
Concept explainers
Propose structures for molecules that meet the following descriptions. Assume that the kinds of carbons (1°, 2°, 3°, or 4°) have been assigned by DEPT-NMR.
a) C6H12O;IR: 1715 cm-1; 13C NMR: 8.0 δ (1°), 18.5 δ (1°), 33.5 δ (2°), 40.6 δ (3°), 214.0 δ (4°)
b) C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13C NMR: 22.6δ (1°), 23.6 8 (3°), 52.8 8 (2°), 202.4 8 (3°)
c) C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13C NMR: 22.9 δ (2°), 25.8 8 (2°), 38.2 δ (2°). 129.8 8 (3°), 150.6 8 (3°), 198.7 δ (4°)
a)

Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C6H12O; IR: 1715 cm-1; 13CNMR: 8.0 δ (10), 18.5 δ (10), 33.5 δ (20), 40.6 δ (30), 214.0 δ (40)
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ. The signals will be observed at downfield if these alkyl groups are attached to electron withdrawing groups.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C6H12O; IR: 1715 cm-1; 13CNMR: 8.0 δ (10), 18.5 δ (10), 33.5 δ (20), 40.6 δ (30), 214.0 δ (40)
Answer:
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is
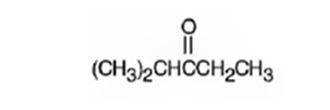
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H12O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has two hydrogen atoms (14-12) less than the parent and hence has one unsaturation unit perhaps a C=O.
The IR absorption at 1715 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 214.0 δ indicate that the compound is a ketone. The 13CNMR further indicates that the carbonyl group is flanked by a secondary and tertiary carbon indicated by the two downfield signals at 33.5 δ and 40.6 δ. The remaining three carbons has to be primary, of which one is attached as methyl(8.0 δ) to the secondary carbon and two others are attached as two methyl groups (18.5δ) on the tertiary carbon. Hence the compound is 2-methyl-3-pentanone.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

b)

Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.6 δ (10), 23.6 δ (30), 52.8 δ (20), 202.4 δ (30).
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ. The signals will be observed at downfield if these alkyl groups are attached to electron withdrawing groups.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C5H10O; IR: 1730 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.6 δ (10), 23.6 δ (30), 52.8 δ (20), 202.4 δ (30).
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H12O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has two hydrogen atoms less than the parent and hence has one unsaturation unit, a carbonyl group.
The IR absorption at 1730 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 202.4 δ indicate that the compound is a saturated aldehyde. The 13CNMR further indicates that the carbonyl group is attached to a secondary carbon indicated by the downfield signal at 52.8 δ. Of the remaining three carbons one has to be tertiary(23.6 δ) which is attached to two methyl groups(22.6 δ). Hence the compound is 2-methylbutanal.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

c)
Interpretation:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given is to be assigned.
C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20), 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30), 198.7 δ (40).
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones show a strong absorption band in IR from 1660-1770 cm-1. Aldehydes show two characteristic C-H absorptions between 2700-2760cm-1 and 2800-2860 cm-1. Saturated aldehydes absorb near 1730 cm-1 while aromatic aldehydes and α, β- unsaturated aldehydes absorb near 1705 cm-1. Saturated ketones and cyclohexanones absorb near 1715 cm-1 while aromatic ketones and α, β- unsaturated ketones absorb near 1685-1690 cm-1. Cyclopentanones absorb around 1750 cm-1.
In 13CNMR, carbons in double bond which are sp2 hybridized absorb from 110 to 220 δ. Saturated aldehydes and ketones usually absorb in the region from 200 to 215 δ While aromatic and unsaturated carbonyl compounds absorb in the 190 to 200 δ region. The primary alkyl carbon absorbs in the range 10-15 δ, a secondary alkyl radical in the range 16-25 δ while a tertiary alkyl in the range 25-35 δ.
To assign:
A structure for the molecule which meets the descriptions given.
C6H8O; IR: 1680 cm-1; 13CNMR: 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20), 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30), 198.7 δ (40).
Answer to Problem 69AP
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is
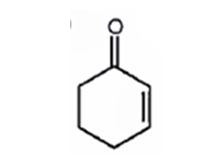
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of the compound is C6H8O. Ignoring oxygen the molecular formula of the parent compound becomes C6H14. Thus the compound has six hydrogen atoms (14-8= 6) less than the parent and hence has three unsaturation units.
The IR absorption at 1680 cm-1 and 13CNMR peak at 198.7 δ indicate that the compound is an α, β- unsaturatedketone. The compound has three unsaturated units. α, β- unsaturatedketone accounts for two unsaturation units. Hence the compound contains a six membered ring. The signals at 129.8 δ (30) 150.6 δ (30) can be attributed to the carbons in double bond. The other three signals at 22.9 δ (20), 25.8 δ (20), 38.2 δ (20) can be attributed to three methylene groups. The signal at 38.2 δ (20) can be assigned to methylene carbon attached to carbonyl carbon, that at 25.8 δ (20) to the methylene carbon carbon attached to C4 while that at 22.9 δ (20) is due to methylene carbon C5.
A structure for the molecule which meets the spectral descriptions given is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


