
a)
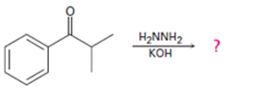
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
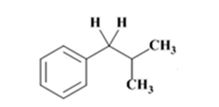
The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
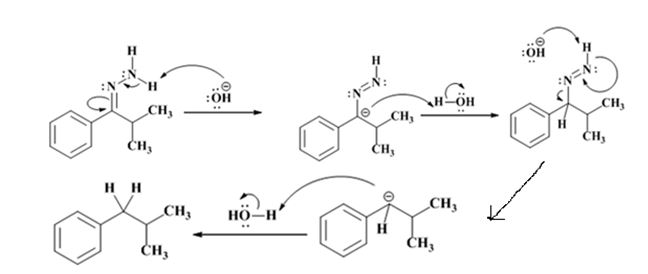
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of isopropyl phenyl ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane, ethyl benzene, as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

b)
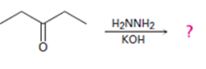
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
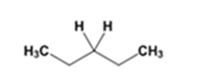
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
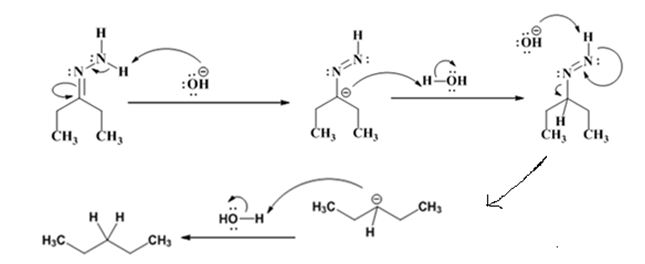
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of diethyl ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane, n-pentane, as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

c)
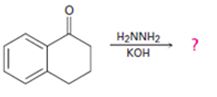
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
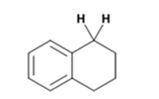
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
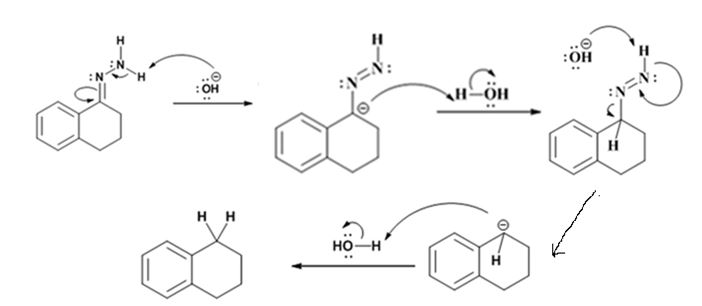
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of the ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

d)
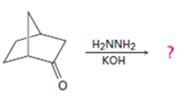
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
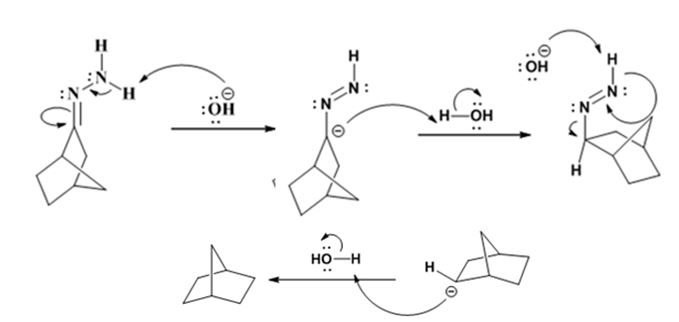
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward
- 3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forwardWrite the aldol condensation mechanism and product for benzaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base. Then trans-cinnamaldehyde + acetone in base. Then, trans-cinnamaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


