
Concept explainers
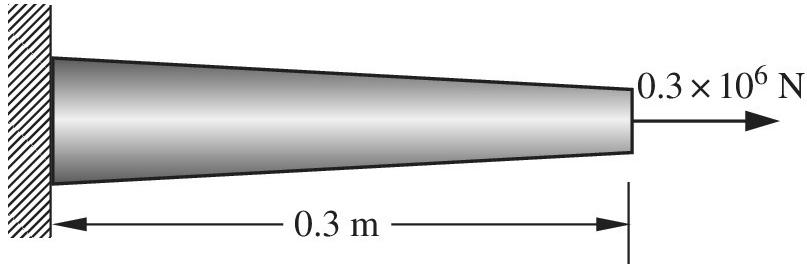
A tapered bar with circular cross section is fixed at
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis And Design
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
- ||! Sign in MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pd X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.pX DE MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p x PDF Lecture W12 - Work and X File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L11.pdf PDE Lecture W11 - Power and X Draw Alla | Ask Copilot ++ 3 of 3 | D 6. If the 50-kg load A is hoisted by motor M so that the load has a constant velocity of 1.5 m/s, determine the power input to the motor, which operates at an efficiency € = 0.8. 1.5 m/s 2 7. The sports car has a mass of 2.3 Mg, and while it is traveling at 28 m/s the driver causes it to accelerate at 5m/s². If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD= 0.3v²N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine at this instant. The engine has a running efficiency of P = 0.68. 8. If the jet on the dragster supplies a constant thrust of T-20 kN, determine the power generated by the jet as a function of time. Neglect drag and rolling resistance, and the loss of fuel. The dragster has a mass of 1…arrow_forwardQ | Sign in PDE Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdi X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.p X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p X Lecture W12-Work and X + File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/Lecture%20W12%20-%20Work%20and%20Energy.pdf ||! Draw | IA | a | Ask Copilot Class Work + 33 of 34 D Question 1 The engine of a 3500-N car is generating a constant power of 50 hp (horsepower) while the car is traveling up the slope with a constant speed. If the engine is operating with an efficiency of € 0.8, determine the speed of the car. Neglect drag and rolling resistance. Use g 9.81 m/s² and 1 hp = 745.7 W. 10 го Question 2 A man pushes on a 60-N crate with a force F. The force is always directed downward at an angle of 30° from the horizontal, as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force is gradually increased until the crate begins to slide. Determine the crate's initial acceleration once it starts to move. Assume the coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.6, the coefficient of kinetic…arrow_forwardstate is Derive an expression for the volume expansivity of a substance whose equation of RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forward
- For a gas whose equation of state is P(v-b)=RT, the specified heat difference Cp-Cv is equal to which of the following (show all work): (a) R (b) R-b (c) R+b (d) 0 (e) R(1+v/b)arrow_forwardof state is Derive an expression for the specific heat difference of a substance whose equation RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardTemperature may alternatively be defined as T = ди v Prove that this definition reduces the net entropy change of two constant-volume systems filled with simple compressible substances to zero as the two systems approach thermal equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Using the Maxwell relations, determine a relation for equation of state is (P-a/v²) (v−b) = RT. Os for a gas whose av Tarrow_forward(◉ Homework#8arrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^ 2. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A бро Barrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^2. Both boxes are 0.25 m long and 0.25 m high. The cord is attached to the bottom of Box A and the middle of box B. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A From бро Barrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning