
Concept explainers
Draw structural formulas for the following amino acids, identify the chiral carbon atom in each one, and circle the four different groups attached to the chiral carbon.
a. valine
b. glutamate
c. asparagine
d. cysteine
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is shown below.
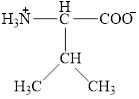
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
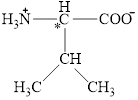
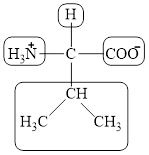
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of valine is given below.

Figure 1
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 2
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 3
The structural formula for the amino acid, valine is shown in Figure 1. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 2. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 3.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is shown below.
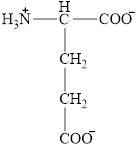
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
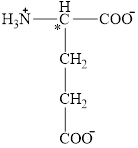
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
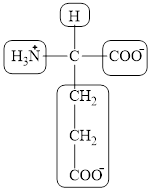
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of glutamate is given below.

Figure 4
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 5
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 6
The structural formula for the amino acid, glutamate is shown in Figure 4. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 5. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 6.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
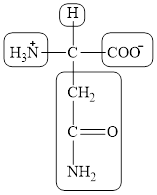
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is shown below.
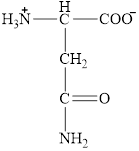
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
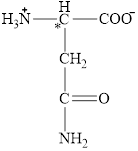
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of aspargine is given below.

Figure 7
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 8
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 9
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspargine is shown in Figure 7. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 8. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 9.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.5E
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is shown below.
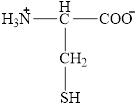
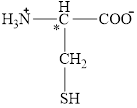
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
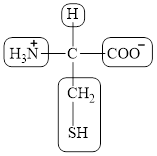
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of cysteine is given below.

Figure 10
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 11
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 12
The structural formula for the amino acid, cysteine is shown in Figure 10. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 11. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Show the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forward
- what are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward
- 19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forwardLi+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forwardQ4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College DivChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College DivChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





