
Concept explainers
Buruli Ulcer
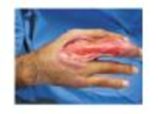
Jacques liked living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)-opportunities abounded for exploration, adventure, and wildlife photography, the countryside was beautiful, and he found the people generally friendly. It was on a photographic excursion in the east of the country that Jacques met a not-so-friendly resident of the DRC: an emerging mycobacterial pathogen.
The photographer thought little of the small insect bite he received while documenting wildlife in the swamps along the great Congo River, but he should have been concerned; Mycobacterium ulcerans had found a new home in his hand. Jacques would pay a grievous price for his lack of care.
He continued to ignore the infection when it produced a small, painless nodule. He even ignored it when his finger swelled to twice its normal size; it was painless, and he could still meet his busy schedule. But the bacterium was producing a potent toxin known as mycolactone that destroys cells below the skin, especially fat and muscle cells. Though his hand continued to swell, making it difficult to work normally, it remained pain free.
After six weeks of this condition, pain began suddenly and excruciatingly. The swollen finger ruptured, and a foul-smelling fluid saturated his camera. It was time to see a doctor.
The physician diagnosed Buruli ulcer, an emerging disease that affects more and more people each year as a result of human encroachment into the swamps where Mycobacterium ulcerans lives. After two surgeries to remove dead tissue and bacteria, several skin grafts, and two months of treatment with the antimicrobial drugs rifampicin and streptomycin, Jacques returned home to France with scars that forever remind him of his adventure with M. ulcerans.
- 1. What might be a reason why a Buruli ulcer is initially painless?
- 2. Why was it necessary to administer antibacterial drugs for two months rather than two weeks?
- 3. What environmental similarities exist in the endemic countries?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
- What is agricuarrow_forwardWhen using the concept of "a calorie in is equal to a calorie out" how important is the quality of the calories?arrow_forwardWhat did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate? What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter? What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment? If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?arrow_forward
- What kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?arrow_forwardWhat is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forwardYou intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forward
- Describe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forwardThe following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forward
- What protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forward
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage





