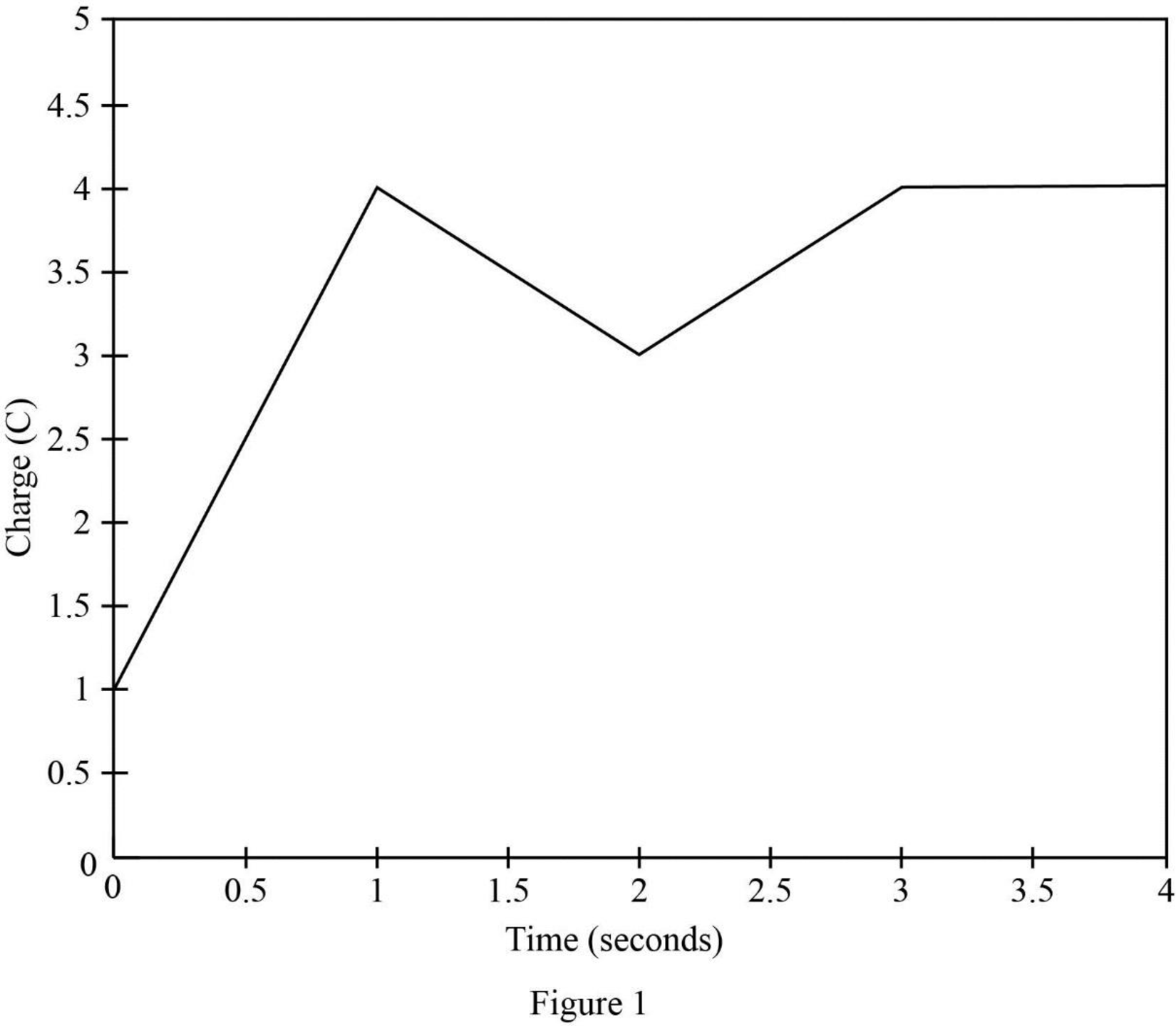
Therefore, the charge
Table 1 shows for
Table 1
| t in seconds | |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 4 |
Figure 1 shows the charge (C) vs time (s) waveform.
Conclusion:
Thus, the waveform for the charge
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- Problems A.1 The square-law modulator is a device for the generation of DSB-PC-AM signals. In the square-law modulator, the sum of the modulating signal and the carrier wave forms the input signal to a nonlinear device. The output signal of the nonlinear device is a linear combination of the input signal and the square of the input signal. The output signal of the nonlinear device is then band-pass filtered. The BPF has a center frequency that is the same as the carrier frequency and a bandwidth that is twice the message bandwidth. Show the output of the BPF is a DSB-PC-AM signal, and determine a requirement between the carrier frequency and the message bandwidth that must be satisfied.arrow_forwardGive the current voltage relationship of the D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET.arrow_forwardAnswer A is wrong.arrow_forward
- The part of machine level instruction, which tells the central processor what was to be done is: A. Address B. None of the above C. Operation code D. Operandarrow_forwardWhich of the following statement is TRUE? 1. In RISC processors, each instruction requires only two clock cycles to complete, resulting in consistent execution time 2. RISC has more transistors and fewer registers 3. RISC has more registers and fewer transistorsarrow_forwardDifferentiate between JFET and BJT.arrow_forward
- Give relation between αdc and βdc.arrow_forwardFind the power delivered across the 45 ohm resistorarrow_forwardA half-wave controlled rectifier is supplied by a 230 Vrms voltage source and has load resistance of 2502. Calculate the delay angle a that produces a load-absorbed power of 200W.arrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forwardFigure 1 shows a half-wave controlled rectifier which is supplied by a Vin = 120 Vrms voltage source. Assume that the load resistance is R = 10 2. Determine: a) The firing angle a of the thyristor to produce an average output voltage 50Vdc. Vin=Vmsinoot b) The average power Po absorbed by the load R. Figure 1 R = 1092arrow_forwardQ1. What is power dissipation in the Zener diode circuit given for a) RL=100 Ohm ? b) RL=∞arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





