
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The molecular formula of the given compound has to be determined by using the ideal gas equation and molar mass of that compound. The possible structures of the compound has to be drawn from the determined molecular formula.
Concept Introduction:
Ideal gas equation:
The ideal gas equation is the combined equation of
Explanation of Solution
The given information in the problem is recored as follows:
The given temperature is converted to kelvin as shown here.
The given volume in millilitres is converted into liters by the conversion factor as follows:
Use the below ideal gas equation to find the moles of the vapour.
Substitute as follows.
Use the below equation to find the molar mass of the compound.
Substitute as follows.
The empirical formula of the compound can be calculated as follows:
Assume that the mass of the sample is
The grams of each element is converted into moles by using the molar mass of the corresponding element.
Now the number of moles of each element is converted into whole numbers, dividing by the lowest mole.
Thus, the empirical formula of the compound is
The molecular formula of the compound can be determined from the empirical formula and the molar mass of that compound as follows.
Use the below equation to find the molecular formula.
Substitute as follows.
Hence, the molecular formula of the compound is
The determined molecular formula for the compound is
There are two carbon atoms in the given compound. So, place the two carbon atoms in a straight-line as the parent carbon chain as shown below.
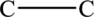
Place the two chlorine atoms on the same carbon atom or for each carbon atom as shown below.
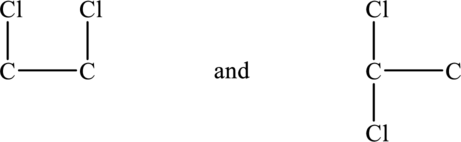
Now add four hydrogen atoms to each carbon atom in order to complete the two structures above because each carbon has four bonds around it. ]
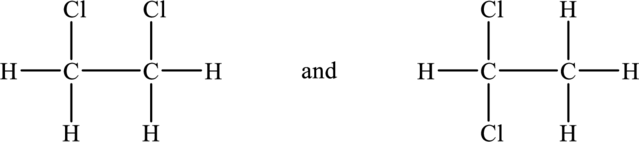
Hence, the possible structures of the compound are show below.
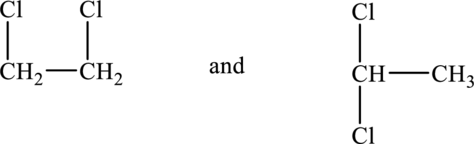
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





