
Concept explainers
The kinetic energy of the space probe after its collision with the meteorite.
Answer to Problem 18.54P
The kinetic energy of the space probe after its collision with the meteorite is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the space probe is
Write the expression of the mass of the meteorite.
Here, weight of the meteorite is
Write the expression of the mass of the space probe.
Here, weight of the meteorite is
Write the expression of angular momentum of the meteorite about
Here, the distance of point A is
Write the Expression of the moment of inertia along x-axis.
Here, the radius of gyration of the space probe along x-axis is
Write the Expression of the moment of inertia along the y-axis.
Here, the radius of gyration of the space probe along y-axis is
Write the Expression of the moment of inertia along z-axis.
Here, the radius of gyration of the space probe along z-axis is
Write the expression of angular momentum of space probe.
Here, moment of inertia along x-axis is
Substitute
Here, angular velocity along x-axis is
Write the expression of kinetic energy of the space probe.
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression that shows the relation between linear momentum of meteorite and the space probe.
Here, the initial velocity along x-axis is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The angular momentum of the space probe is
Write the expression of the relation between
Substitute
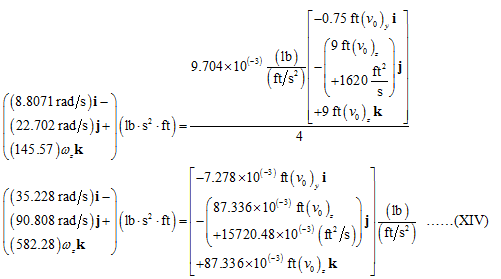
Compare x-component of Equation (IX) on both side.
Compare y-component of Equation (XIV) on both side.
Compare z-component of Equation (XIV) on both side.
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the kinetic energy is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
- Create a report: An example of two people who do not understand each other due to lack of communication, and mention ways to resolve the issue between them .arrow_forwardI want the kinematic diagram to be draw like this plsarrow_forwardAccording to the principles and steps above, draw the kinematic diagram of following mechanisms. Mark the appropriate scale, calculates the degree of freedom. NO.1 NO.2 NO: 3 NO.: 4arrow_forward
- An office building is planned with a lateral-force-resisting system designed for earthquake resistance in aseismic zone. The seismic capacity of the proposed system, expressed as a force factor, is assumed tofollow a lognormal distribution with a median of 6.5 and a standard deviation of 1.5. The ground motionfrom the largest expected earthquake at the site is estimated to correspond to an equivalent force factor of 5.5.(a) What is the estimated probability that the building will experience damage when subjected to the largest expected earthquake? (b) If the building survives (i.e., experiences no damage) during a previous moderate earthquake with aforce factor of 4.0, what is the updated probability of failure of the building under the largest expectedearthquake?(c) Suppose future occurrences of the largest expected earthquake follow a Poisson process with a mean return period of 500 years. Assuming that damage events from different earthquakes are statisticallyindependent,…arrow_forwardDuring a plant visit, it was noticed that a 12-m-long section of a 10-cm-diameter steam pipe is completely exposed to the ambient air. The temperature measurements indicate that the average temperature of the outer surface of the steam pipe is 75°C when the ambient temperature is 5°C. There are also light winds in the area at 10 km/h. The emissivity of the outer surface of the pipe is 0.8, and the average temperature of the surfaces surrounding the pipe, including the sky, is estimated to be 0°C. Determine the amount of heat lost from the steam during a 10-h-long work day. Steam is supplied by a gas-fired steam generator that has an efficiency of 80 percent, and the plant pays $1.05/therm of natural gas. If the pipe is insulated and 90 percent of the heat loss is saved, determine the amount of money this facility will save a year as a result of insulating the steam pipes. Assume the plant operates every day of the year for 10 h. State your assumptions.arrow_forwardAn old fashioned ice cream kit consists of two concentric cylinders of radii Ra and Rb. The inner cylinder is filled with milk and ice cream ingredients while the space between the two cylinders is filled with an ice-brine mixture. Ice cream begins to form on the inner surface of the inner cylinder. To expedite the process, would you recommend rotating the inner cylinder? Justify your recommendation. icecream/ ice-brine Ra Rbarrow_forward
- Find temperatures STRICTLY USING RITZ APPROXIMATION METHODarrow_forwardSolve this Problem using RITZ APPROXIMATION. STEP BY STEParrow_forwardB/40 The body is constructed of a uniform square plate, a uniform straight rod, a uniform quarter‐circular rod, and a particle (negligible dimensions). If each part has the indicated mass, determine the mass moments of inertia of the body about the x‐, y‐, and z‐axes. Answer Given.arrow_forward
- (read image) Answer:arrow_forward(read image) Answer Givenarrow_forwardB/16. The plane area shown in the top portion of the figure is rotated 180° about the x‐axis to form the body of revolution of mass m shown in the lower portion of the figure. Determine the mass moment of inertia of the body about the x‐axis. Answer Givenarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





