
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of propanal with the given reagents has to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong reducing agents. They are inorganic compounds which are used as the reducing agents in
In the reaction of
By catalytic hydrogenation, aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols. Grignard reagents react with ketones and aldehydes to form alcohols. These reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions. The Grignard reagent adds to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen.
An organolithium reagent acts like a good nucleophiles and strong bases. They used for the conversion of aldehydes and ketones into primary and secondary alcohols. Acetal is an organic compound with general formula RHC(OR')2.
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
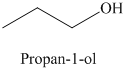
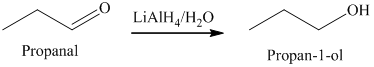
a) The product of the reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water is shown below.
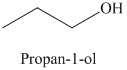
b) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, methanol is shown below.
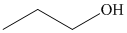
c) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrogen (nickel catalyst) is shown below.
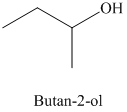
d) The product of the reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
e) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
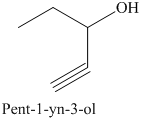
f) The product of the reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
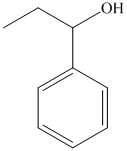
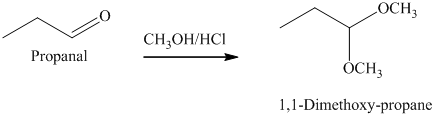
g) The product of the reaction of propanal with methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride is shown below.
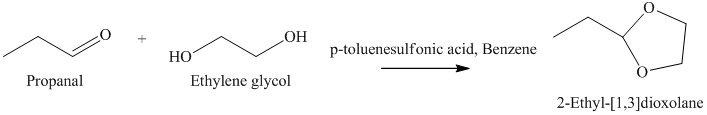
h) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
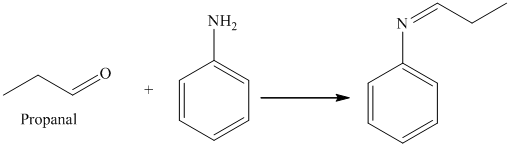
i) The product of the reaction of propanal with aniline (C6H5NH2) is shown below.
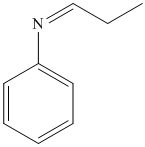
j) The product of the reaction of propanal with dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
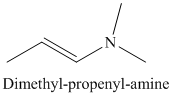
k) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine is shown below.
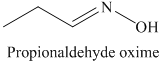
l) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrazine is shown below.
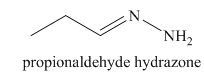
m) The product of the reaction of propanal with product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide is shown below.
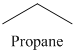
n) The product of the reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine is shown below.
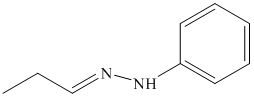
o) The product of the reaction of propanal with semicarbazide is shown below.
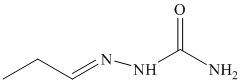
p) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane is shown below.
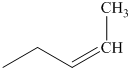
q) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid is shown below.
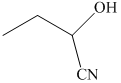
r) The product of the reaction of propanal with chromic acid is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
a) The product obtained by the reaction between, propanal and the reagent, lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water.
The reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
b) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium borohydride, methanol.
The reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, followed by methanol gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
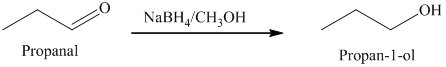
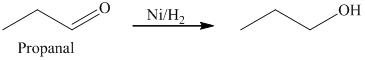
c) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrogen (nickel catalyst).
The reaction of propanal with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst gives propan-1-ol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
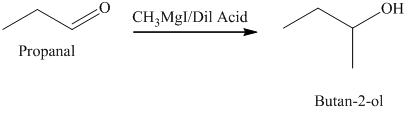
d) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide that is Grignard reagent, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
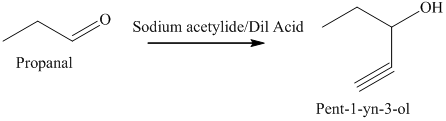
e) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium acetylide is fundamentally similar to the Grignard reaction. The reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
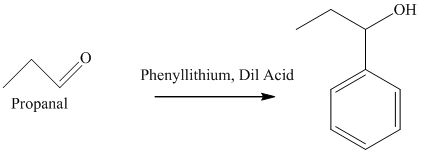
f) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
g) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride.
The reaction of aldehydes with two equivalents of an alcohol results in the formation of acetals. The product of this reaction is shown below.
h) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, Ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
In the reaction of aldehyde with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene, the protection of the carbonyl group of aldehyde takes place. For carbonyl protection, ethylene glycol is the commonly used group. The final product resembles like ether and known as ketal during the protection of carbonyl group using ethylene glycol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
i) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, aniline (C6H5NH2).
The reaction of aldehyde with primary
j) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
The reaction of aldehyde with secondary amine forms enamine as the final product. The reaction of propanal with dimethylamine in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene gives dimethyl-propenyl-amine as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.

k) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydroxylamine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydroxylamine gives oxime as the final product. The reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine results in the formation of propionaldehyde oxime. The product of this reaction is shown below.
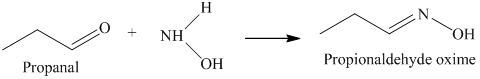
l) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
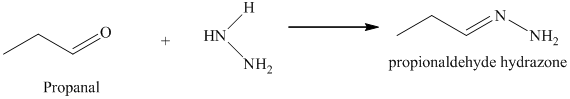
m) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The heating of propionaldehyde hydrazone in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide forms

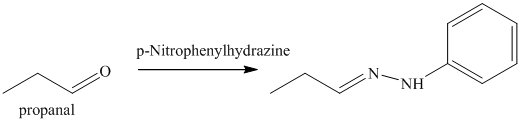
n) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and p-nitrophenylhydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine gives propionaldehyde phenylhydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
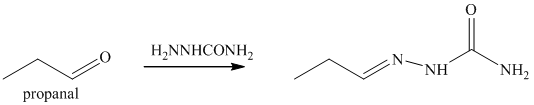
o) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and semicarbazide.
The reaction of aldehyde with semicarbazide results in the formation of semicarbazone. The reaction of propanal with H2NNHCONH2 forms H3CH2C-HC=N-NHCONH2. The final product of this reaction is shown below.
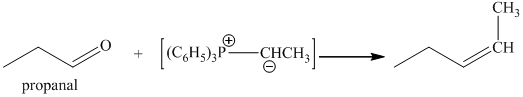
p) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane.
The reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane gives pent-2-ene as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
q) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium cyanide results in the formation of cyanohydrin. The product of this reaction is shown below.
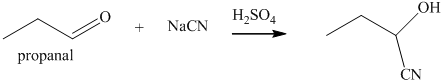
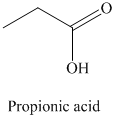
r) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and chromic acid.
The reaction of propanal with chromic acid gives propionic acid as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- An expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forward
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

