
Concept explainers
In Problem S1-5 assume that Nicole, with the help of a financial newsletter and some library research, has been able to assign probabilities to each of the possible interest rates during the next year as follows:
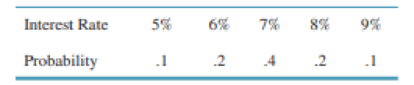
- a. Using expected value, determine her best investment decision.
- b. Nicole is considering hiring a financial analyst to help her determine the best investment. What is the maximum amount she should pay an analyst?
Nicole Nelson has come into an inheritance from her grandparents. She is attempting to decide among several investment alternatives. The return after one year is dependent primarily on the interest rate during the next year. The rate is currently 7%, and she anticipates it will stay the same or go up or down by at most 2 points. The various investment alternatives plus their returns ($10,000s) given the interest rate changes are shown in the following table.
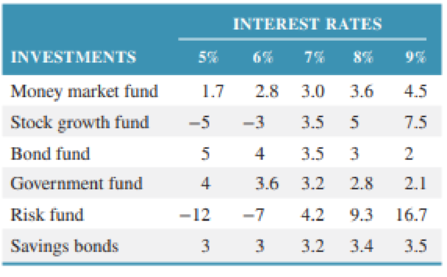
Determine the best investment using the following decision criteria.
- a. Maximax
- b. Maximin
- c. Equal likelihood
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Operations and Supply Chain Management 9th edition
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Operations Management
Auditing And Assurance Services
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
- Cariveh Co sells automotive supplies from 25 different locations in one country. Each branch has up to 30 staff working there, although most of the accounting systems are designed and implemented from the company's head office. All accounting systems, apart from petty cash, are computerised, with the internal audit department frequently advising and implementing controls within those systems. Cariveh has an internal audit department of six staff, all of whom have been employed at Cariveh for a minimum of five years and some for as long as 15 years. In the past, the chief internal auditor appoints staff within the internal audit department, although the chief executive officer (CEO) is responsible for appointing the chief internal auditor. The chief internal auditor reports directly to the finance director. The finance director also assists the chief internal auditor in deciding on the scope of work of the internal audit department. You are an audit manager in the internal audit…arrow_forwardPlease show all steps and answers, thank you!arrow_forwardI am not sure if this is correct, because 8 cannot go directly to 10.arrow_forward
- A practical application in real life to the Critical Path Method is the construction of a bridge with references, give a detailed essay on the stages involved in constructing a bridgearrow_forwardPlease assist in writing a complete reasearch project of the following title: Title of research: Study on the impact of Technology in the Work Place.arrow_forwardIntuition is both an emotional experience and a nonconscious analytic process. One problem, however, is that not all emotions signaling that there is a problem or opportunity represent intuition. Please in your Personal opinion how we would know if our “gut feelings” are intuition or not, and if not intuition, suggest what might be causing them.arrow_forward
- A coworker suggests that the company where you both work would be much more effective if there were no organizational politics. Please in your personal and detailed opinion, What would you say to this person in reply?arrow_forwardWhat is a bottleneck? Would you try to reduce a bottleneck? Why or why not? Please provide a referencearrow_forwardYour firm has been the auditor of Caribild Products, a listed company, for a number of years. The engagement partner has asked you to describe the matters you would consider when planning the audit for the year ended 31January 2022. During recent visit to the company you obtained the following information: (a) The management accounts for the 10 months to 30 November 2021 show a revenue of $260 million and profit before tax of $8 million. Assume sales and profits accrue evenly throughout the year. In the year ended 31 January 2021 Caribild Products had sales of $220 million and profit before tax of $16 million. (b) The company installed a new computerised inventory control system which has operated from 1 June 2021. As the inventory control system records inventory movements and current inventory quantities, the company is proposing: (i) To use the inventory quantities on the computer to value the inventory at the year-end (ii) Not to carry out an inventory count at the year-end (c)…arrow_forward
- Develop and implement a complex and scientific project for an organisation of your choice. please include report include the following: Introduction Background research to the project The 5 basic phases in the project management process Project Initiation Project Planning Project Execution Project Monitoring and Controlling Project Closing Conclusionarrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 51 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $11.00 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 95 bags/week > Order cost $52.00/order > Annual holding cost = 25 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent >Lead time 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 95 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 75 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $ higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

