
Draw the structure of hexanoic acid. Label the alpha carbon.
Interpretation:
The structure of hexanoic acid is to be drawn. The alpha carbon is to be labeled.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids come under the classification of organic acids. They contain a carboxyl group and a hydroxyl group attached to each other. The general formula for carboxylic acids is
Answer to Problem 19.1E
The structure of hexanoic acid with the labeled alpha carbon is shown below.
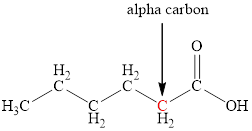
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids are named by adding the suffix –oic acid to the name of the base alkane. The name of hexanoic acid suggests that the base alkane is six carbon atoms long. The alpha carbon is the one which is directly attached to the carbonyl group. Therefore, the structure of hexanoic acid with the labeled alpha carbon is shown below.

Figure 1
The structure of hexanoic acid with the labeled alpha carbon is shown in Figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Explain why only the lone pairs on the central atom are taken into consideration when predicting molecular shapearrow_forward(ME EX1) Prblm #9/10 Can you explain in detail (step by step) I'm so confused with these problems. For turmber 13 can u turn them into lewis dot structures so I can better understand because, and then as well explain the resonance structure part. Thanks for the help.arrow_forwardProblems 19 and 20: (ME EX1) Can you please explain the following in detail? I'm having trouble understanding them. Both problems are difficult for me to explain in detail, so please include the drawings and answers.arrow_forward
- (ME EX1) Prblm #4-11 Can you please help me and explain these I'm very confused in detail please. Prblm number 9 I don't understand at all (its soo confusing to me and redraw it so I can better depict it).arrow_forwardME EX1) Prblm #19-20 I'm so confused with these problems. Can you please help me solve them and explain them? Problems number 19-20, and thanks! step by step and in detail for me please helparrow_forwardCalculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere, given that: Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturatedarrow_forward
- ( ME EX1) Prblm 27-28: Can you explain to me both prblms in detail and for prblm 28 what do you mean bi conjugated bi ponds and those structures I'm confused...arrow_forwardA. Determine the number of electrons in a system of cyclic conjugation (zero if no cyclic conjugation). B. Specify whether the species is "a"-aromatic, "aa"-anti-aromatic, or "na"-non-aromatic (neither aromatic nor anti-aromatic). (Presume rings to be planar unless structure obviously prevents planarity. If there is more than one conjugated ring, count electrons in the largest.) 1. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 18 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) a 2. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 10 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) naarrow_forwardWater is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid water evaporates in 30 min. Find the rate of heat transfer to the water (kW).arrow_forward
- Could you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the resonance structures that were given please.arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the question.arrow_forwardplease solve. If the answer is "no error" and it asks me to type something, and i typed a-helix, its always wrong.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER  General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning





