
Concept explainers
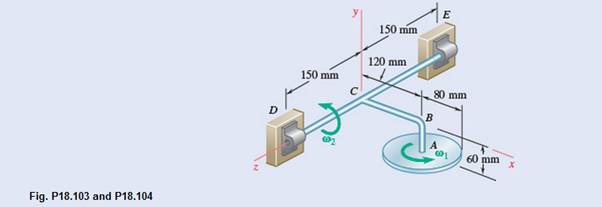
A 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates at the constant rate
(a)
The couple applied to shaft to produce acceleration.
Answer to Problem 18.104P
The couple applied to shaft to produce acceleration is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass of homogeneous disk is
The figure is represented below.
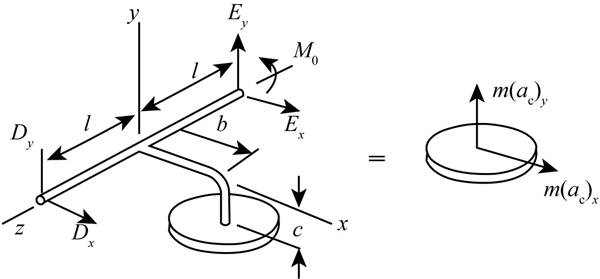
Figure (1)
Write the expression for the angular velocity of disk in x direction.
Write the expression for the total angular velocity of the disk
Here
Substitute,
Write the expression for the angular momentum about point
Here, mass moment of inertia about the x-axis is
Substitute
Write the expression for angular velocity in vector form of shaft
Write the expression for rate of angular velocity of the reference frame
Here,
Write the expression for rate of total angular velocity.
Substitute
Write the expression for Matrix multiplication of the vector product for Equation (10).
Write the expression for the mass moment of inertia about the y-direction.
Here mass of the disk is
Write the expression for the mass moment of inertia about the z- direction.
Substitute
Write the expression for the velocity of mass centre of the disk.
Here, velocity of mass centre is
Write the expression for
Here, horizontal distance is
Substitute
Write the expression for the matrix multiplication of the vector product for Equation (17).
Write the expression for the acceleration of the mass centre of the disk.
Substitute
Write the expression for the matrix multiplication of the vector product for Equation (20).
Write the expression for the the sum of the forces acting on the system.
Here, force at
Write the expression for the force in terms of mass and acceleration.
Substitute
Substitute
Compare the coefficients of the unit vector of
Compare the coefficients of the unit vector of
Write the expression for the rate of angular momentum about
Here, distance of
Write the expression for
Here distance from point
Substitute
Write the expression for the matrix multiplication for vector product for equation (30).
Write the expression for the moment about
Here, moment couple when system is at rest is
Write the expression for the matrix multiplication for the vector product for equation (32).
The sum of the moment at
Substitute
Compare the coefficients of the unit vector of
Calculation:
Substitute values of
Thus value of couple
Conclusion:
The couple applied to shaft to produce acceleration is
(b)
The dynamic reaction at
The dynamic reaction at
Answer to Problem 18.104P
The dynamic reactions at
The dynamic reactions at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Compare the coefficients of the unit vector of
Compare the coefficients of the unit vector of
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression for the angular velocity in terms of time in y-direction.
Write the expression for the angular velocity in terms of time in y-direction
Calculation:
Substitute values of
Substitute values of
Hence, dynamic reaction at
Substitute values of
Substitute values of
Hence, dynamic reaction at
Conclusion:
The dynamic reactions at
The dynamic reactions at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
- (read image)arrow_forwardQu 2 Schematically plot attractive, repulsive, and net energies versus interatomic separation for two atoms or ions. Note on this plot the equilibrium separation (distance) ro and the bonding energy Eo. Qu 3 How many atoms (or molecules) are in one mole of the substance? Qu 4 Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of gram-mole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a pound-mole of a substance? Qu 5 The atomic radii of Mg* and F ions are 0.072 and 0.133 nm, respectively. Calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another). What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?show all work step by step problems formulaarrow_forwardQu 4 Silver has FCC crystal structure at room temperature, and a lattice constant, a, of 0.407 nm. Draw a reduced sphere silver unit cell in the grids provided below, clearly label the lattice dimensions. Within the unit cell you drew, shade the (1 0 0) plane. How many atoms are contained within the (1 0 0) plane? Calculate the area of (1 0 0) plane in [nm?]. Express your answer in [nm?] to three significant figures. Calculate the planar density of the (1 0 0) plane in [atoms/nm?]. Express the answer in atoms/nm to three significant figures. show all work step by steparrow_forward
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
- The volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston–cylinder device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 3 m3 while its pressure is maintained constant at 130 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as the work required to compress it, in kJ. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.0769 kJ/kg·K. The initial temperature of helium is K. The final temperature of helium is K. The work required to compress helium is kJ.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 140°C. Nitrogen is now expanded isothermally to a pressure of 80 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. The properties of nitrogen are R= 0.2968 kJ/kg-K and k= 1.4. N₂ 160 kPa 140°C The boundary work done during this process is KJ.arrow_forward! Required information An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in, is 1/16 in thick, and has a 3/4-in bore. The wheel weighs 4.80 oz and runs at 11,700 rev/min. The wheel material is isotropic, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.20, and has an ultimate strength of 12 kpsi. Choose the correct equation from the following options: Multiple Choice о σmax= (314) (4r2 — r²) - о σmax = p² (3+) (4r² + r²) 16 σmax = (314) (4r² + r²) σmax = (314) (4² - r²)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





