
a)

Interpretation:
How mass spectrometry is useful in distinguishing between 3-methyl-2-hexanone and 4-methyl-2-hexanone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In the mass spectrum of organic compounds, normally peaks due to Mc Lafferty rearrangement and α cleavage are generally visible. In Mc Lafferty rearrangement,
To state:
How to distinguish between 3-methyl-2-hexanone and 4-methyl-2-hexanone using mass spectrometry.
b)

Interpretation:
How mass spectrometry is useful in distinguishing between 3-heptanone and 4-heptanone is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In the mass spectrum of organic compounds, normally peaks due to Mc Lafferty rearrangement and α cleavage are generally visible. In Mc Lafferty rearrangement, aldehydes and ketones that have hydrogens on the γ carbons transfer the hydrogen on the carbon to the carbonyl oxygen and the bond between the α and β carbons is broken to yield an alkene. The charge remains with the oxygen containing fragment. In the α cleavage, the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the α carbon breaks to yield a neutral radical and a resaonance stabilized acyl cation.
To state:
How to distinguish between 3-heptanone and 4-heptanone using mass spectrometry.
c)
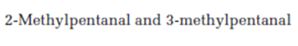
Interpretation:
How mass spectrometry is useful in distinguishing between 2-methylpentanal and 3-methylpentanal is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In the mass spectrum of organic compounds, normally peaks due to Mc Lafferty rearrangement and α cleavage are generally visible. In Mc Lafferty rearrangement, aldehydes and ketones that have hydrogens on the γ carbons transfer the hydrogen on the carbon to the carbonyl oxygen and the bond between the α and β carbons is broken to yield an alkene. The charge remains with the oxygen containing fragment. In the α cleavage, the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the α carbon breaks to yield a neutral radical and a resaonance stabilized acyl cation.
To show:
How to distinguish between 2-methylpentanal and 3-methylpentanal using mass spectrometry.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- LIOT S How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate? View Rubricarrow_forwardSteps and explantions pleasearrow_forwardMatch the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forward
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





