
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
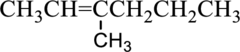
Concept introduction:
IUAC gives rules for the naming of chemical compounds. These rules are,
For
In the nomenclature, Find the parent chin first then number the carbon atoms in the parent chain by giving lest number to the unsaturated double/triple bonded carbon followed by designate the substituent in its position in parent chain.
If more than one same substituent were occurs, add a prefix (di-, tri-, tetra-, ect..) in front of parent chain name.
If compound contains double bond means, name end with suffix of ene or if compound contains triple bond means name end with suffix of yne.
Finally the systematic name was written as, the substituent position number with prefix (di-, tri-, tetra-, ect..) of number of substituents followed by name of the substituent then write the parent chain name (which contains large number of carbon atoms in the chain) with suffix of suffix ene/yne.
The parent chain names based on the carbon atoms are,
The substituent names based on the carbon atoms are,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name of given compound is,
Parent chain name of given compound is 2-hexene,
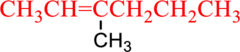
From the structure given structure, methyl group is present at third carbon so substitution name is 3-methyl.
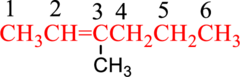
Combine the substituent name followed by parent name to get complete name of the compound.
Hence, the complete IUPAC name of the compound is,
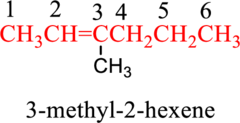
(b)
Interpretation:
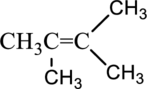
IUPAC name of given below compound has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name of given compound is,
Parent chain name of given compound is 2-butene,
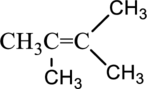
From the given structure, two methyl groups are present at 2 and 3 carbon atom of parent chain so substitution name is 2,3-dimethyl.
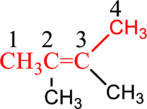
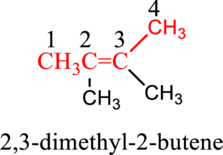
Combine the substituent name followed by parent name to get complete name of the compound.
Hence, the complete IUPAC name of the compound is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
- Macmillan Learning One of the molecules shown can be made using the Williamson ether synthesis. Identify the ether and draw the starting materials. А со C Strategy: Review the reagents, mechanism and steps of the Williamson ether synthesis. Determine which of the molecules can be made using the steps. Then analyze the two possible disconnection strategies and deduce the starting materials. Identify the superior route. Step 6: Put it all together. Complete the two-step synthesis by selecting the reagents and starting materials. C 1. 2. Answer Bank NaH NaOH NaOCH, снен, сен, он Сиси, Сне (СН), СОН (Сн, Свarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 O CH3-CH-CH-C-CH3 OH HV. CH3-C-CH-CH2-CH3 OH CH3 O HO—CH, CH–CH—C CH3 OH 오-오 name X G ☐arrow_forwardHI Organic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? HO OH H +回 + H₂O 60013 Naomi V Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 1 2 #3 $ 4 2025 % ala5 'a :☐ G & 67 8 Ar K enter Accessible 9 Q W E R TY U 1 tab , S H J Karrow_forward
- Please help me with number 5 using my data and graph. I think I might have number 3 and 4 but if possible please check me. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwarddict the major products of this organic reaction. C Explanation Check 90 + 1.0₂ 3 2. (CH3)2S Click and drag f drawing a stru © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. • 22 4 5 7 8 Y W E R S F H Bilarrow_forwardcan someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all the curly arrows and 2. Draw the GPNA molecule and identify the phenylalanine portion. 3. Draw L-phenylalanine with the correct stereochemistryarrow_forward
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardPredict the major products of both organic reactions. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. esc esc Explanation Check 2 : + + X H₁₂O + Х ง WW E R Y qab Ccaps lock shift $ P X Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil T FR F18 9 G t K L Z X V B N M control opption command command T C darrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrohalogenation of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for caps lock Explanation Check 2 W E R + X 5 HCI Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil Y F G H K L ZZ X C V B N M control opption command F10 F10 command 4 BA Ar Carrow_forward
- I don't understand why the amide on the top left, with the R attached to one side, doesn't get substituted with OH to form a carboxylic acid. And if only one can be substituted, why did it choose the amide it chose rather than the other amide?arrow_forwardesc Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. Explanation Check BBB + X 0 1. Hg (OAc)2, H₂O 2. Na BH 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bl P 豆 28 2 28 N 9 W E R T Y A S aps lock G H K L Z X C V B N M T central H command #e commandarrow_forwardC A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. (X) This transformation can't be done in one step. + Tarrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning


